Abstract
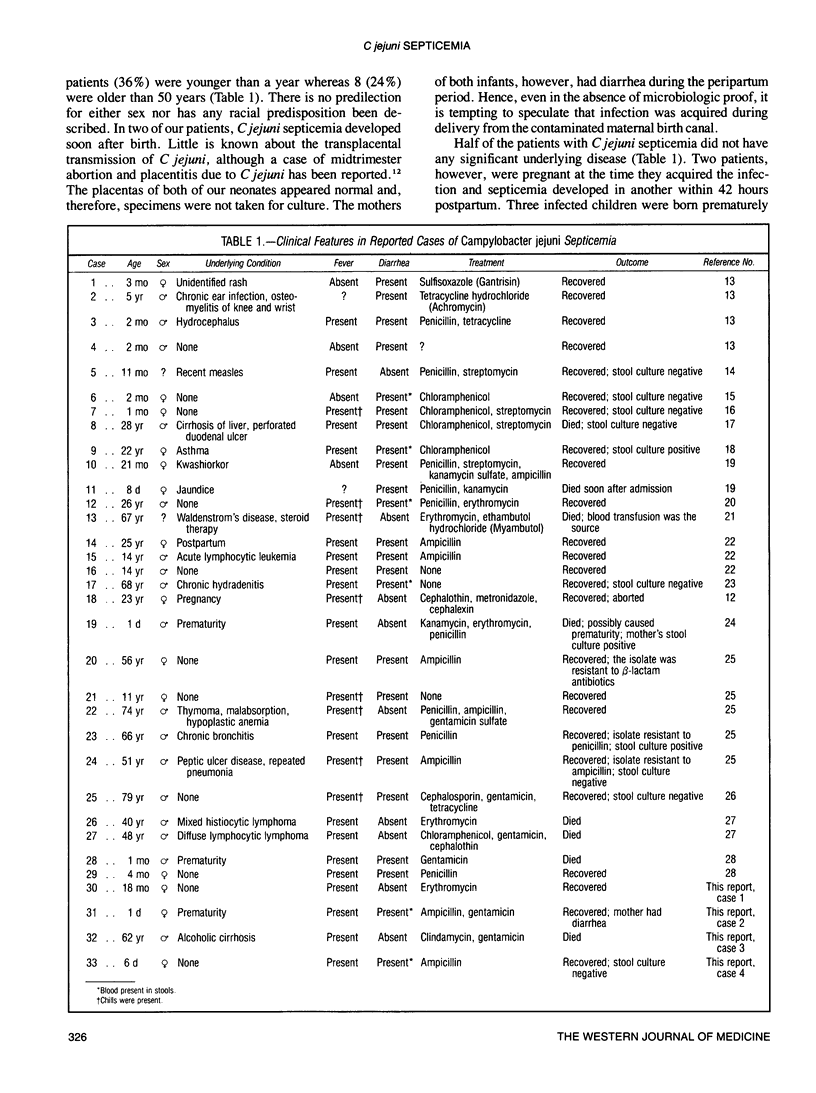
In 33 cases of Campylobacter jejuni septicemia, the disease was more common at the extremes of age: infants made up a third of the reported cases while 24% of patients were older than 50 years. Fever was noted in more than 80% of patients and chills in about a fourth. Enteritis was present in 70% of cases, and the gastrointestinal tract was the principal source of septicemia. Half of the patients did not have significant underlying disease but were at extremes of age, which may reflect relative host impairment. Mortality (25%) owing to C jejuni septicemia occurs mostly in compromised hosts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wang W. L. Campylobacter infections in human beings. J Pediatr. 1980 Feb;96(2):343–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80844-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Farrell B. C., Mulligan R. A. Case of human vibriosis. Br Med J. 1967 Apr 29;2(5547):287–289. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5547.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J., Moseley G., Dalton H. P. Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni bacteremia. South Med J. 1980 Aug;73(8):1092–1093. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198008000-00045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. L., Davoren R. A., Cole M. E., Radford N. J. Midtrimester abortion associated with septicaemia caused by Campylobacter jejuni. Med J Aust. 1981 May 30;1(11):585–586. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1981.tb135843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett A. F., Botha P. L., Logan A. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus from recent cases of human vibriosis. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Dec;79(3):381–389. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O. Human infections with Vibrio fetus and a closely related vibrio. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longfield R. N., Crane J. M., Pasquale D. N. Campylobacter fetus subsp jejuni bacteremia in diffuse lymphoma. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981 Sep;56(9):582–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longfield R., O'Donnell J., Yudt W., Lissner C., Burns T. Acute colitis and bacteremia due to Campylobacter fetus. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Dec;24(12):950–953. doi: 10.1007/BF01311952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDDELKAMP J. N., WOLF H. A. Infection due to a "related" Vibrio. J Pediatr. 1961 Sep;59:318–321. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(61)80283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. C., Guard R. W. A case of premature labour due to Campylobacter jejuni infection. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1982 May;22(2):118–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1982.tb01420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepersack F., Prigogyne T., Butzler J. P., Yourassowsky E. Campylobacter jejuni post-transfusional septicaemia. Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):911–911. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthucheary S. D., Lin H. P. Bacteraemic enteritis due to Campylobacter jejuni. Med J Malaysia. 1982 Dec;37(4):378–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig P. J. Campylobacter infections in human beings. J Pediatr. 1979 Jun;94(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben F. L., Wolinsky E. Human infection with Vibrio fetus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. N., Stamper L. L. Acute campylobacter gastroenteritis and bacteremia. N C Med J. 1979 Aug;40(8):505–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. R., Weinstein W. M., Bryner J. H. Campylobacter fetus infection in human subjects: association with raw milk. Am J Med. 1979 May;66(5):779–783. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy D. E., Bond W. W. Campylobacter fetus infections in children. Pediatrics. 1979 Dec;64(6):898–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoof R., Gordts B., Dierickx R., Coignau H., Butzler J. P. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of 24 antimicrobial agents against Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):118–121. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER W. E., BORCHERS J. Vibrionic enteritis in infants. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Jan;101:60–66. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1961.04020020062010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M., Lindberg A., Schalén C., Ohman L. Five cases of Campylobacter jejuni/coli bacteremia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(3):201–205. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-3.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


