Abstract
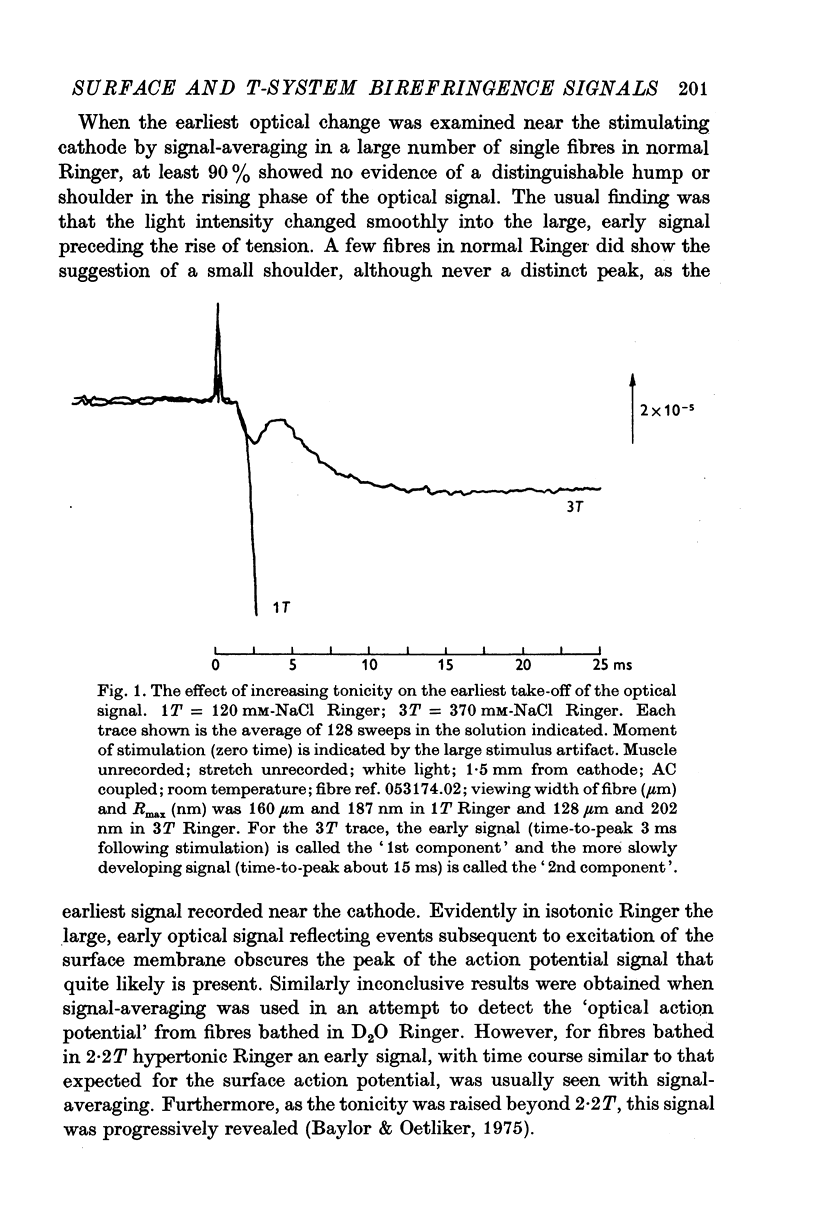
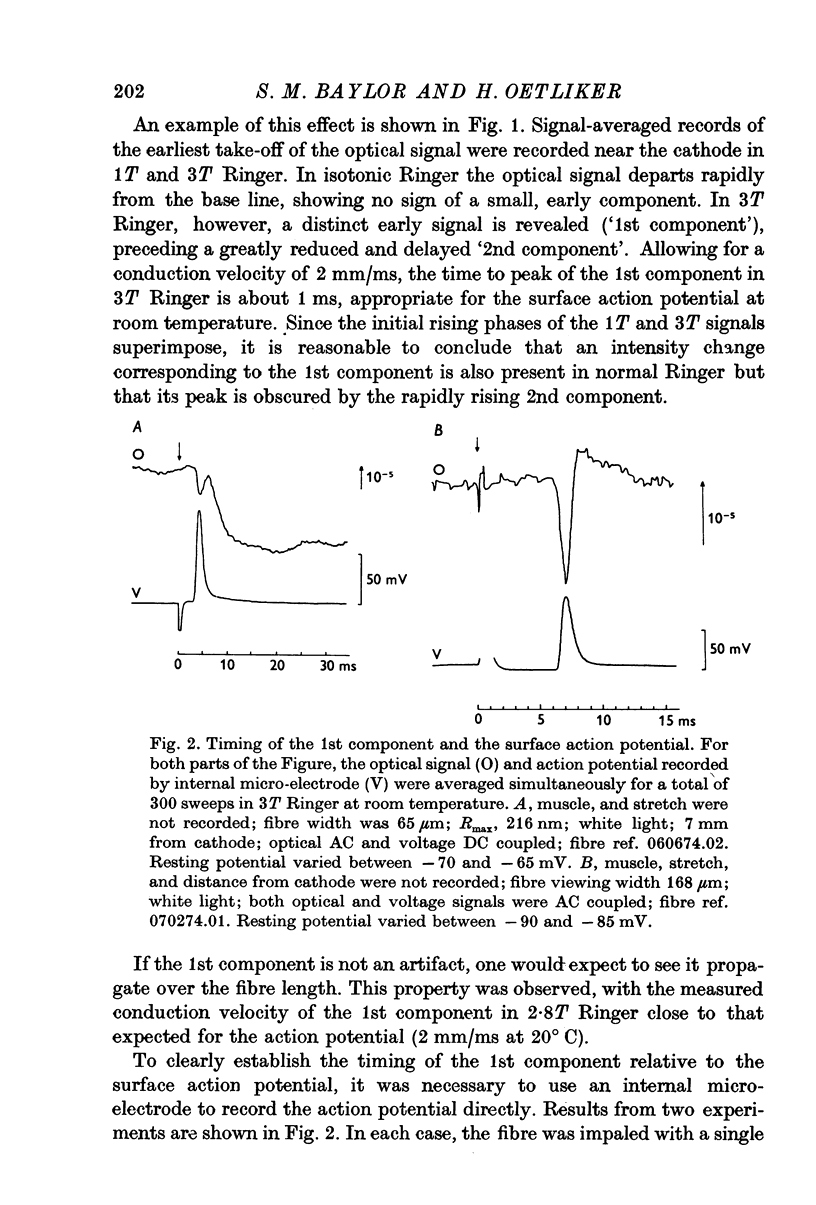
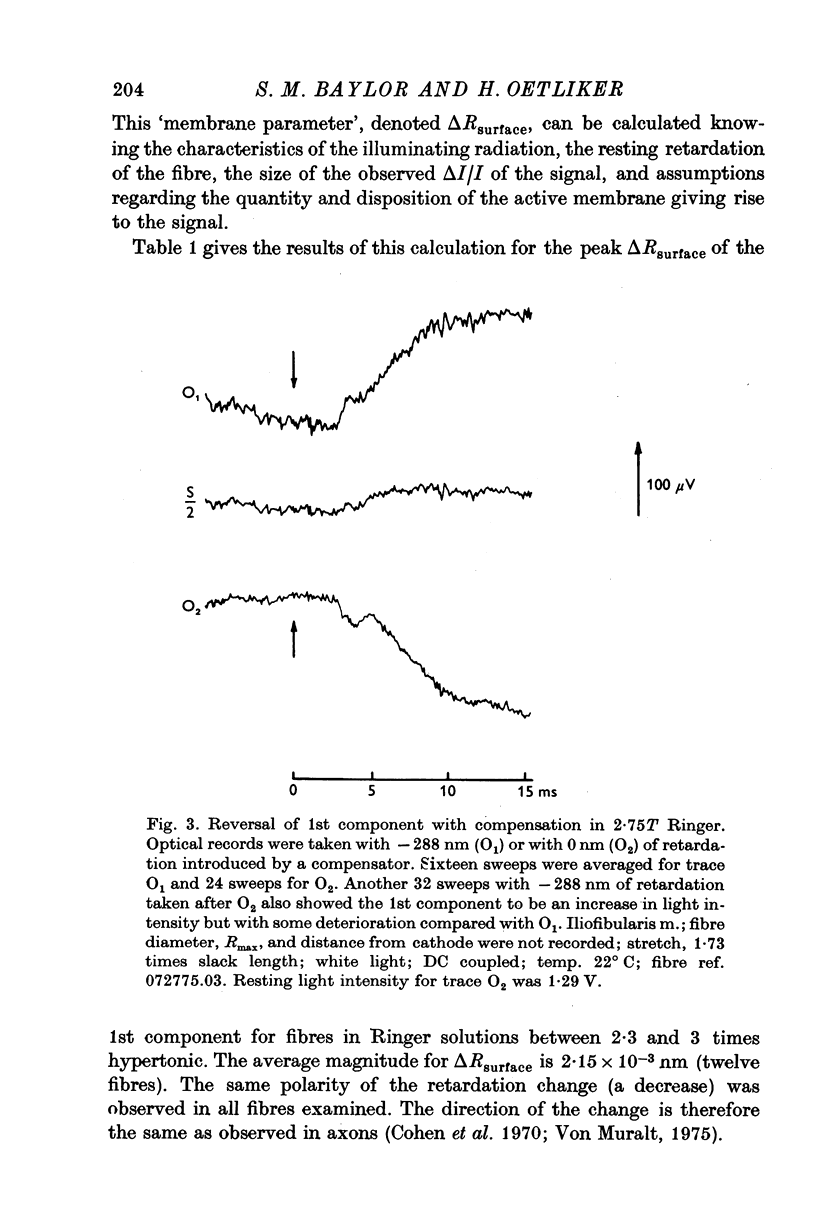
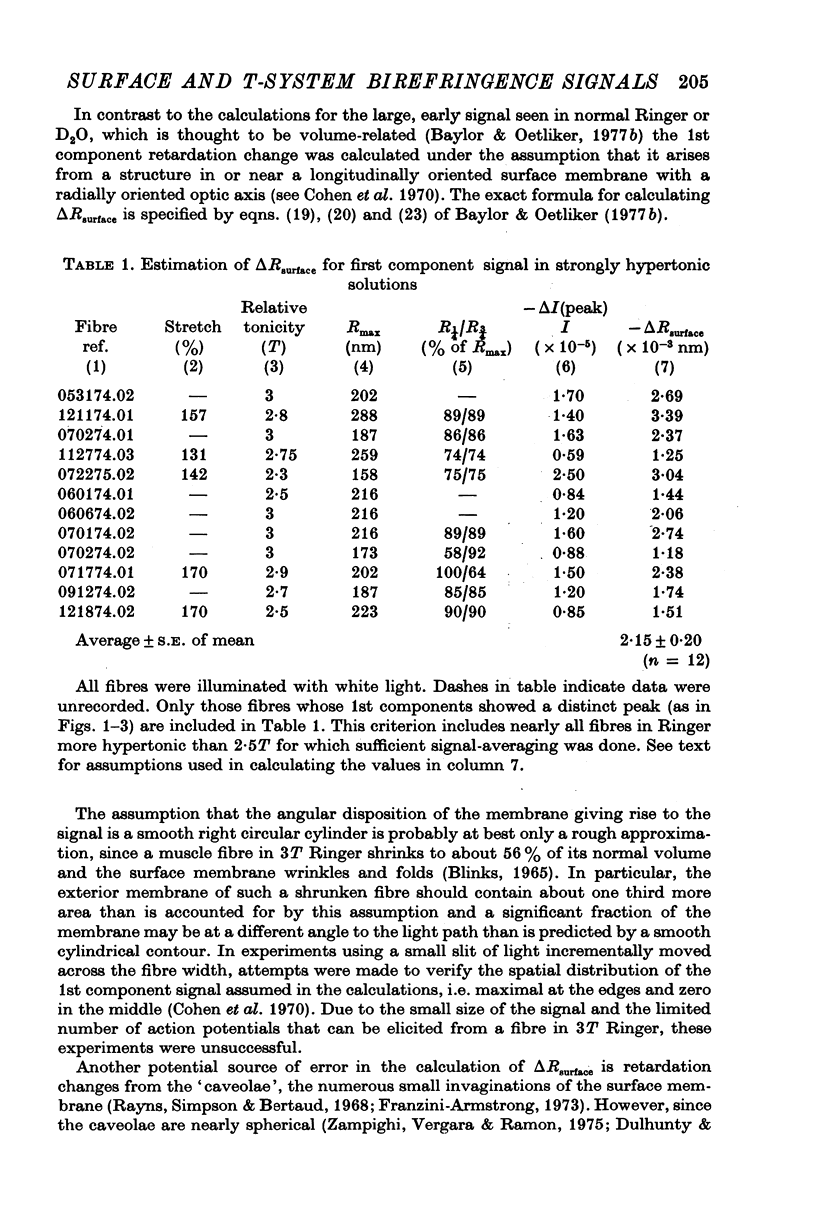
1. When the tonicity of Ringer is increased above 2-5 times normal and a single fibre stimulated externally, the large, early birefringence signal preceding twitch tension (Baylor & Oetliker, 1975, 1977 a,b) is sufficiently reduced and delayed so as to reveal a small but distinct signal ('1st component") preceding it. For an average-sized fibre, the deltaI/I of the 1st component was (minus) 1 to 2 x 10-5. 2. The time course of the 1st component superimposed with the surface action potential simultaneously recorded by an internal micro-electrode. The polarity of the 1st component reversed with compensation. 3. From these characteristics, the 1st component is thought to arise from a small change in optical retardation of the surface membrane due to the action potential. 4. When a fibre was impaled with two micro-electrodes, retardation changes accompanying small hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current steps were detected. In some cases the polarity of the observed signal was opposite in sign to that expected for a retardation change only from the surface membrane. 5. Because the anatomical orientation of the T-system appears to be primarily transverse rather than longitudinal, these signals of opposite polarity are probably, on balance, due to retardation changes from the membranes of the T-system. 6. The possible origin of the large birefringence signal preceding contraction is discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLINKS J. R. INFLUENCE OF OSMOTIC STRENGTH ON CROSS-SECTION AND VOLUME OF ISOLATED SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:42–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Oetliker H. A large birefringence signal preceding contraction in single twitch fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):141–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Oetliker H. Birefringence experiments on isolated skeletal muscle fibres suggest a possible signal from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1975 Jan 10;253(5487):97–101. doi: 10.1038/253097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Oetliker H. The optical properties of birefringence signals from single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):163–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Horowicz P. Fluorescence intensity changes associated with contractile activation in frog muscle stained with Nile Blue A. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):709–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Hille B., Keynes R. D. Changes in axon birefringence during the action potential. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):495–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Hille B., Keynes R. D., Landowne D., Rojas E. Analysis of the potential-dependent changes in optical retardation in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):205–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Salzberg B. M., Davila H. V., Ross W. N., Landowne D., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H. Changes in axon fluorescence during activity: molecular probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(1):1–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01869968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby R. H. Intrinsic birefringence of glycerinated myofibrils. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):763–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Franzini-Armstrong C. The relative contributions of the folds and caveolae to the surface membrane of frog skeletal muscle fibres at different sarcomere lengths. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(3):513–539. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E., HANSON J. Quantitative studies on the structure of cross-striated myofibrils. I. Investigations by interference microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):229–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetliker H., Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K. Simultaneous changes in fluorescence and optical retardation in single muscle fibres during activity. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):693–696. doi: 10.1038/257693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D., Schild R. F. The distribution of the T-system along the sarcomeres of frog and toad sartorius muscles. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):249–258. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachey L. D. The sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubules of the frog's sartorius. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):209–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayns D. G., Simpson F. O., Bertaud W. S. Surface features of striated muscle. II. Guinea-pig skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci. 1968 Dec;3(4):475–482. doi: 10.1242/jcs.3.4.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampighi G., Vergara J., Ramón F. On the connection between the transverse tubules and the plasma membrane in frog semitendinosus skeletal muscle. Are caveolae the mouths of the transverse tubule system? J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):734–740. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Muralt A. The optical spike. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):411–423. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


