Abstract
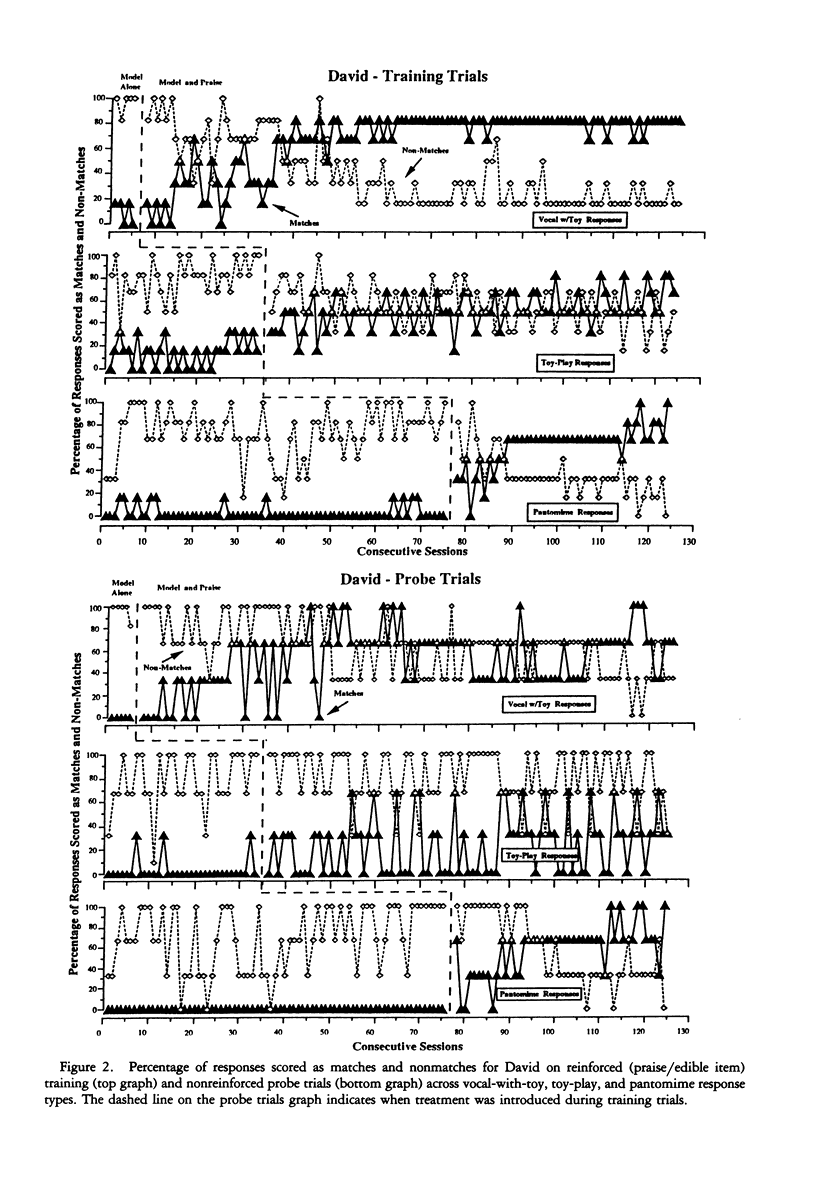
An experimental analysis of imitation was conducted to examine the influence of response topography on generalization of imitation across three response types. Four children with autism were presented with both reinforced training trials and nonreinforced probe trials of models from vocal, toy-play, and pantomime response types. The probe trials were used to examine generalization within each response type. A multiple baseline design was used to analyze percentage of matching and nonmatching responses to models across response types. This study, the first to analyze imitative response classes in children with autism, showed that imitation generalized from reinforced training models to nonreinforced probe models within a response type, but it did not generalize across response types. Thus, functional response classes determined by topographical boundaries were exhibited within generalized imitation.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Peterson R. F., Sherman J. A. The development of imitation by reinforcing behavioral similarity to a model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):405–416. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham T. A., Sherman J. A. An experimental analysis of verbal imitation in preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):151–158. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E., Baer D. M., Firestone I. The development of generalized imitation within topographically determined boundaries. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Summer;4(2):101–112. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring T. G., Breen C. G., Laitinen R. E. Stimulus class formation and concept learning: establishment of within- and between-set generalization and transitive relationships via conditional discrimination procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1989 Jul;52(1):13–25. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1989.52-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring T. G. Teaching between-class generalization of toy play behavior to handicapped children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Summer;18(2):127–139. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Firestone P. B., Kramme K. W., Dunlap G. Increasing spontaneous play by suppressing self-stimulation in autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):521–528. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Berberich J. P., Perloff B. F., Schaeffer B. Acquisition of imitative speech by schizophrenic children. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace F. C., Hock M. L., Lalli J. S., West B. J., Belfiore P., Pinter E., Brown D. K. Behavioral momentum in the treatment of noncompliance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1988 Summer;21(2):123–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1988.21-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neef N. A., Shafer M. S., Egel A. L., Cataldo M. F., Parrish J. M. The class specific effects of compliance training with "do" and "don't" requests: analogue analysis and classroom application. J Appl Behav Anal. 1983 Spring;16(1):81–99. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1983.16-81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish J. M., Cataldo M. F., Kolko D. J., Neef N. A., Egel A. L. Experimental analysis of response covariation among compliant and inappropriate behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1986 Fall;19(3):241–254. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1986.19-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulson C. L., Kymissis E. Generalized imitation in infants. J Exp Child Psychol. 1988 Dec;46(3):324–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(88)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulson C. L., Kymissis E., Reeve K. F., Andreators M., Reeve L. Generalized vocal imitation in infants. J Exp Child Psychol. 1991 Apr;51(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(91)90036-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman W. M. The social control of generalized imitation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Fall;3(3):159–167. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryon A. S., Keane S. P. Promoting imitative play through generalized observational learning in autisticlike children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1986 Dec;14(4):537–549. doi: 10.1007/BF01260522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


