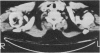
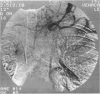
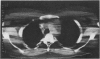
Abstract
Central venous catheter-related infection and evidence for central venous thrombosis developed in five patients. On the basis of ongoing bacteremia after catheter removal and venographic confirmation, catheter-related septic central venous thrombosis (CR-SCVT) was confirmed. These patients were treated successfully with anticoagulation and antibiotics; none required surgical exploration or drainage.
CR-SCVT is a complication of modern venous access techniques and is easily confused with sepsis from other anatomic sites. Even when recognized antemortem, CR-SCVT carries an excessive morbidity and mortality. The therapy for this complication is not standardized, but catheter removal, anticoagulation and a prolonged course of antibiotics are appropriate initial therapy. Surgical vein ligation or excision are reserved for refractory sepsis or abscess formation.
Full text
PDF
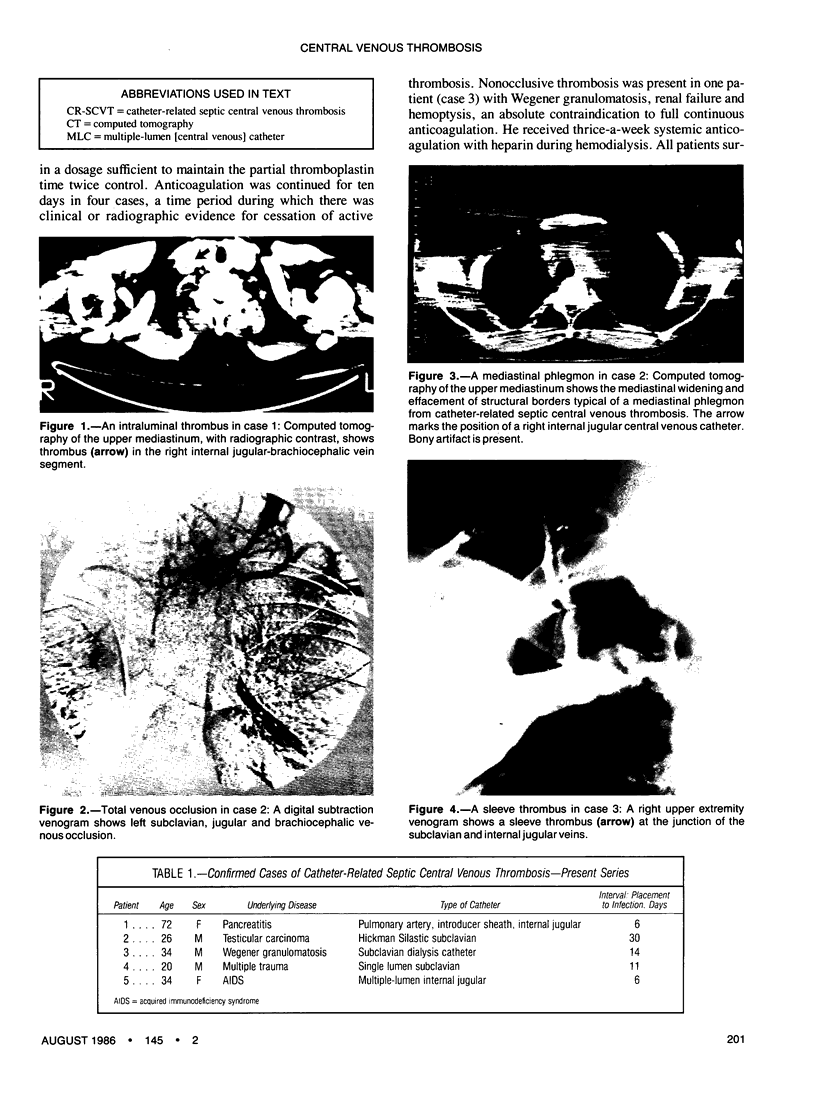


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed N. Thrombosis after central venous cannulation. Med J Aust. 1976 Feb 21;1(8):217–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Petersen S. R., Sheldon G. F. Septic phlebitis: a neglected disease. Am J Surg. 1979 Jul;138(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar B., Hårdstedt C., Jacobson S. Diagnosis of thrombosis by catheter phlebography after prolonged central venous catheterization. Ann Surg. 1981 Dec;194(6):779–783. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198112000-00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar B., Malmborg A. S. Prophylaxis against microbial colonization of venous catheters. J Hosp Infect. 1981 Mar;2(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(81)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE C. Venous interruption for septic thrombophlebitis. N Engl J Med. 1960 May 12;262:947–951. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196005122621901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D., Petersen J., Feldman R., Cho C., Stevick C. A. Subclavian venous stenosis. A complication of subclavian dialysis. JAMA. 1984 Dec 28;252(24):3404–3406. doi: 10.1001/jama.252.24.3404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner D. B., Stubbs D. H., Shadur C. A., Flynn C. T. Percutaneous subclavian vein catheter hemodialysis--impact on vascular access surgery. Surgery. 1982 Jun;91(6):712–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon W. F., Jr, Golocovsky M., Paul B. K., Champion H. R. Suppurative mediastinitis as a complication of long-term total parenteral nutrition therapy via subclavian vein. Crit Care Med. 1981 Jul;9(7):558–559. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198107000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman E. K., Pakter R. L., Gayler B. W., Wheeler P. S., Siegelman S. S. Jugular venous thrombosis: diagnosis by computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Oct;8(5):963–968. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198410000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley D. P., White R. A., Nelson R. J., Mehringer C. M. Pulmonary embolism secondary to venous thrombosis of the arm. Am J Surg. 1984 Feb;147(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henzel J. H., DeWeese M. S. Morbid and mortal complications associated with prolonged central venous cannulation. Awareness, recognition, and prevention. Am J Surg. 1971 May;121(5):600–605. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar P. F., Wilson R. M., Mangano D. T., Avery G. J., 2nd, Szarnicki R. J., Hill J. D. Heparin bonding reduces thrombogenicity of pulmonary-artery catheters. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 22;305(17):993–995. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110223051707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. B., Yeager M. Thrombotic and infectious complications of Hickman-Broviac catheters. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Aug;144(8):1597–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichan J. C., Michel L. Guide wire-sheath technique for pulmonary artery catheterization and central vein cannulation. Intensive Care Med. 1979 Mar;5(1):37–39. doi: 10.1007/BF01739001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitre R. J., Rotheran E. B., Jr Anaerobic septicemia from thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. Successful treatment with metronidazole. JAMA. 1974 Nov 25;230(8):1168–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. A., Jr, Pruitt B. A., Jr, Foley F. D., Moncrief J. A. Suppurative thrombophlebitis--a lethal complication of intravenous therapy. J Trauma. 1968 Mar;8(2):256–267. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196803000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S., Brennan J. Diagnosis of internal jugular vein thrombosis by computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981 Apr;5(2):197–200. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198104000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. C., Bivins B. A., Bell R. M., Sachatello C. R., Griffen W. O., Jr Bacterial endocarditis in the critically ill surgical patient. Arch Surg. 1981 Mar;116(3):311–314. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380150039010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W., Ramsey P. G., Larson E. B., Fefer A., Hickman R. O. Hickman catheter infections in patients with malignancies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Jul;63(4):189–200. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198407000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe F. M. Suppurative thrombosis of the superior vena cava: a lethal complication of central venous catheters. Intensive Care Med. 1985;11(5):265–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00260362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. A., Jr, Abel R. M., Abbott W. M., Hopkins C. C., Chesney T. M., Colley R., Phillips K., Fischer J. E. Catheter complications in total parenteral nutrition. A prospective study of 200 consecutive patients. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):757–761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders R. A., Sheldon G. F. Septic complications of total parenteral nutrition. A five year experience. Am J Surg. 1976 Aug;132(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbeck A., Brittinger W. D., Henning G. E., Strauch M. Cannulation of subclavian vein for hemodialysis using Seldinger's technique. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1978;24:27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. M., Pruitt B. A., Jr Suppurative thrombophlebitis. A lethal iatrogenic disease. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 25;282(26):1452–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006252822603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman R. M., Soliman F., Garcia L., Sawyer P. N. Etiology of catheter-associated sepsis. Correlation with thrombogenicity. Arch Surg. 1977 Dec;112(12):1497–1499. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370120087011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strinden W. D., Helgerson R. B., Maki D. G. Candida septic thrombosis of the great central veins associated with central catheters. Clinical features and management. Ann Surg. 1985 Nov;202(5):653–658. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198511000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vic-Dupont, Cormier J. M., Lecompte Y. La ligature veineuse dans les thrombophlébites suppurées secondaires aux cathétérismes veineux. Chirurgie. 1973 Mar 21;99(5):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman L. D., Kirkemo A., Johnston M. R. Venous access: a prospective, randomized study of the Hickman catheter. Surgery. 1984 Mar;95(3):303–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden G. D., Wilmore D. W., Pruitt B. A., Jr Central venous thrombosis: a hazard of medical progress. J Trauma. 1973 Jul;13(7):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R. E., Tuttle K. L., Gilbert D. N. Surgical approach to extensive suppurative thrombophlebitis of the central veins of the chest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1981 Apr;81(4):564–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]