Abstract
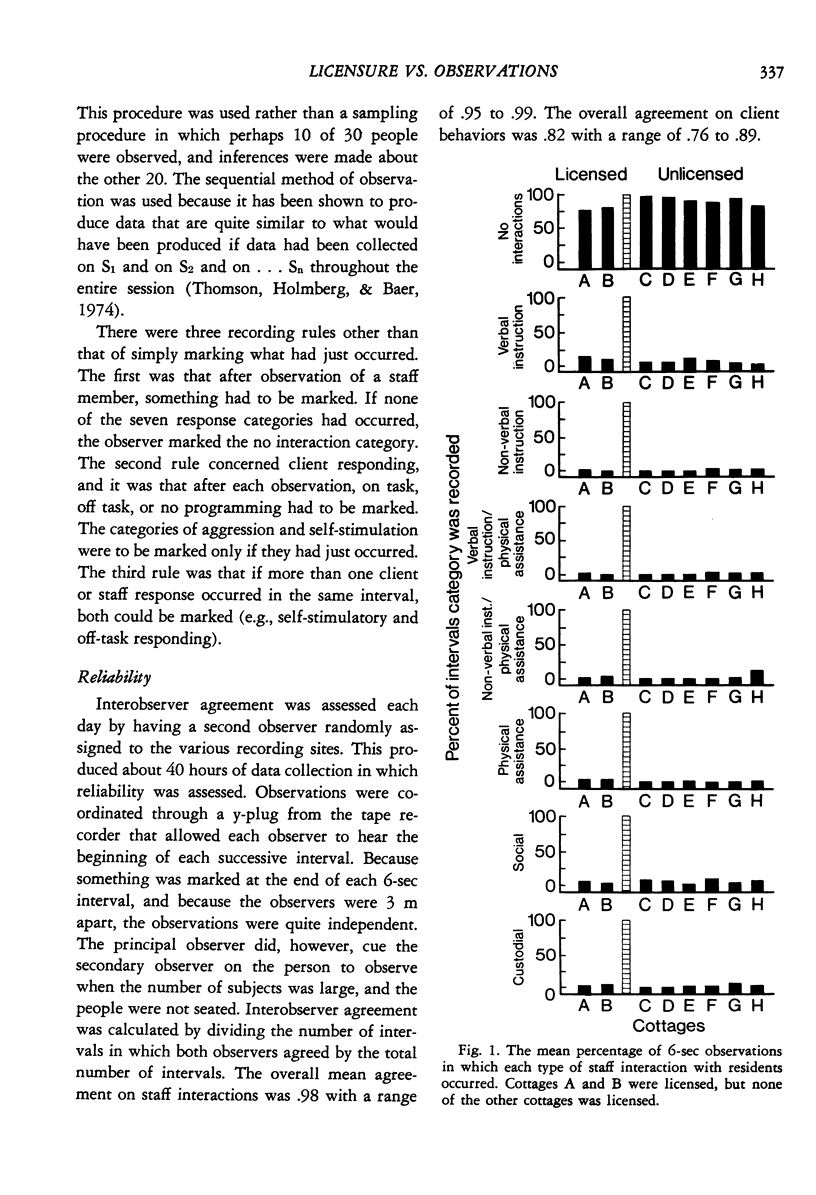
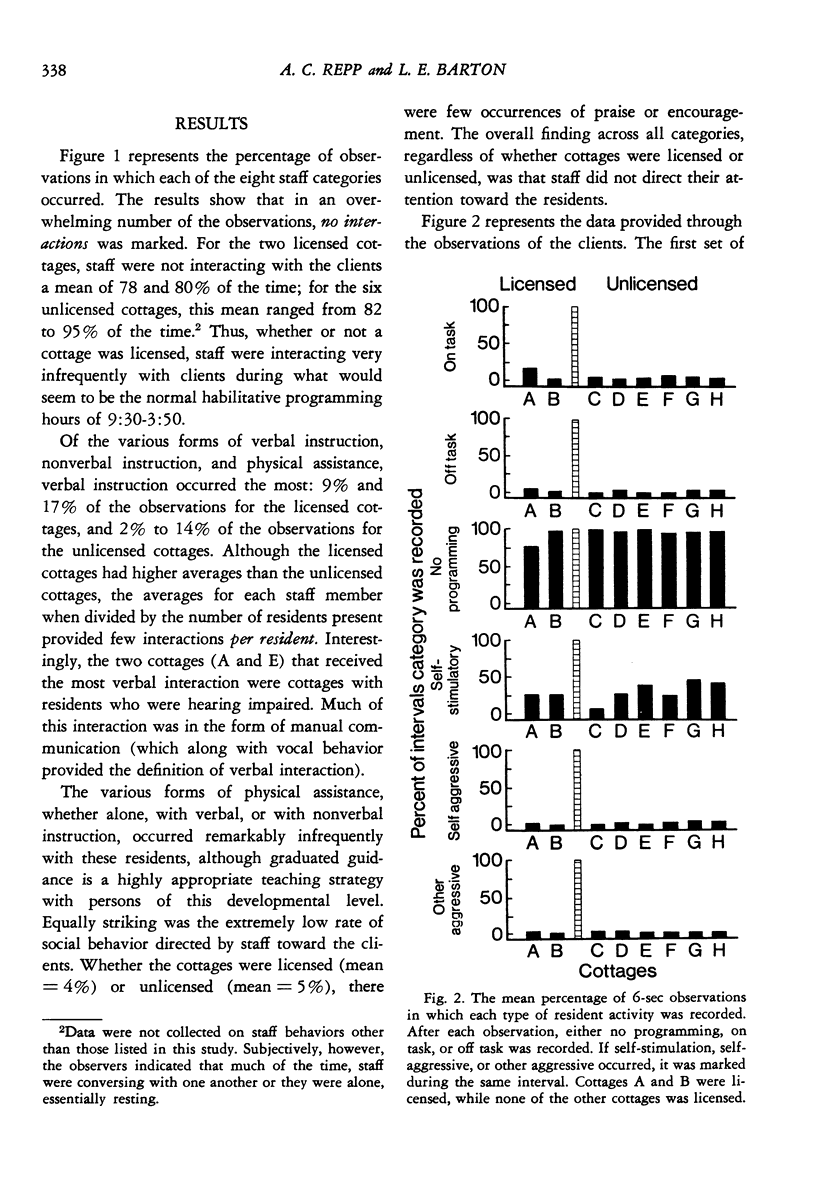
In the last several years, various organizations have produced strikingly similar documents by which institutions for retarded persons are judged for licensure. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether residential units that were licensed differed from residential units that were not licensed in terms of the active programming behaviors of their staff and residents. Data were collected through a time-sampling procedure that yielded about 160,000 observations on eight staff and six resident behaviors. Results showed that the licensed units were just as derelict as unlicensed units in providing habilitative programming for their retarded residents. Maladaptive responding by residents occurred at least as much as task-related residents. Maladaptive responding by residents occurred at least as much as task-related behaviors: residents spent as much time self-stimulating as they did in programming; they also engaged in self-abusive behavior about as much time as they engaged in on-task responding. Results were discussed in terms of the failure of governmental regulations that are not based on observation to adequately assess habilitative programming.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bible G. H., Sneed T. J. Some effects of an accreditation survey on program completion at a state institution. Ment Retard. 1976 Oct;14(5):14–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby K. G. Essentials of active programming. Ment Retard. 1976 Apr;14(2):3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repp A. C. A tracking system for residents' records to meet JCAH standards and ICF-MR regulations. Ment Retard. 1976 Dec;14(6):18–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson C. A brief report on a comparison of time-sampling procedures. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):623–626. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


