Abstract
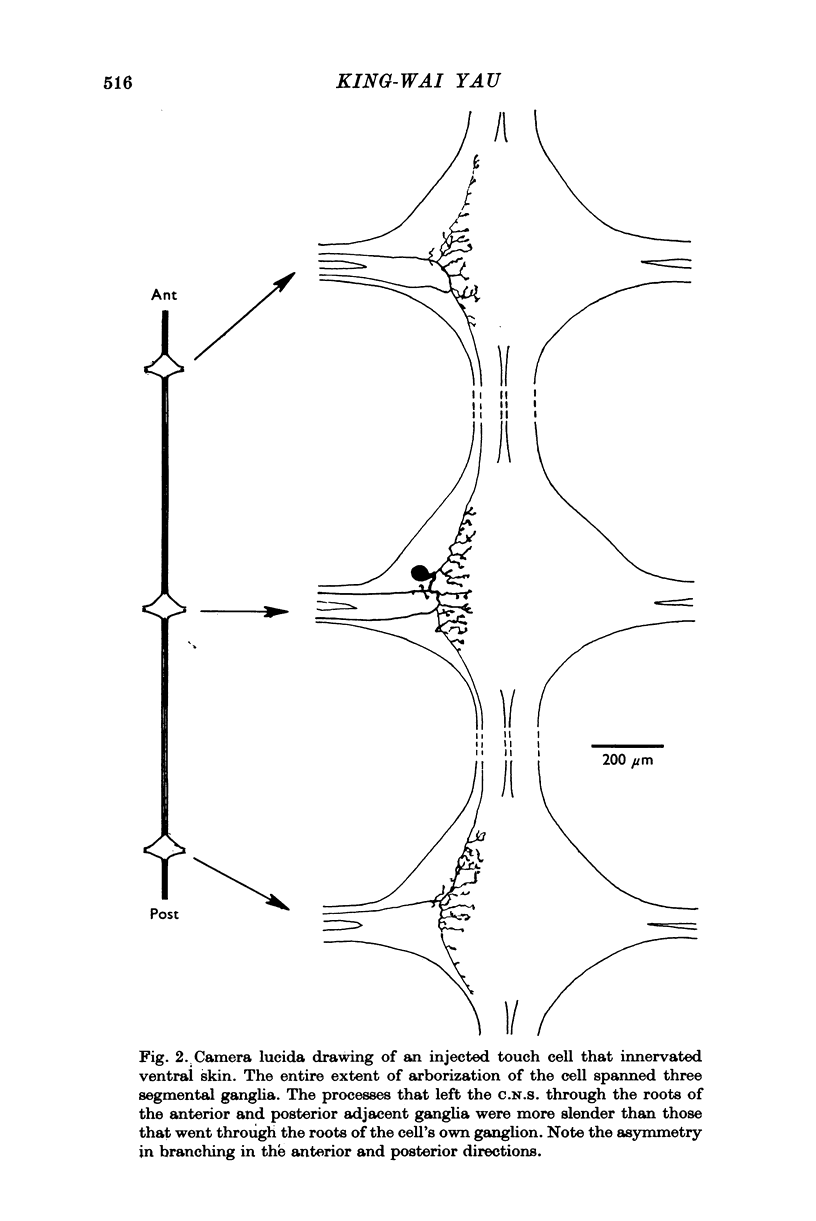
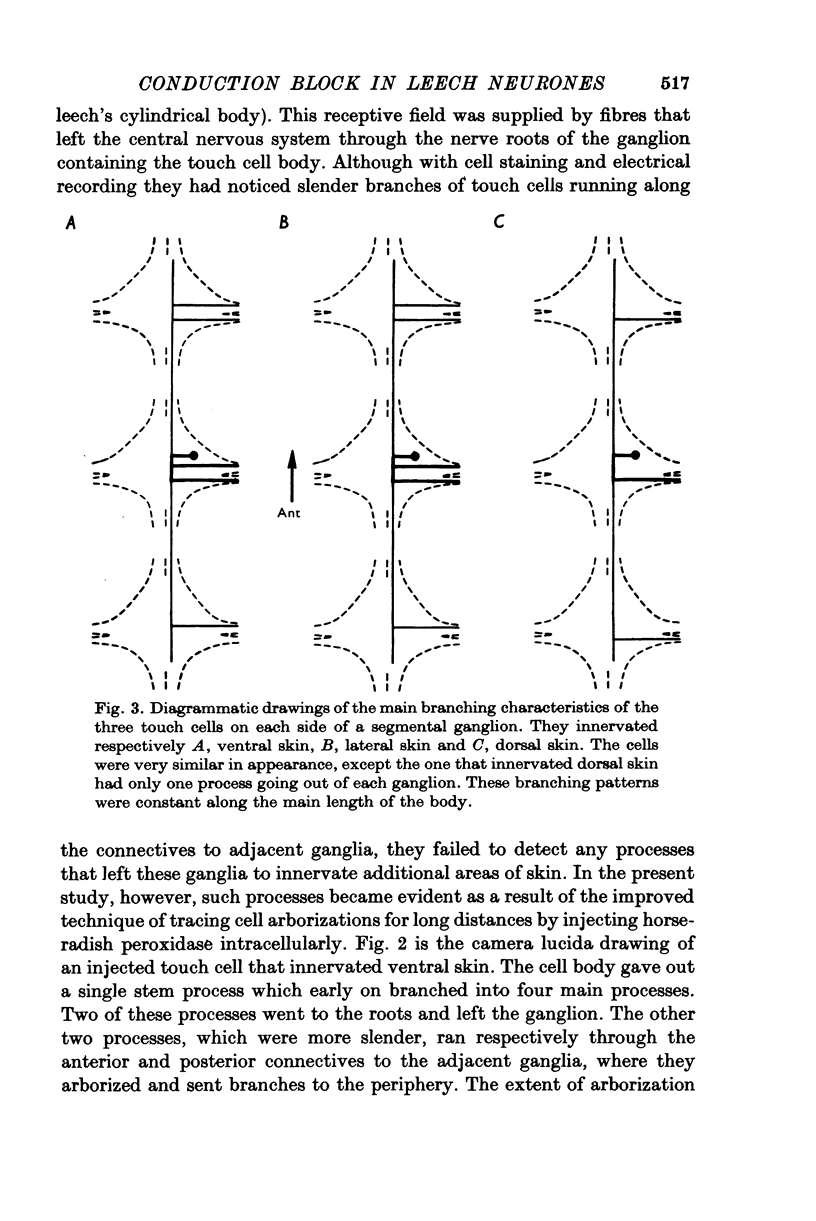
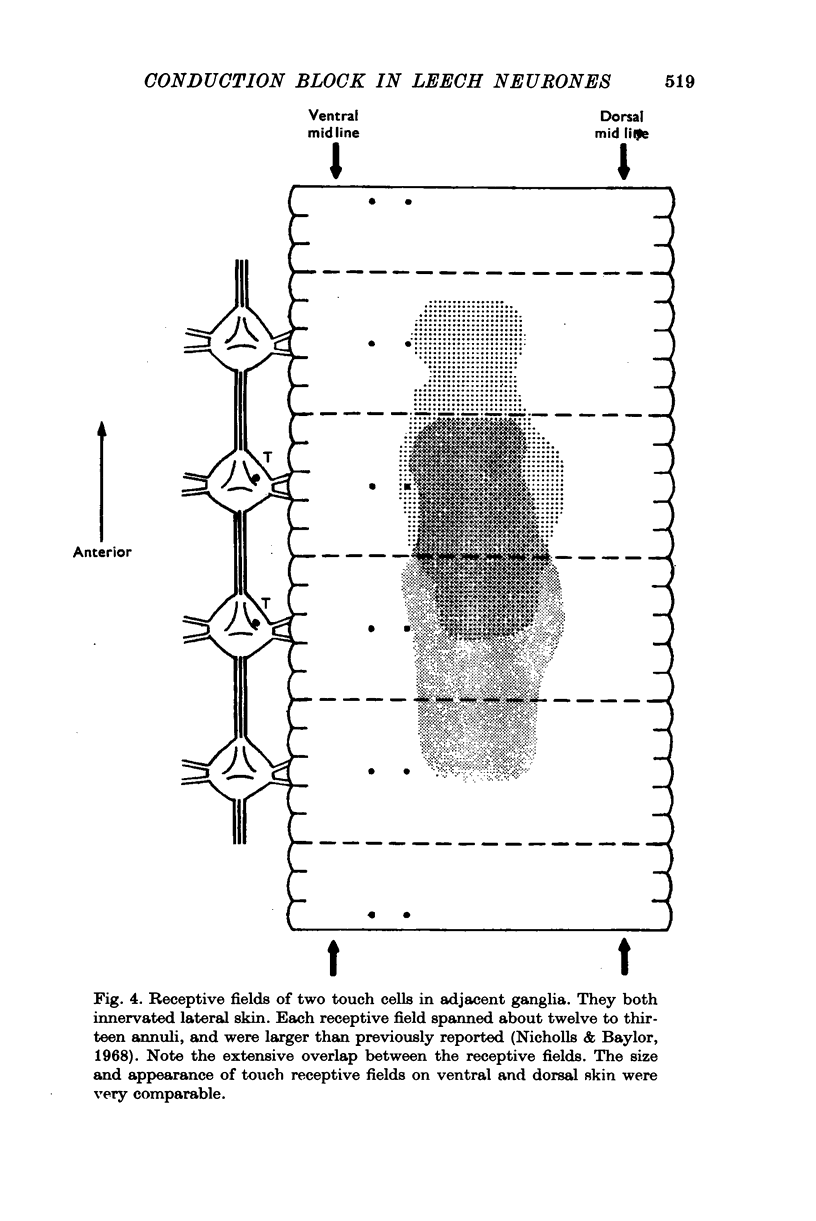
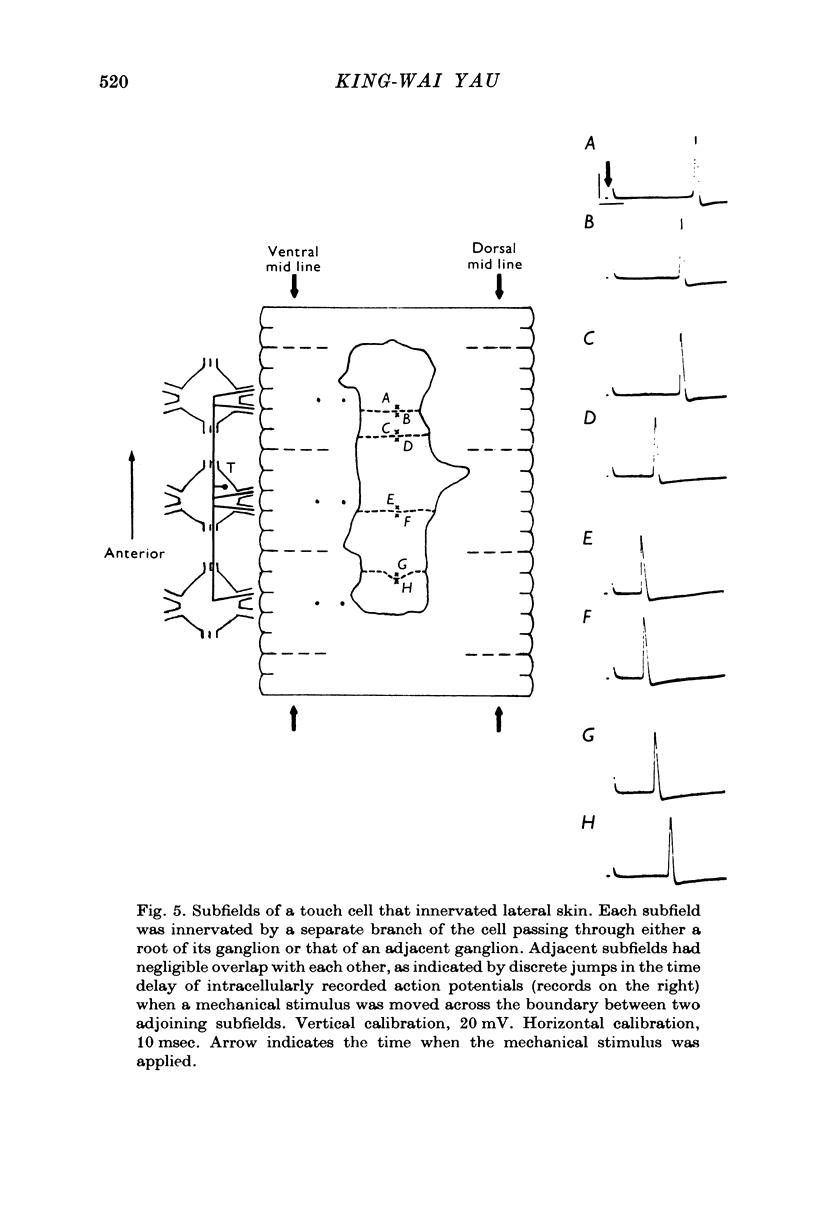
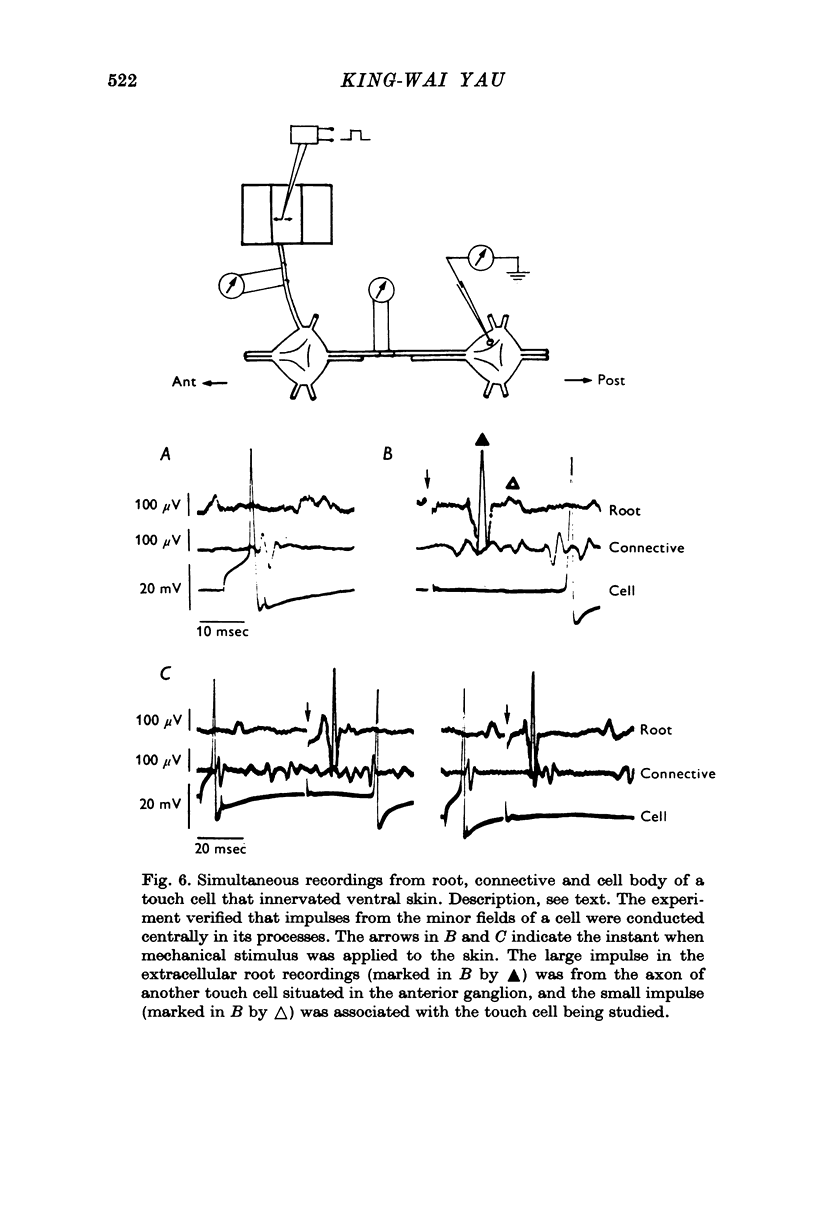
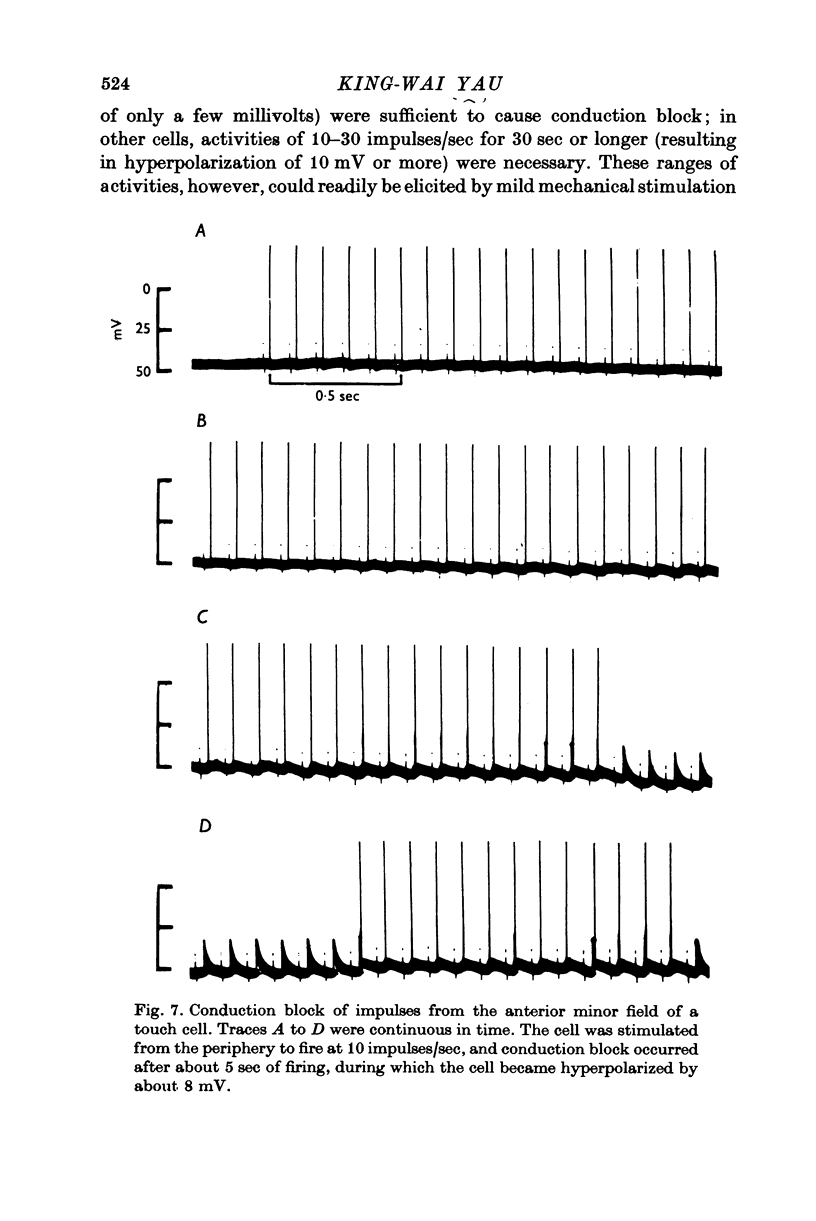
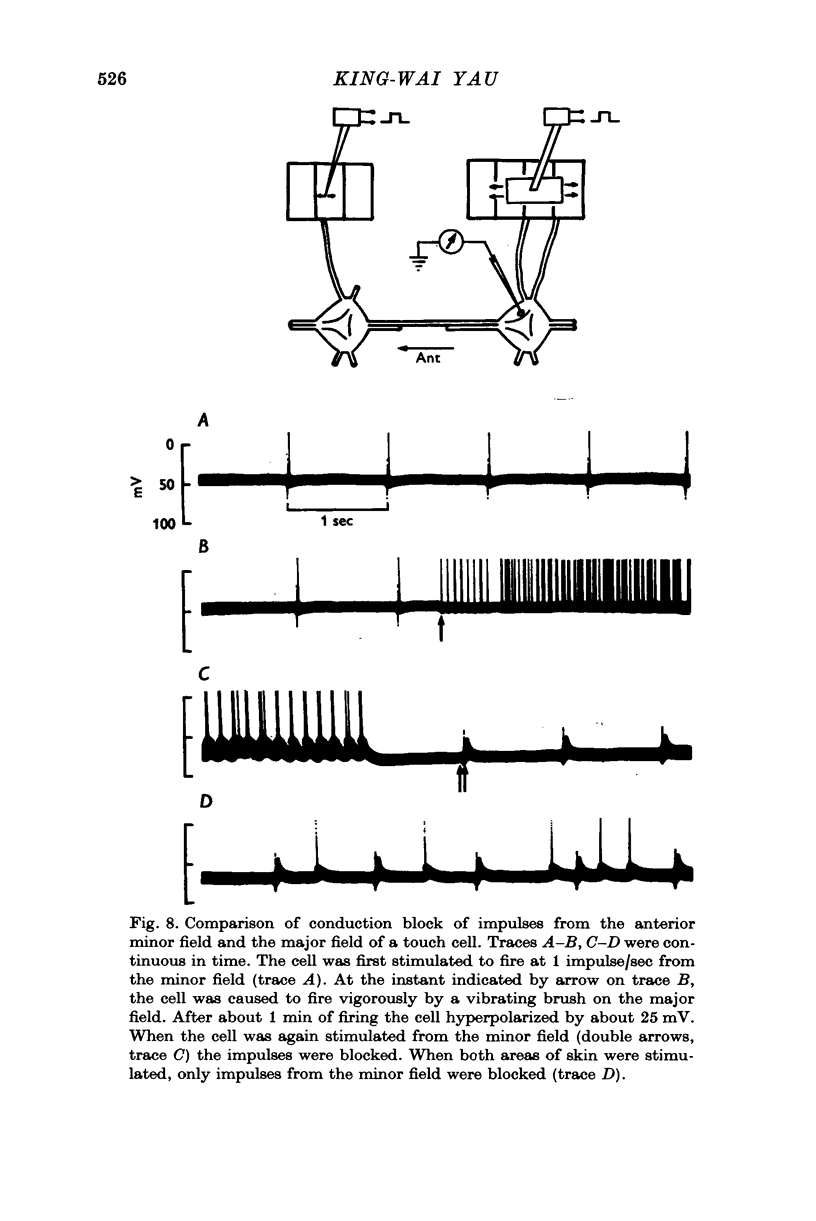
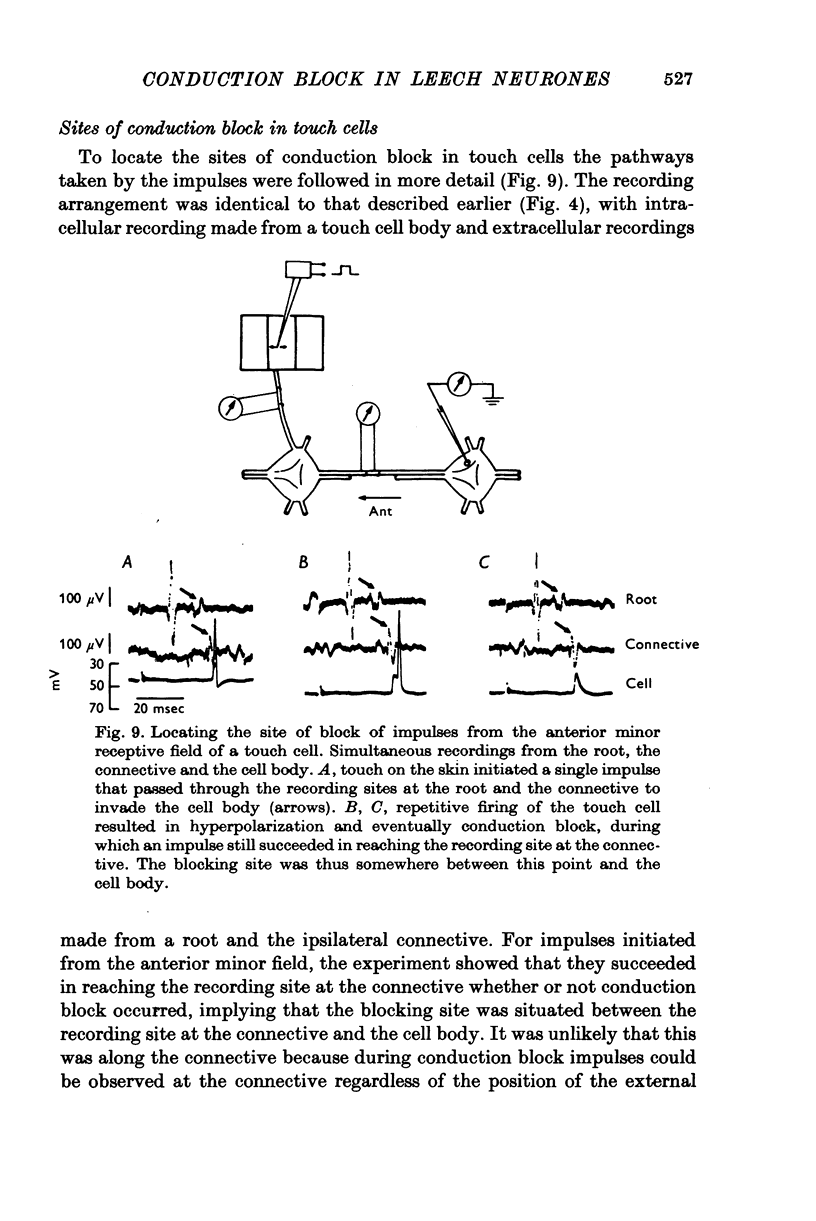
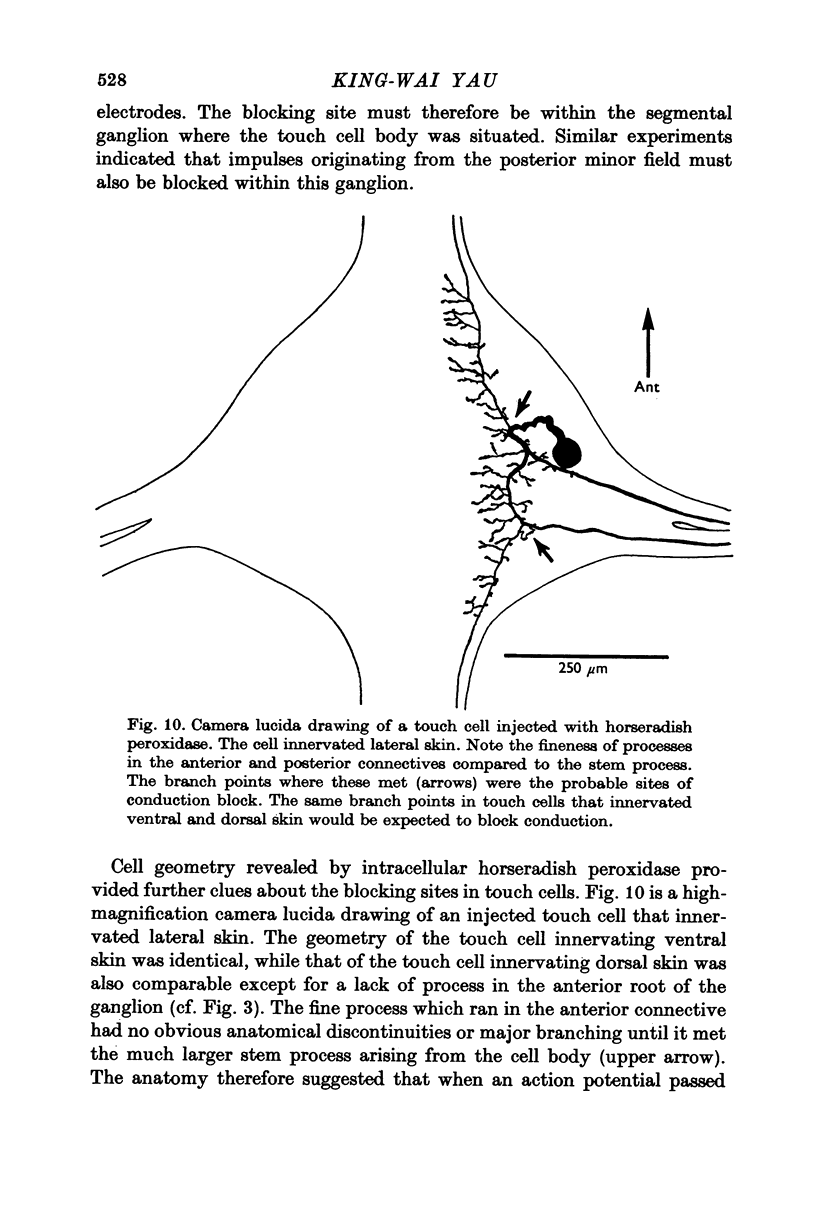
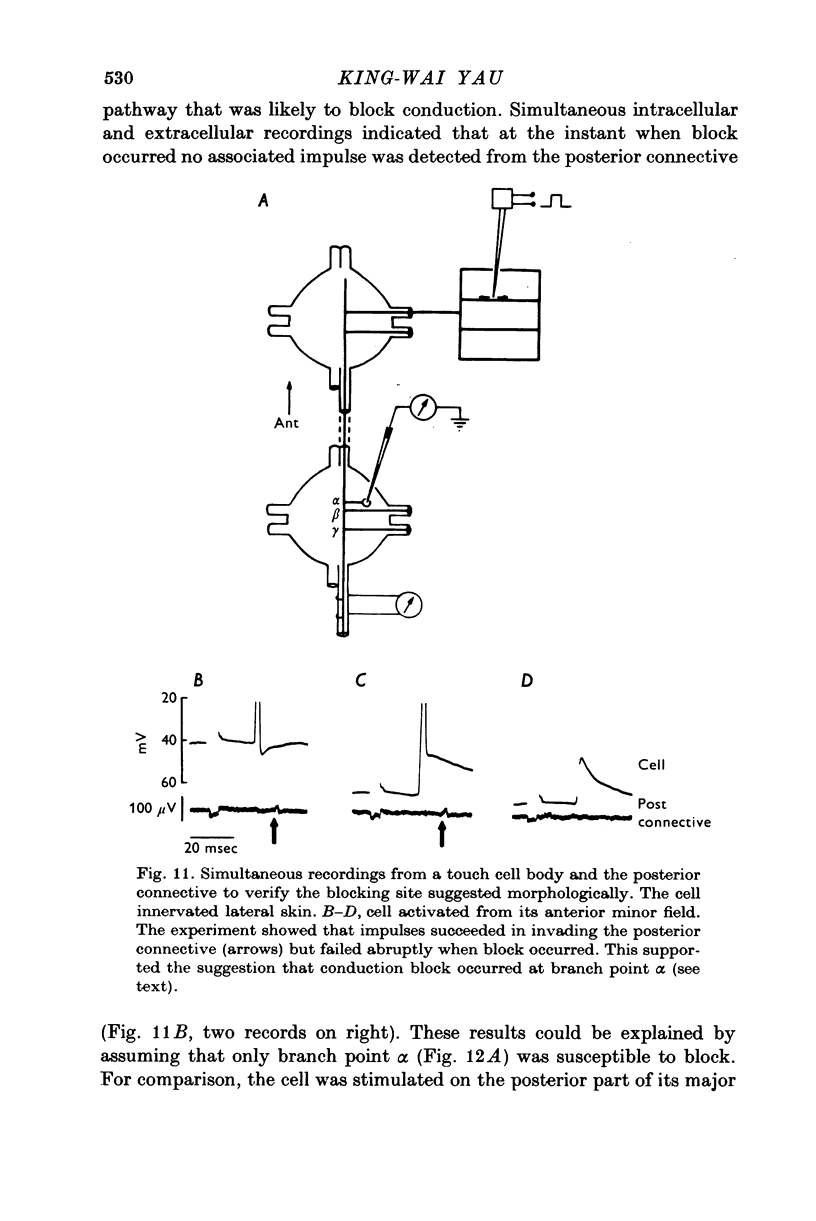
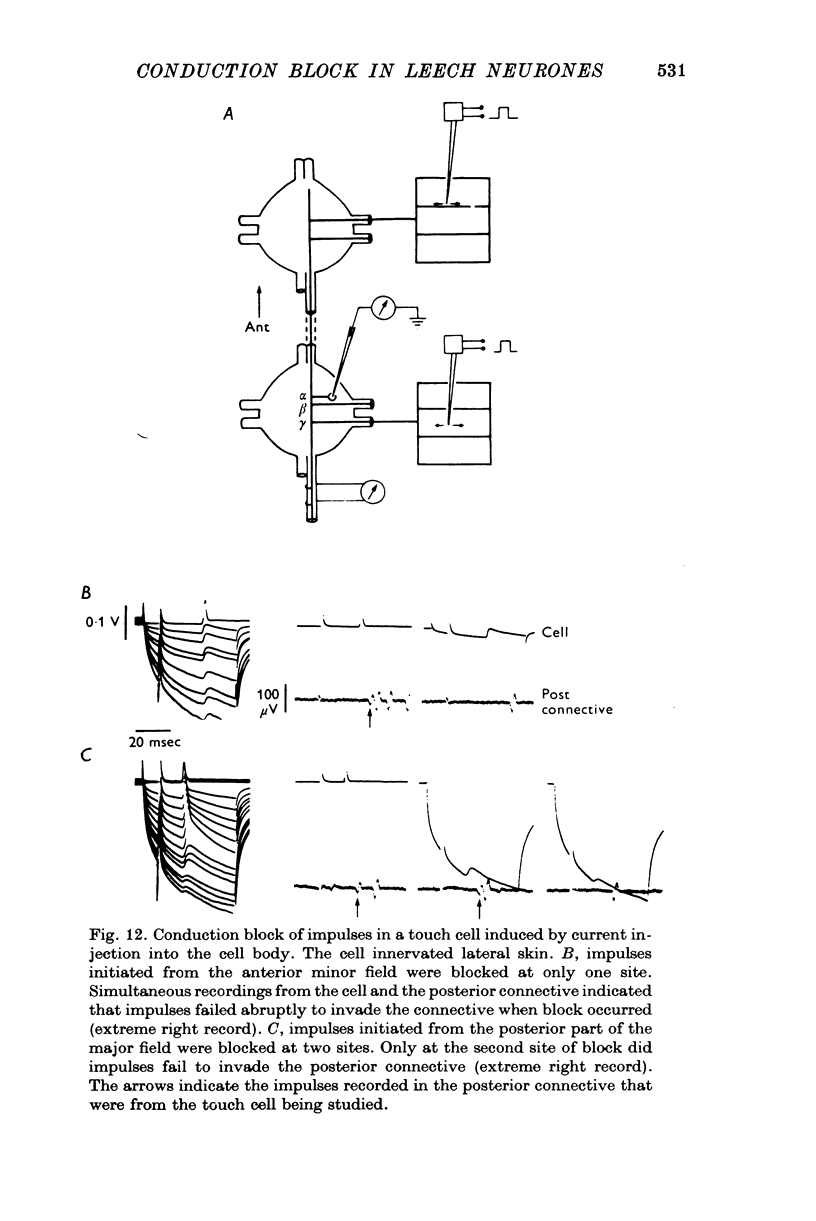
1. In segmental ganglia of the leech, the cutaneous mechanosensory neurones responding to to touch innervated the skin of their own segment and of part of the anterior and posterior adjacent segments. Each touch receptive field could be divided into three non-overlapping areas: a central part innervated by the branches of the cell which ran in the nerve roots of the ganglion containing the cell body, and anterior and posterior parts innervated by its branches which ran in the nerve roots of the anterior and posterior adjacent ganglia. 2. Impulses originating from the anterior and posterior parts of the receptive fields were susceptible to conduction block within the central nervous system when the touch cells fired repetitively at frequencies that could readily be elicited with weak mechanical stimulation. In contrast, impulses originating from the central part of the receptive fields were less susceptible to block. 3. The morphology of touch cells revealed by intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase suggested that conduction block occurred at specific bifurcation points where small cell processes joined the main process. Different physiological experiments supported this conclusion. 4. In some touch cells, bifurcation points with particularly low safety margins of conduction operated as low-pass filters, limiting the frequency of impulses capable of invading certain branches. 5. The results suggest that mechanical stimuli which would likely be encountered by the animal can lead to conduction block within its central nervous system and as a result modify its integrative activities.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron D. H., Matthews B. H. Intermittent conduction in the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1935 Aug 22;85(1):73–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nicholls J. G. After-effects of nerve impulses on signalling in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):571–589. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner G. D. Differentiation of nerve terminals in the crayfish opener muscle and its functional significance. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jun;51(6):731–758. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):198–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C., KUFFLER S. W. Further study of soma, dendrite, and axon excitation in single neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):121–153. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUORTES M. G., FRANK K., BECKER M. C. Steps in the production of motoneuron spikes. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):735–752. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman Y., Spira M. E., Parnas I. Differential flow of information into branches of a single axon. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 21;64:379–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Nicholls J. G. Conductance changes, an electrogenic pump and the hyperpolarization of leech neurones following impulses. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):635–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Presynaptic failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Baylor D. A. Specific modalities and receptive fields of sensory neurons in CNS of the leech. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):740–756. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Purves D. Monosynaptic chemical and electrical connexions between sensory and motor cells in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):647–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas I. Differential block at high frequency of branches of a single axon innervating two muscles. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Nov;35(6):903–914. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.6.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUC L., HUGHES G. M. Modes of initiation and propagation of spikes in the branching axons of molluscan central neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Jan;46:533–549. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.3.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Essen D. C. The contribution of membrane hyperpolarization to adaptation and conduction block in sensory neurones of the leech. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):509–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W. Physiological properties and receptive fields of mechanosensory neurones in the head ganglion of the leech: comparison with homologous cells in segmental ganglia. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):489–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


