Abstract
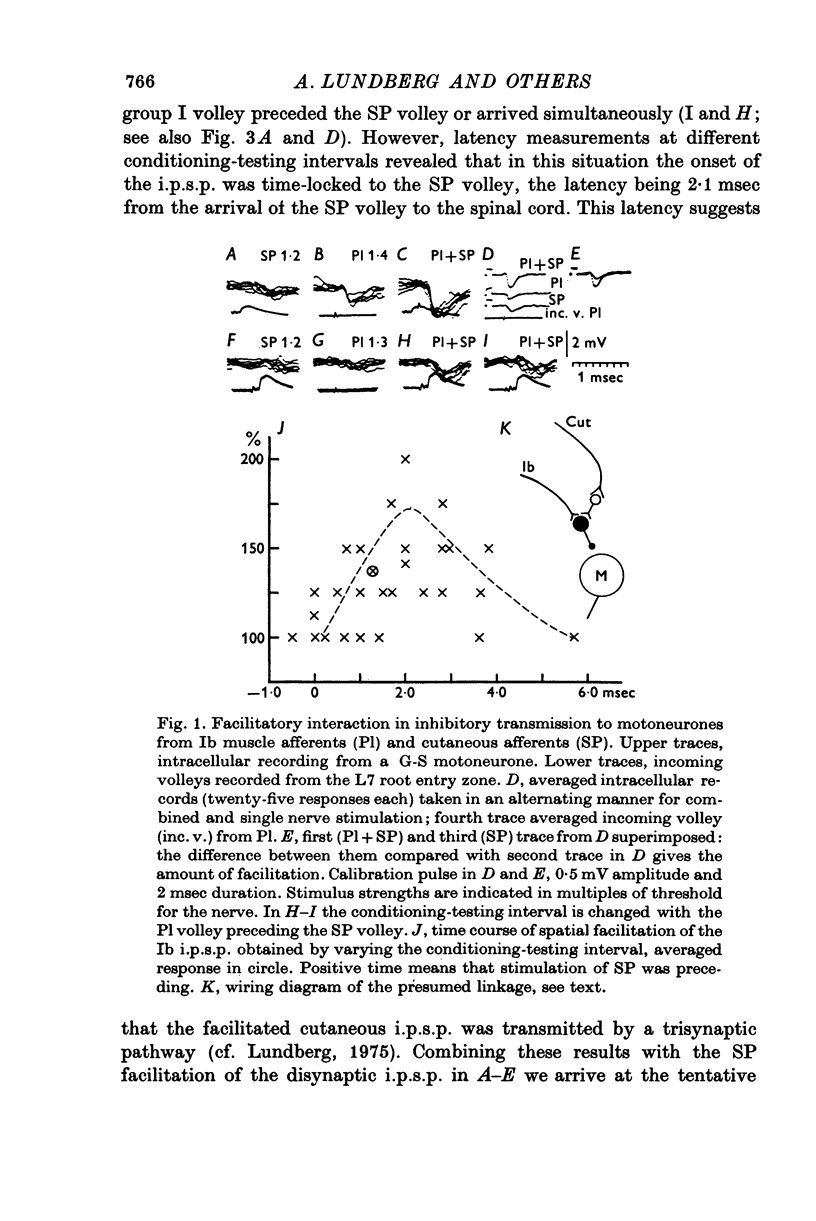
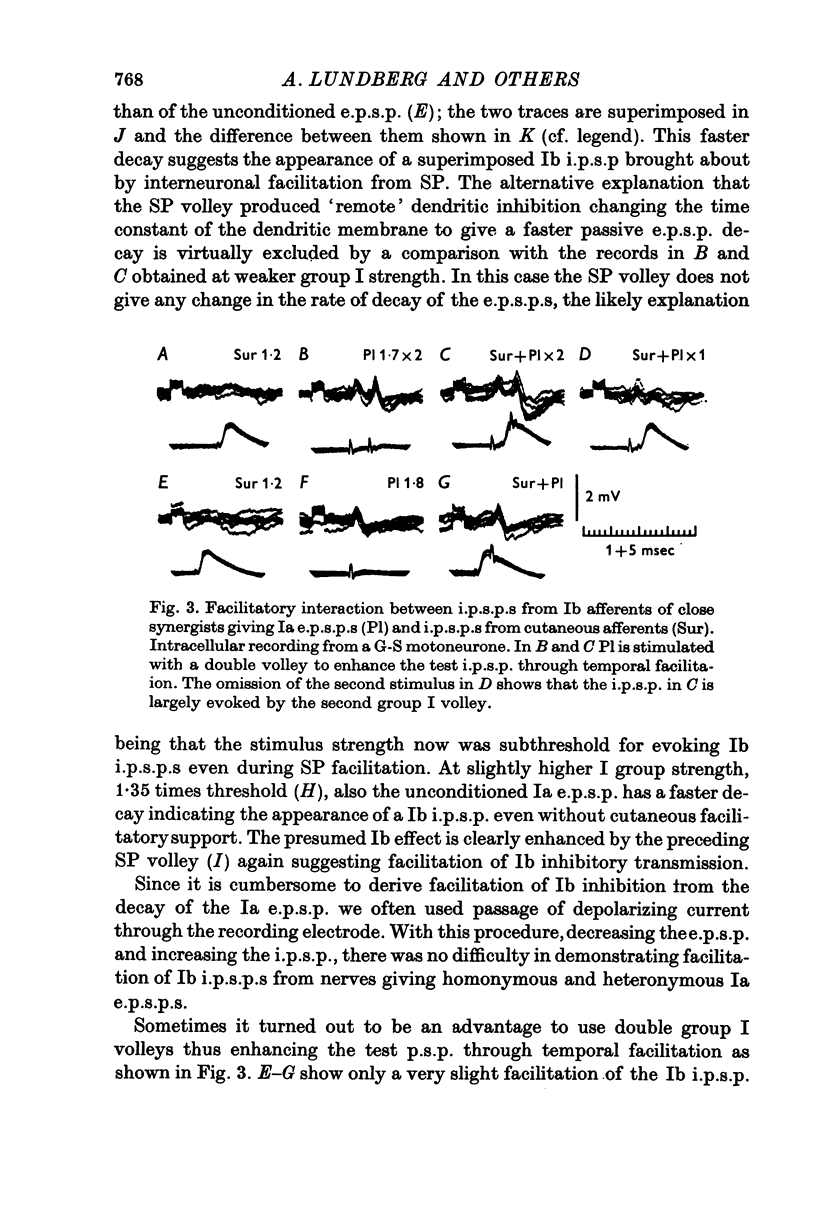
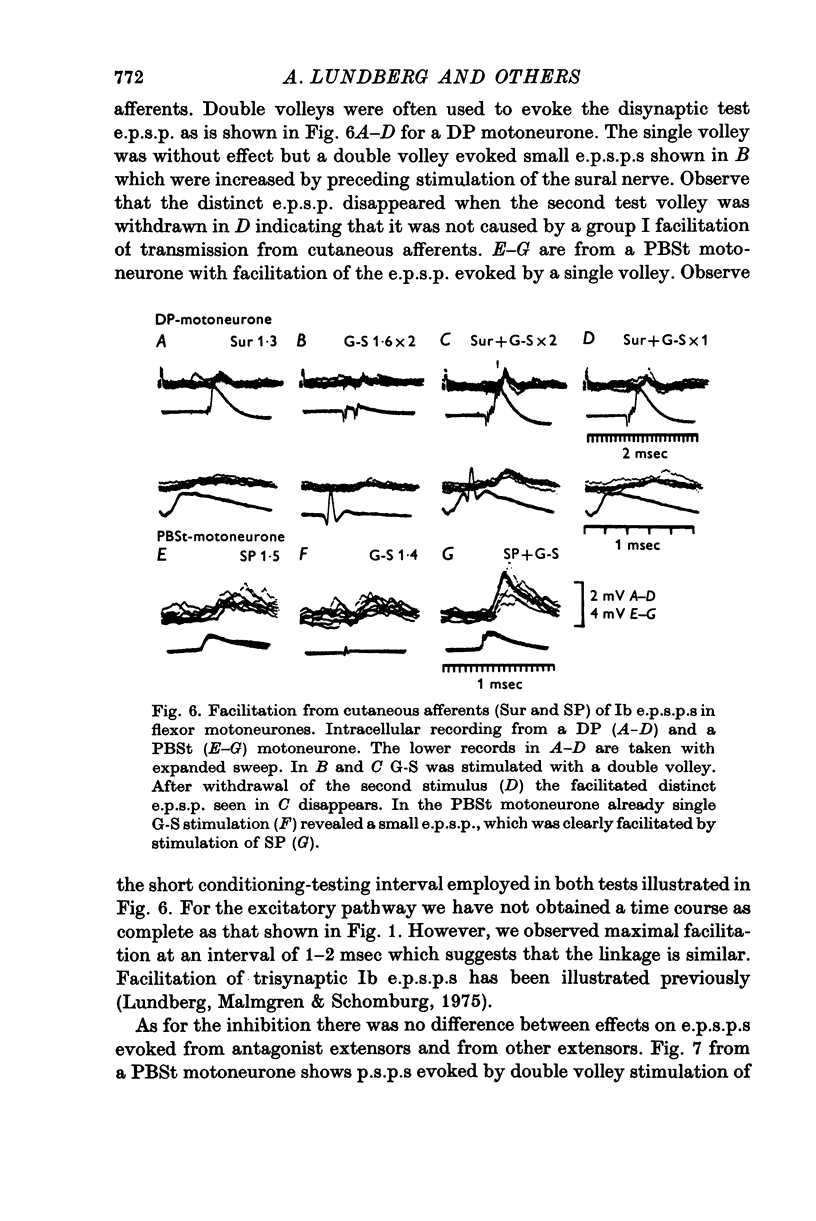
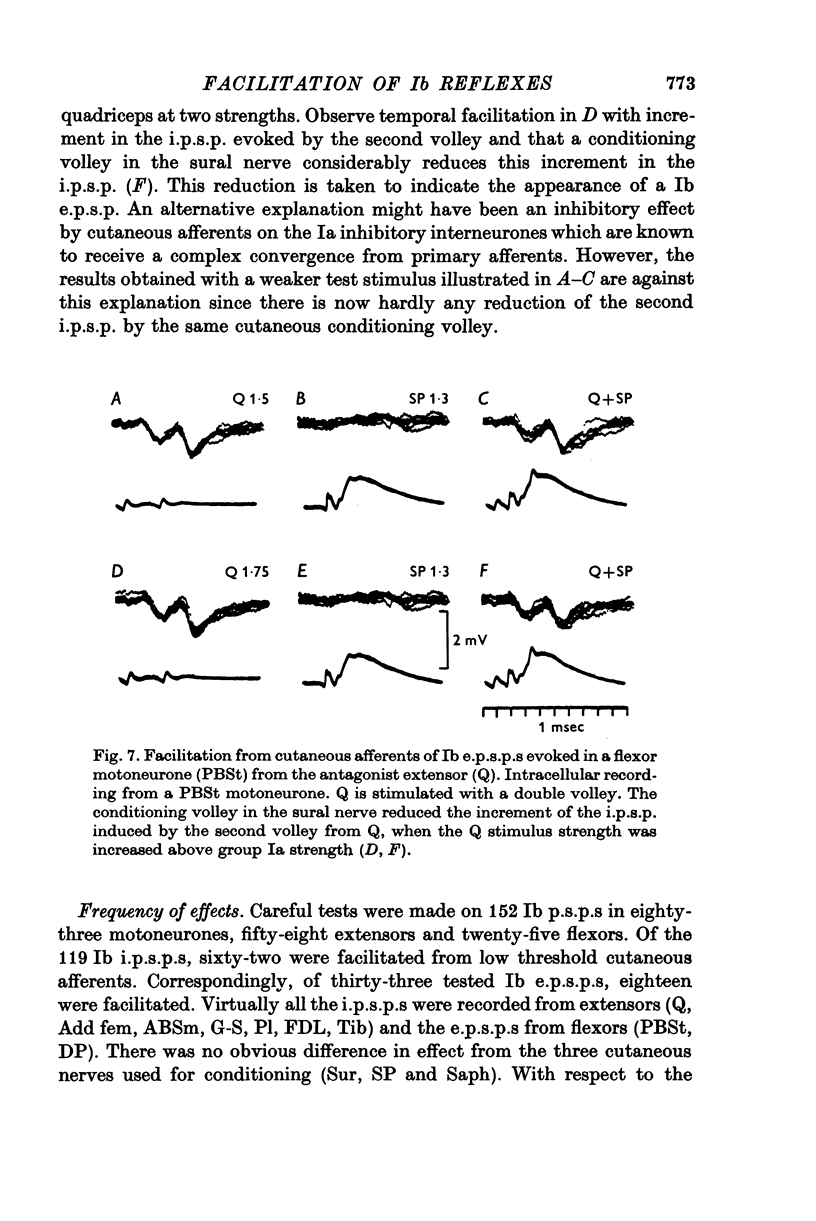
1. The effect of volleys in low threshold cutaneous afferents upon transmission of synaptic action from Ib afferents to motoneurones has been investigated with intracellular recording from alpha motoneurones to hind limb muscles. 2. There was facilitation from cutaneous afferents of transmission in excitatory and inhibitory reflex pathways from Ib afferents without any evidence for difference in effect on di- and trisynaptic pathways. It is postulated that volleys in cutaneous afferents evoke excitatory action in interneurones of these reflex pathways. 3. The time course of the facilitation suggest that cutaneous afferents have disynaptic excitatory connexions with the interneurones intercalated in the disynaptic Ib inhibitory pathways to motoneurones. 4. Some observations are reported suggesting that interneuronal transmission in Ib inhibitory pathways to motoneurones might be facilitated from Ia afferents. 5. The findings are discussed in relation to the presumed role of Ib reflex action in regulating muscle tension.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Jukes M. G., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 1. Influence on transmission from primary afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jul-Aug;67(3):373–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans J., Burke R., Fedina L., Lundberg A. The effect of dopa on the spinal cord. 8. Presynaptic and "remote" inhibition of transmission from Ia afferents to alpha motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Mar;90(3):618–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., McIntyre A. K. Properties of group I afferent fibres from semitendinosus muscle in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarkowska J., Jankowska E., Sybirska E. Axonal projections of spinal interneurones excited by group I afferents in the cat, revealed by intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 10;118(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90844-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Sears T. A. The proprioceptive reflex control of the intercostal muscles during their voluntary activation. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):711–738. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Lundberg A., Ryall R. W. Reticulospinal inhibition of transmission in reflex pathways. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):201–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedina L., Hultborn H. Facilitation from ipsilateral primary afferents of interneuronal transmission in the Ia inhibitory pathway to motoneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Sep;86(1):59–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., McINTYRE A. K. An analysis of fibre diameter and receptor characteristics of myelinated cutaneous afferent fibres in cat. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:99–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(4):338–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00237706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. IV. Effects on interneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1972;15(1):54–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00234958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J. C., Singer J. J., Goldman M. R. An evaluation of length and force feedback to soleus muscles of decerebrate cats. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Nov;33(6):784–811. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H. Transmission in the pathway of reciprocal Ia inhibition to motoneurones and its control during the tonic stretch reflex. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:235–255. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60736-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illert M., Lundberg A., Tanaka R. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 2. Convergence on neurones mediating disynaptic cortico-motoneuronal excitation. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Dec 22;26(5):521–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00238825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):597–622. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., BESSOU P. Etude des sous-groupes lent et rapide du groupe I (fibres afférentes d'origine musculaire de grand diamètre) chez le chat. J Physiol (Paris) 1957 Nov;49(5):1025–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström S., Schomburg E. D. Group I inhibition in Ib excited ventral spinocerebellar tract neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):166–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Convergence from Lb, cutaneous and joint afferents in reflex pathways to motoneurones. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 4;87(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. R., Houk J. C. Improvement in linearity and regulation of stiffness that results from actions of stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):119–142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOGLUND S. Anatomical and physiological studies of knee joint innervation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1956;36(124):1–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


