Abstract
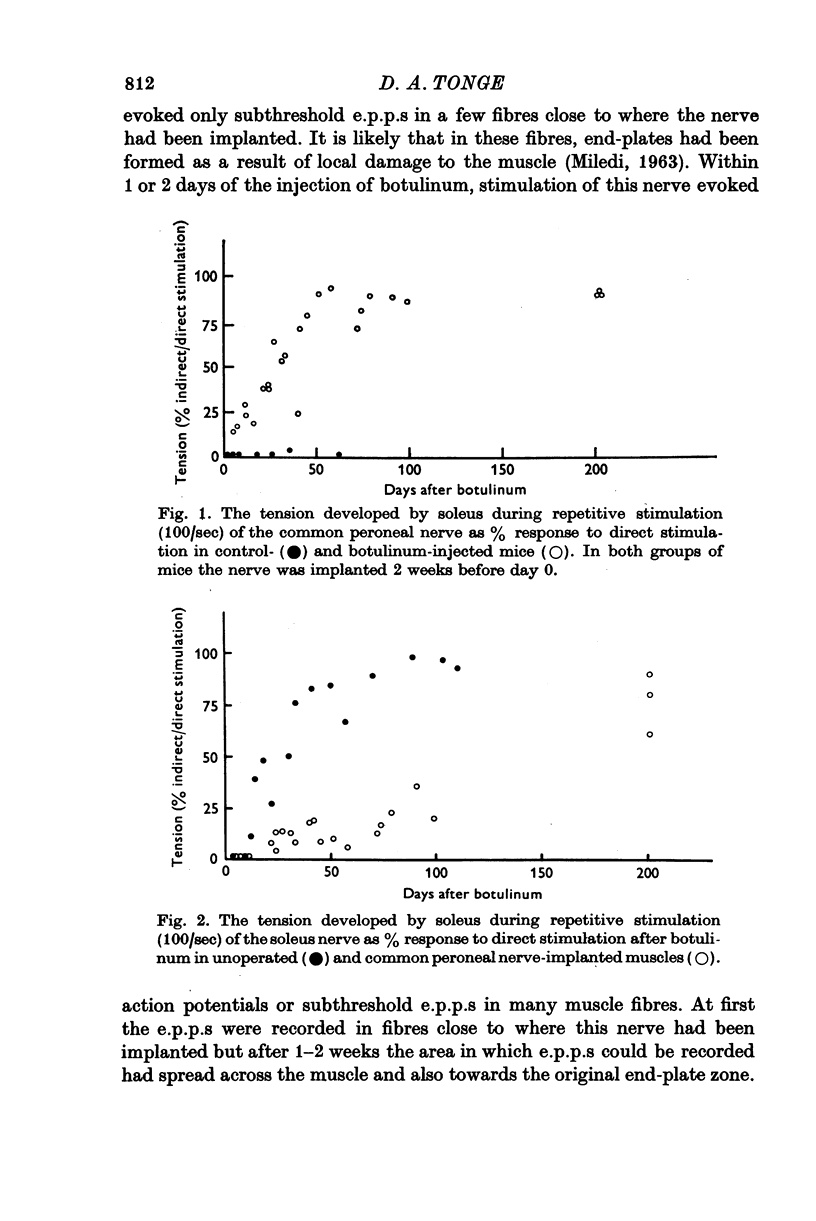
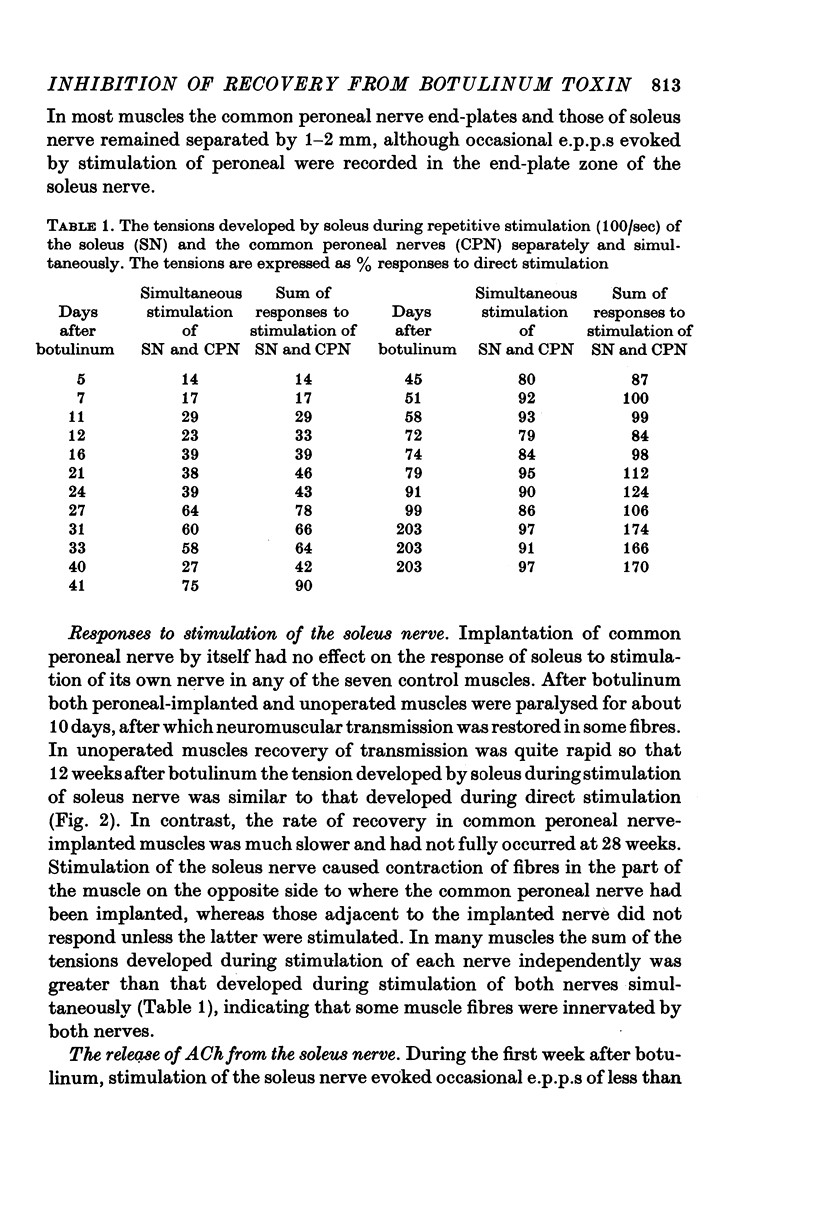
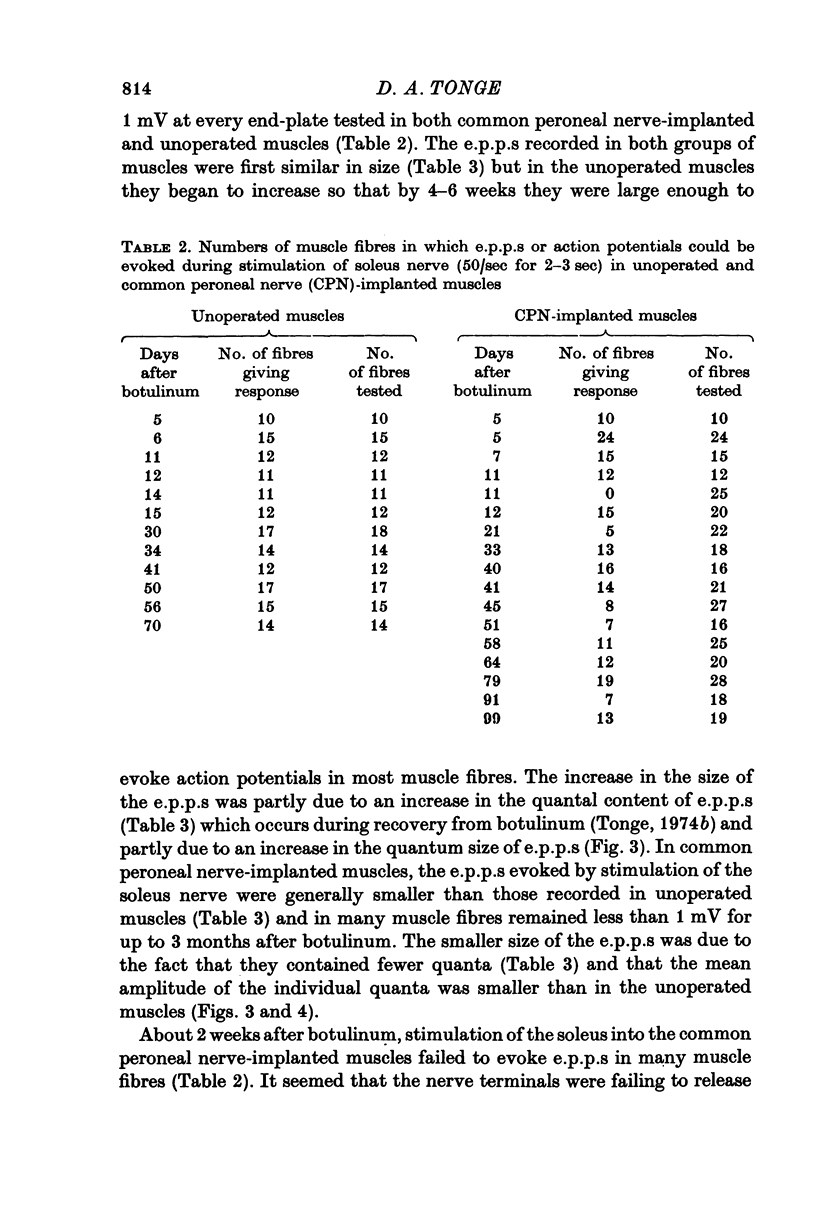
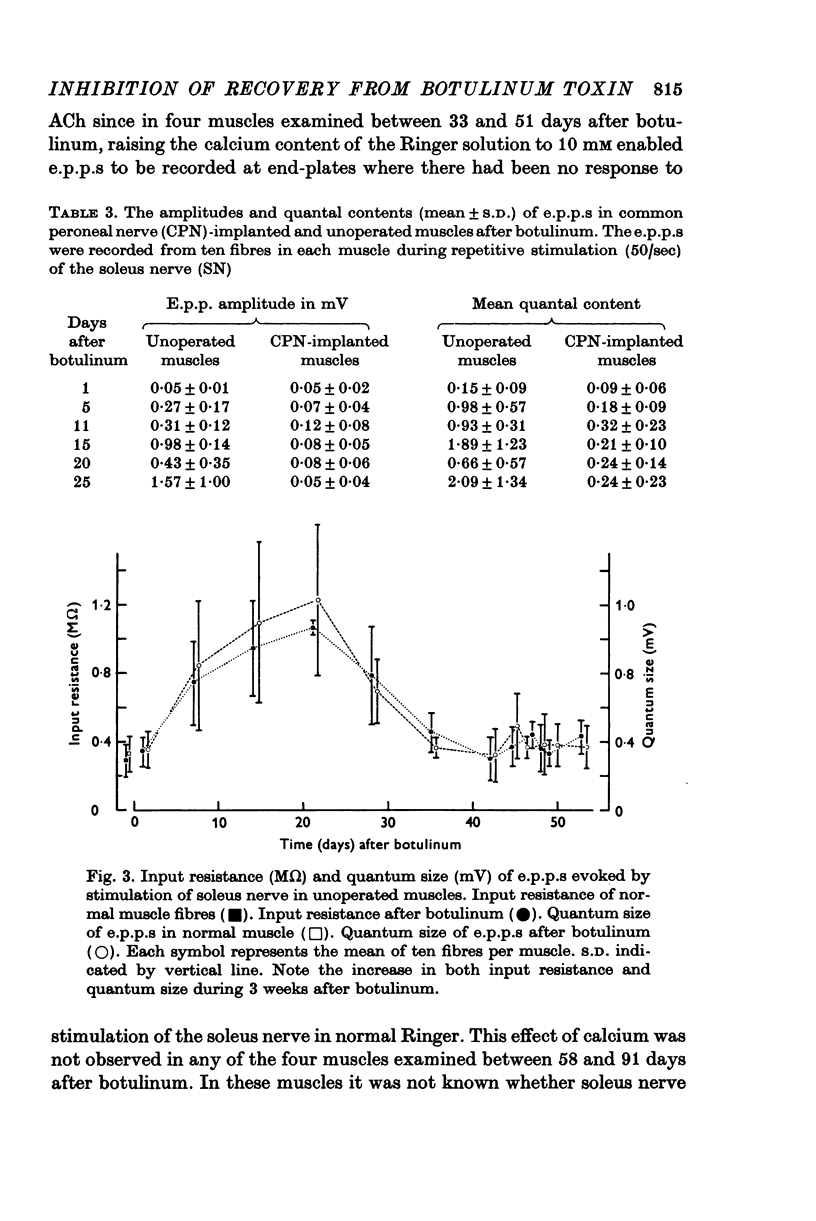
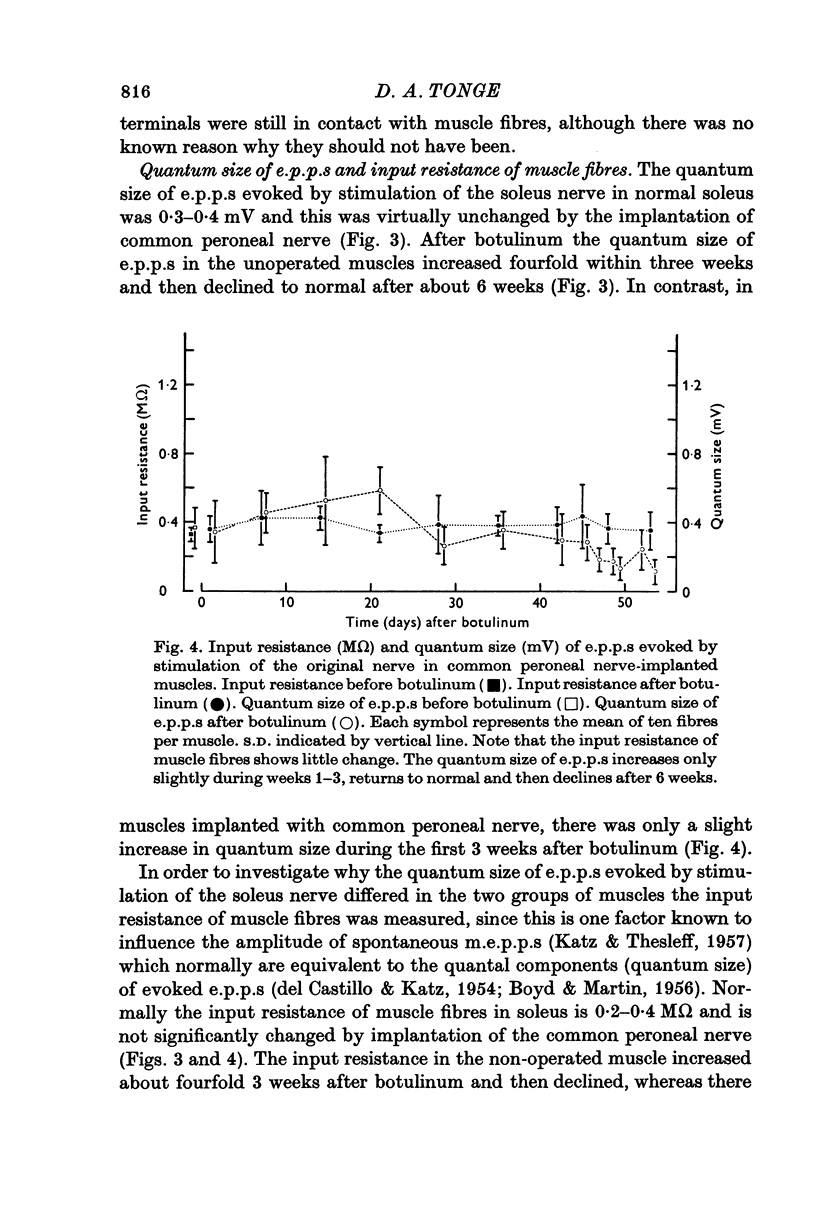
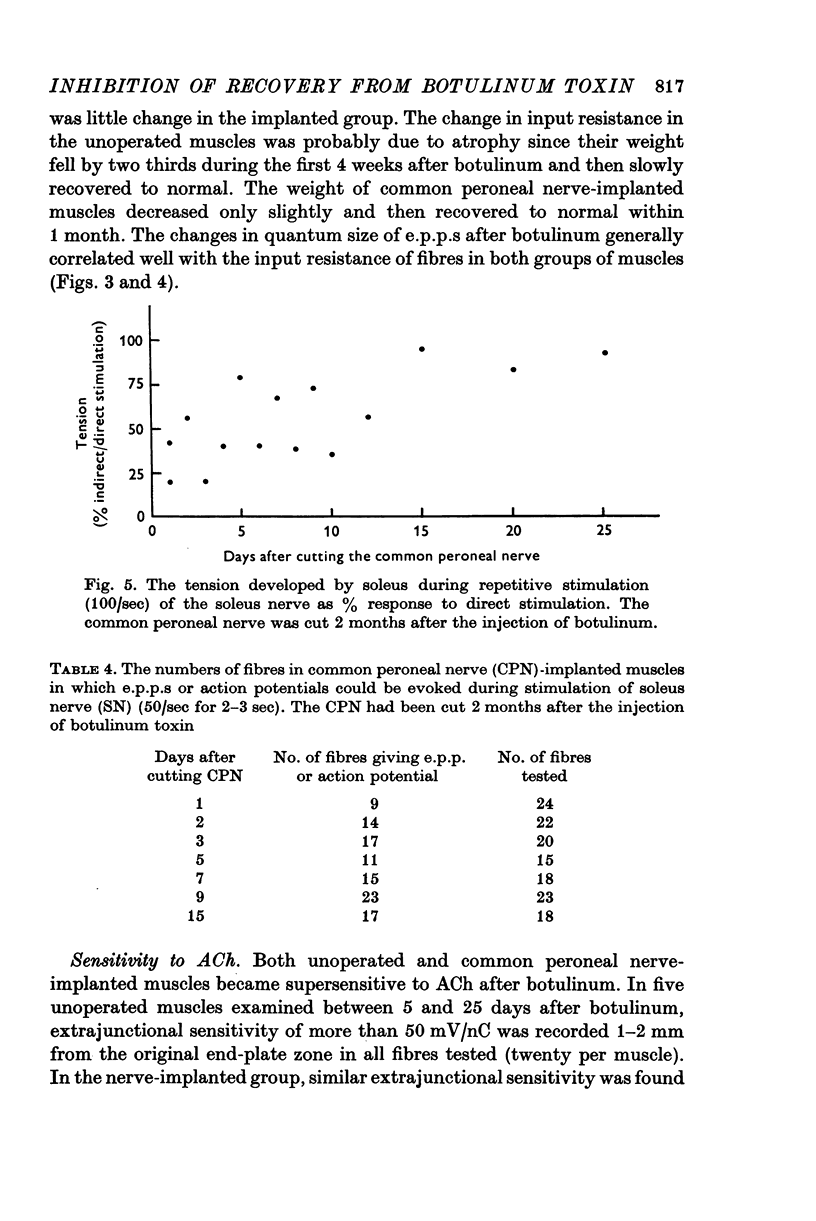
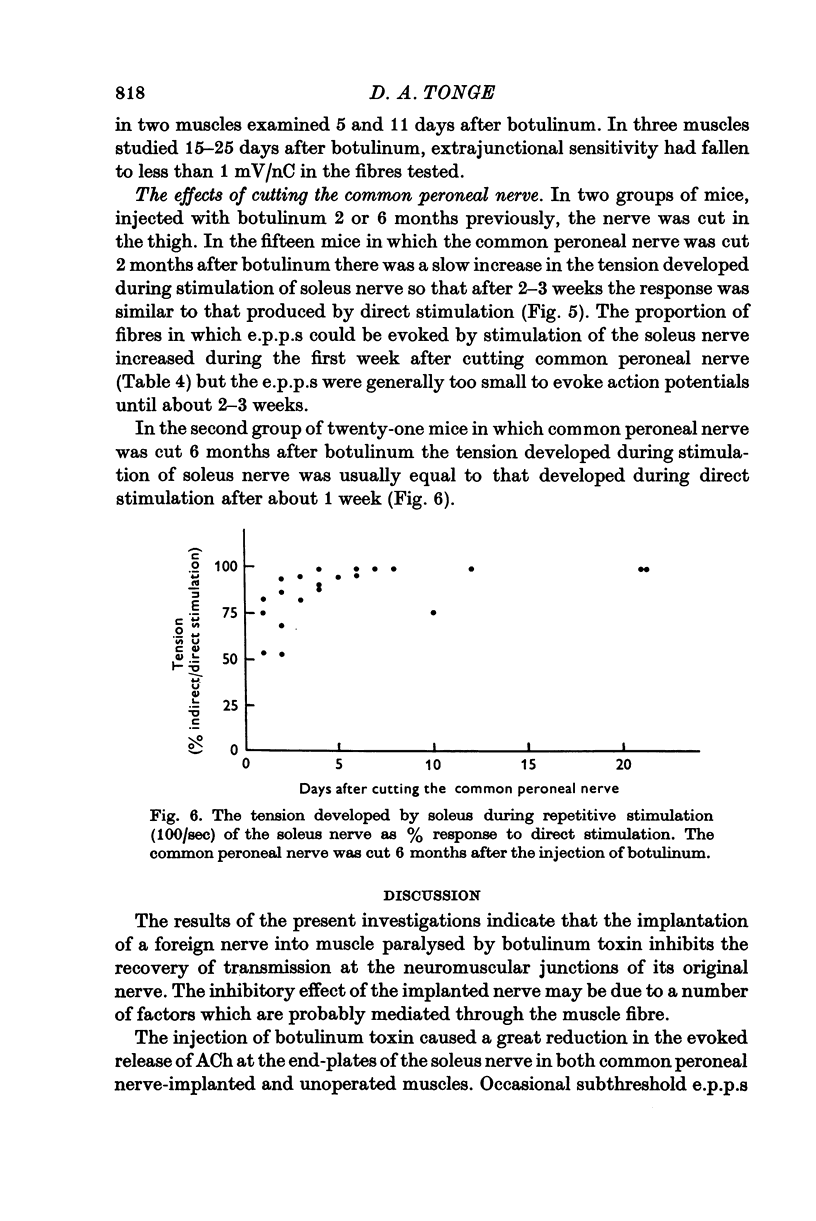
1. The common peroneal nerve was implanted into soleus in the mouse and 2 weeks later a sublethal dose of botulinum toxin injected causing a block of neuromuscular transmission at the terminals of the soleus nerve. Most muscle fibres became innervated by the common peroneal nerve. 2. Recovery of neuromuscular transmission at the soleus nerve terminals was delayed in the common peroneal nerve implanted muscles. 3. Stimulation of the soleus nerve after botulinum-evoked subthreshold end-plate potentials (e.p.p.s) in virtually every fibre tested in unoperated muscles. In common peroneal nerve-implanted muscles stimulation of the soleus nerve failed to evoke e.p.p.s in about 40% of fibres tested and where e.p.p.s were recorded their amplitudes were generally smaller. 4. When the common peroneal nerve was cut 2 months after botulinum, neuromuscular transmission at soleus nerve terminals occurred after 4 weeks. When the common peroneal nerve was cut 6 months after botulinum, transmission was found at soleus nerve terminals within 1 week. 5. Recovery of transmission at soleus nerve terminals from the effects of botulinum toxin is delayed if the muscle fibres become innervated by the common peroneal nerve and a proportion of soleus nerve terminals cease to release acetylcholine (ACh) until after the peroneal nerve has been cut.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S. V., DICKENS F., ZATMAN L. J. The action of botulinum toxin on the neuro-muscular junction. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):10–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Strich S. J. The effects of botulinum toxin on the pattern of innervation of skeletal muscle in the mouse. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Jan;53(1):84–89. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Sonesson B., Thesleff S., Zelená J. Nerve implants in botulinum poisoned mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):872–882. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. FORMATION OF EXTRA NERVE-MUSCLE JUNCTIONS IN INNERVATED MUSCLE. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1191–1192. doi: 10.1038/1991191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge D. A. Chronic effects of botulinum toxin on neuromuscular transmission and sensitivity to acetylcholine in slow and fast skeletal muscle of the mouse. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):127–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge D. A. Proceedings: Synaptic function in experimental dually innervated muscle in the mouse. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):96P–97P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


