Abstract
Hepatitis G virus (HGV) and GB virus C (GBV-C) are two newly discovered viral agents, different isolates of a positive-sense RNA virus that represents a new genus of Flaviviridae. The purpose of this review is to analyze new data that have recently been published on the epidemiology and associations between HGV and liver diseases such as posttransfusion hepatitis, acute and chronic non-A-E hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The role of HGV in coinfection with other hepatitis viruses, the response to antiviral therapy, and the impact of HGV on liver transplantation are also discussed. HGV is a transmissible blood-borne viral agent that frequently occurs as a coinfection with other hepatitis viruses due to common modes of transmission. The prevalence of HGV ranges from 0.9 to 10% among blood donors throughout the world and is found in 1.7% of volunteer blood donors in the United States. The majority of patients infected with HGV by blood transfusion do not develop chronic hepatitis, but hepatitis G viremia frequently persists without biochemical evidence of hepatitis. Serum HGV RNA has been found in 0 to 50% of patients with fulminant hepatitis of unknown etiology and 14 to 36% of patients with cryptogenic cirrhosis. The association between HGV and chronic non-A-E hepatitis remains unclear. Although HGV appears to be a hepatotrophic virus, its role in independently causing acute and chronic liver diseases remains uncertain.
Full text
PDF
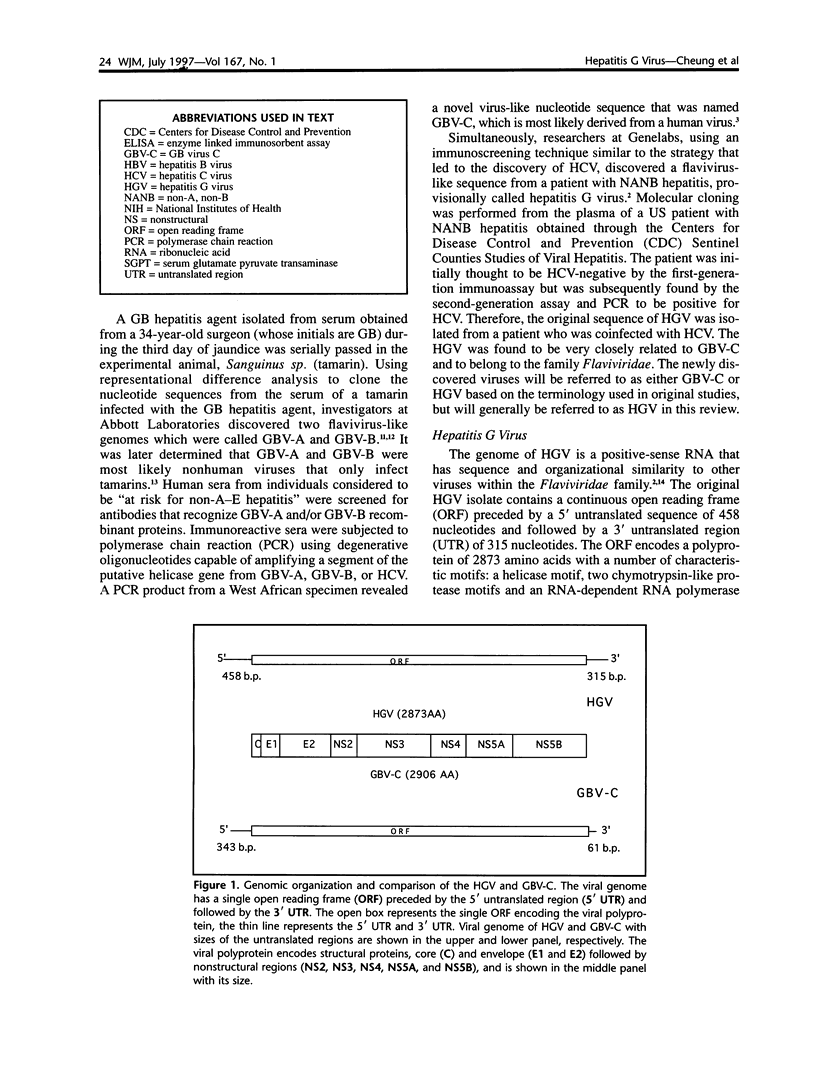
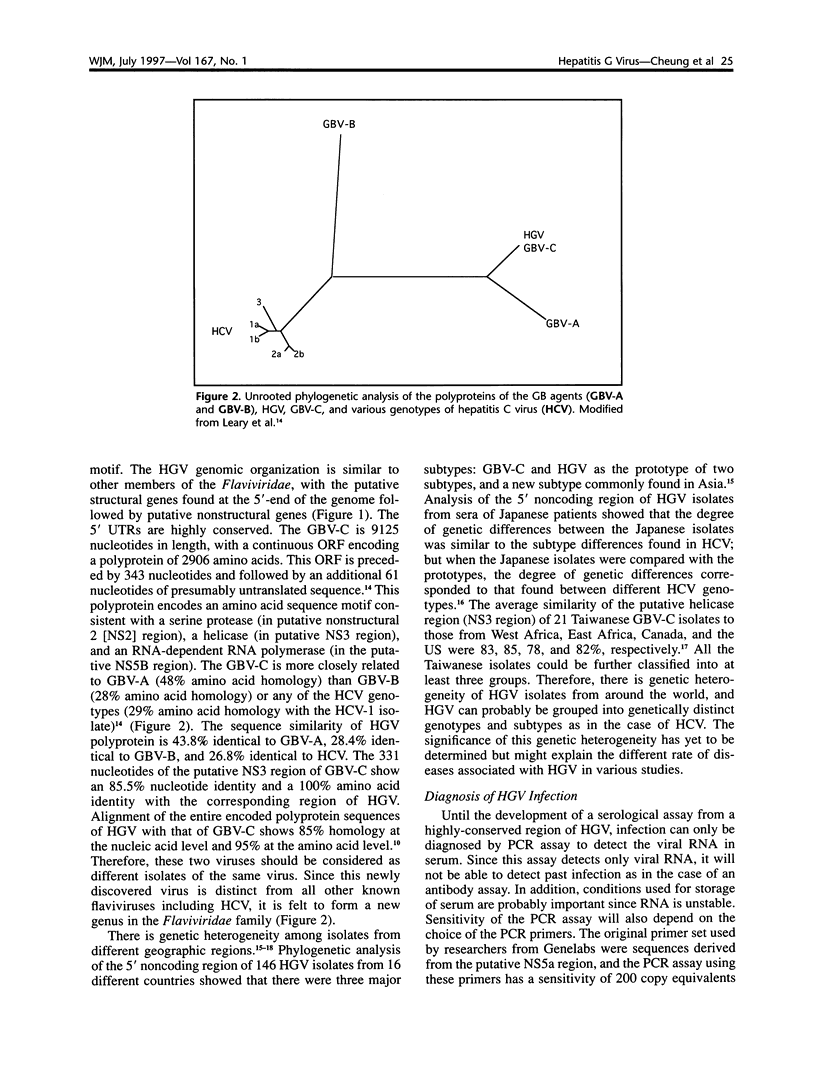








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aach R. D., Stevens C. E., Hollinger F. B., Mosley J. W., Peterson D. A., Taylor P. E., Johnson R. G., Barbosa L. H., Nemo G. J. Hepatitis C virus infection in post-transfusion hepatitis. An analysis with first- and second-generation assays. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 7;325(19):1325–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111073251901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Nakatsuji Y., Melpolder J., Wages J., Wesley R., Shih J. W., Kim J. P. The incidence of transfusion-associated hepatitis G virus infection and its relation to liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1997 Mar 13;336(11):747–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199703133361102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Shih J. W., Melpolder J. C., Houghton M., Choo Q. L., Kuo G. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 30;321(22):1494–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911303212202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Gallagher M., Morris T. T., Moyer L. A., Meeks E. L., Krawczynski K., Kim J. P., Margolis H. S. Acute non-A-E hepatitis in the United States and the role of hepatitis G virus infection. Sentinel Counties Viral Hepatitis Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1997 Mar 13;336(11):741–746. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199703133361101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Margolis H. S., Krawczynski K., Judson F. N., Mares A., Alexander W. J., Hu P. Y., Miller J. K., Gerber M. A., Sampliner R. E. The natural history of community-acquired hepatitis C in the United States. The Sentinel Counties Chronic non-A, non-B Hepatitis Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 31;327(27):1899–1905. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212313272702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blajchman M. A., Bull S. B., Feinman S. V. Post-transfusion hepatitis: impact of non-A, non-B hepatitis surrogate tests. Canadian Post-Transfusion Hepatitis Prevention Study Group. Lancet. 1995 Jan 7;345(8941):21–25. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. S., Moaven L. D., Locarnini S. A. New hepatitis viruses: are there enough letters in the alphabet? Med J Aust. 1996 Jan 15;164(2):87–89. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb101355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E., Popper H., Cook E. H., Ebert J. W., McCaustland K. A., Schable C. A., Fields H. A. Posttransfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis: physicochemical properties of two distinct agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):254–265. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Banks A. T., Piatack M., Jr, Kim J. P. Hepatitis G-associated aplastic anaemia. Lancet. 1996 Aug 17;348(9025):472–472. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)64562-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deka N., Sharma M. D., Mukerjee R. Isolation of the novel agent from human stool samples that is associated with sporadic non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):7810–7815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.7810-7815.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Ellis D. S., Tovey G. M., Lloyd G., Smith H. M., Portmann B., Tan K. C., Zuckerman A. J., Williams R. Toga virus-like particles in acute liver failure attributed to sporadic non-A, non-B hepatitis and recurrence after liver transplantation. J Med Virol. 1992 Sep;38(1):71–77. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890380115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feucht H. H., Zollner B., Polywka S., Laufs R. Vertical transmission of hepatitis G. Lancet. 1996 Mar 2;347(9001):615–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiordalisi G., Zanella I., Mantero G., Bettinardi A., Stellini R., Paraninfo G., Cadeo G., Primi D. High prevalence of GB virus C infection in a group of Italian patients with hepatitis of unknown etiology. J Infect Dis. 1996 Jul;174(1):181–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi S., Kurihara C., Ishiyama N., Okamura H., Hoshino F. B., Oya A., Katayama K. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region of hepatitis G virus isolated from Japanese patients: comparison with reported isolates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Sep 13;226(2):314–318. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon G. H., Jarvis L. M., Simpson K. J., Hayes P. C., Simmonds P. The clinical significance of the detection of hepatitis GBV-C RNA in the serum of patients with fulminant, presumed viral, hepatitis. J Viral Hepat. 1997 Jan;4(1):45–49. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1997.00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heringlake S., Tillmann H. L., Manns M. P. New hepatitis viruses. J Hepatol. 1996 Aug;25(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Carithers R. L., Jr, Shapiro C., Ascher N. Fulminant hepatic failure: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 1995 Jan;21(1):240–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. H., Chen P. J., Chen D. S. GBV-C in the aetiology of fulminant hepatitis. Lancet. 1996 Jan 13;347(8994):120–121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. H., Chen P. J., Hsiang S. C., Chen W., Chen D. S. Phylogenetic analysis of GB virus C: comparison of isolates from Africa, North America, and Taiwan. J Infect Dis. 1996 Aug;174(2):410–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karayiannis P., Hadziyannis S. J., Kim J., Pickering J. M., Piatak M., Hess G., Yun A., McGarvey M. J., Wages J., Thomas H. C. Hepatitis G virus infection: clinical characteristics and response to interferon. J Viral Hepat. 1997 Jan;4(1):37–44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1997.00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki T., Nishiguchi S., Tanaka M., Enomoto M., Kobayashi K. Does GBV-C cause fulminant hepatitis in Japan? Lancet. 1996 Mar 30;347(9005):908–908. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary T. P., Muerhoff A. S., Simons J. N., Pilot-Matias T. J., Erker J. C., Chalmers M. L., Schlauder G. G., Dawson G. J., Desai S. M., Mushahwar I. K. Consensus oligonucleotide primers for the detection of GB virus C in human cryptogenic hepatitis. J Virol Methods. 1996 Jan;56(1):119–121. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(95)01956-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary T. P., Muerhoff A. S., Simons J. N., Pilot-Matias T. J., Erker J. C., Chalmers M. L., Schlauder G. G., Dawson G. J., Desai S. M., Mushahwar I. K. Sequence and genomic organization of GBV-C: a novel member of the flaviviridae associated with human non-A-E hepatitis. J Med Virol. 1996 Jan;48(1):60–67. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199601)48:1<60::AID-JMV10>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnen J., Wages J., Jr, Zhang-Keck Z. Y., Fry K. E., Krawczynski K. Z., Alter H., Koonin E., Gallagher M., Alter M., Hadziyannis S. Molecular cloning and disease association of hepatitis G virus: a transfusion-transmissible agent. Science. 1996 Jan 26;271(5248):505–508. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko K., Mitsui T., Iwano K., Yamazaki C., Okuda K., Meguro T., Murayama N., Inoue T., Tsuda F., Okamoto H. Infection with hepatitis GB virus C in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1996 Jun 6;334(23):1485–1490. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199606063342301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moaven L. D., Hyland C. A., Young I. F., Bowden D. S., McCaw R., Mison L., Locarnini S. A. Prevalence of hepatitis G virus in Queensland blood donors. Med J Aust. 1996 Oct 7;165(7):369–371. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb125019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moaven L. D., Tennakoon P. S., Bowden D. S., Locarnini S. A. Mother-to-baby transmission of hepatitis G virus. Med J Aust. 1996 Jul 15;165(2):84–85. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1996.tb124854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muerhoff A. S., Leary T. P., Simons J. N., Pilot-Matias T. J., Dawson G. J., Erker J. C., Chalmers M. L., Schlauder G. G., Desai S. M., Mushahwar I. K. Genomic organization of GB viruses A and B: two new members of the Flaviviridae associated with GB agent hepatitis. J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5621–5630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.9.5621-5630.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaluder G. G., Dawson G. J., Simons J. N., Pilot-Matias T. J., Gutierrez R. A., Heynen C. A., Knigge M. F., Kurpiewski G. S., Buijk S. L., Leary T. P. Molecular and serologic analysis in the transmission of the GB hepatitis agents. J Med Virol. 1995 May;46(1):81–90. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890460117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. N., Leary T. P., Dawson G. J., Pilot-Matias T. J., Muerhoff A. S., Schlauder G. G., Desai S. M., Mushahwar I. K. Isolation of novel virus-like sequences associated with human hepatitis. Nat Med. 1995 Jun;1(6):564–569. doi: 10.1038/nm0695-564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. N., Pilot-Matias T. J., Leary T. P., Dawson G. J., Desai S. M., Schlauder G. G., Muerhoff A. S., Erker J. C., Buijk S. L., Chalmers M. L. Identification of two flavivirus-like genomes in the GB hepatitis agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3401–3405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacke M., Kiyosawa K., Stark K., Schlueter V., Ofenloch-Haehnle B., Hess G., Engel A. M. Detection of antibodies to a putative hepatitis G virus envelope protein. Lancet. 1997 Feb 1;349(9048):318–320. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)06461-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka E., Alter H. J., Nakatsuji Y., Shih J. W., Kim J. P., Matsumoto A., Kobayashi M., Kiyosawa K. Effect of hepatitis G virus infection on chronic hepatitis C. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Nov 1;125(9):740–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-125-9-199611010-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassopoulos N. C., Hatzakis A., Delladetsima I., Koutelou M. G., Todoulos A., Miriagou V. Role of hepatitis C virus in acute non-A, non-B hepatitis in Greece: a 5-year prospective study. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):969–972. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90184-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. T., Tsai F. C., Lee C. Z., Chen P. J., Sheu J. C., Wang T. H., Chen D. S. A prospective study of transfusion-transmitted GB virus C infection: similar frequency but different clinical presentation compared with hepatitis C virus. Blood. 1996 Sep 1;88(5):1881–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. L. Etiology of fulminant hepatic failure: is another virus involved? Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):640–643. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90437-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. L., Mamish D., Combs C., Kim M., Donegan E., Ferrell L., Lake J., Roberts J., Ascher N. L. Hepatitis B virus and apparent fulminant non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1992 Apr 18;339(8799):952–955. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91530-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiba M., Okamoto H., Mishiro S. Detection of the GBV-C hepatitis virus genome in serum from patients with fulminant hepatitis of unknown aetiology. Lancet. 1995 Oct 28;346(8983):1131–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi Y., Chapman C. S., Myint S. Aplastic anaemia after HGV infection. Lancet. 1996 Aug 17;348(9025):471–472. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)64561-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman A. J. Alphabet of hepatitis viruses. Lancet. 1996 Mar 2;347(9001):558–559. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91267-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


