Abstract
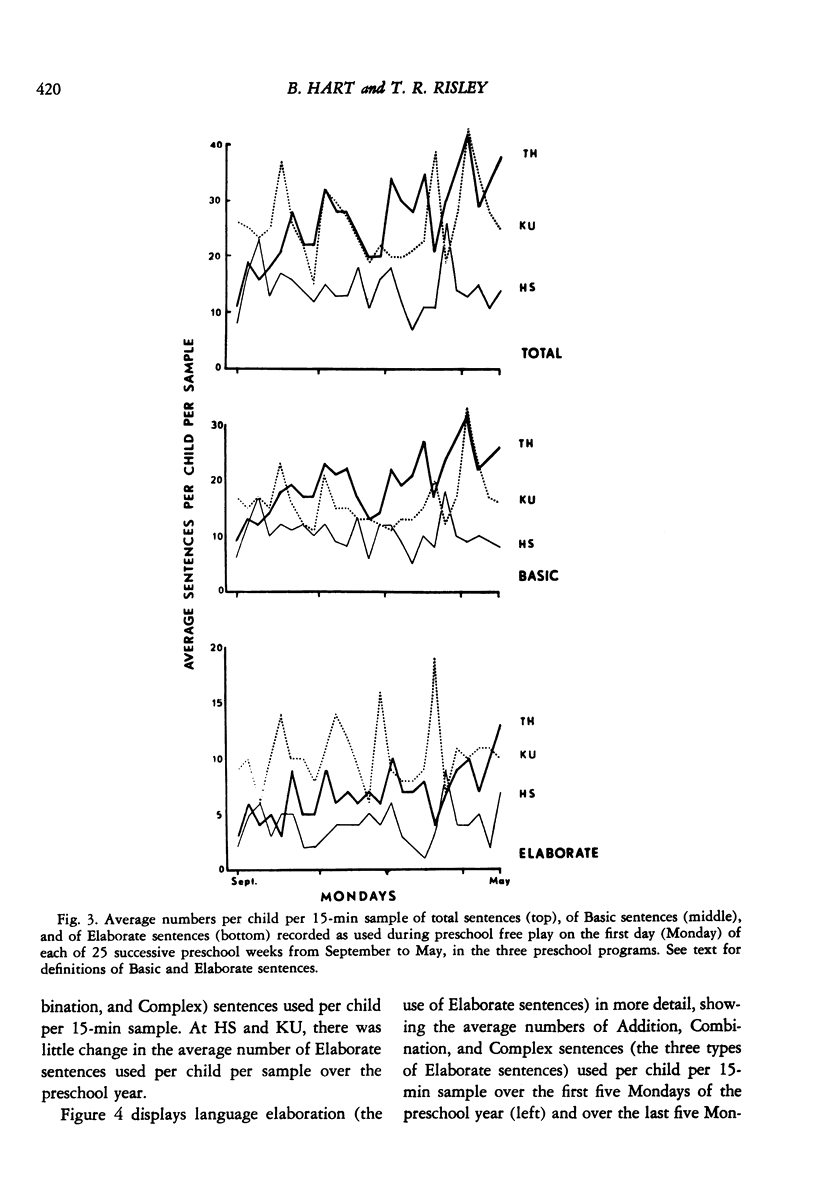
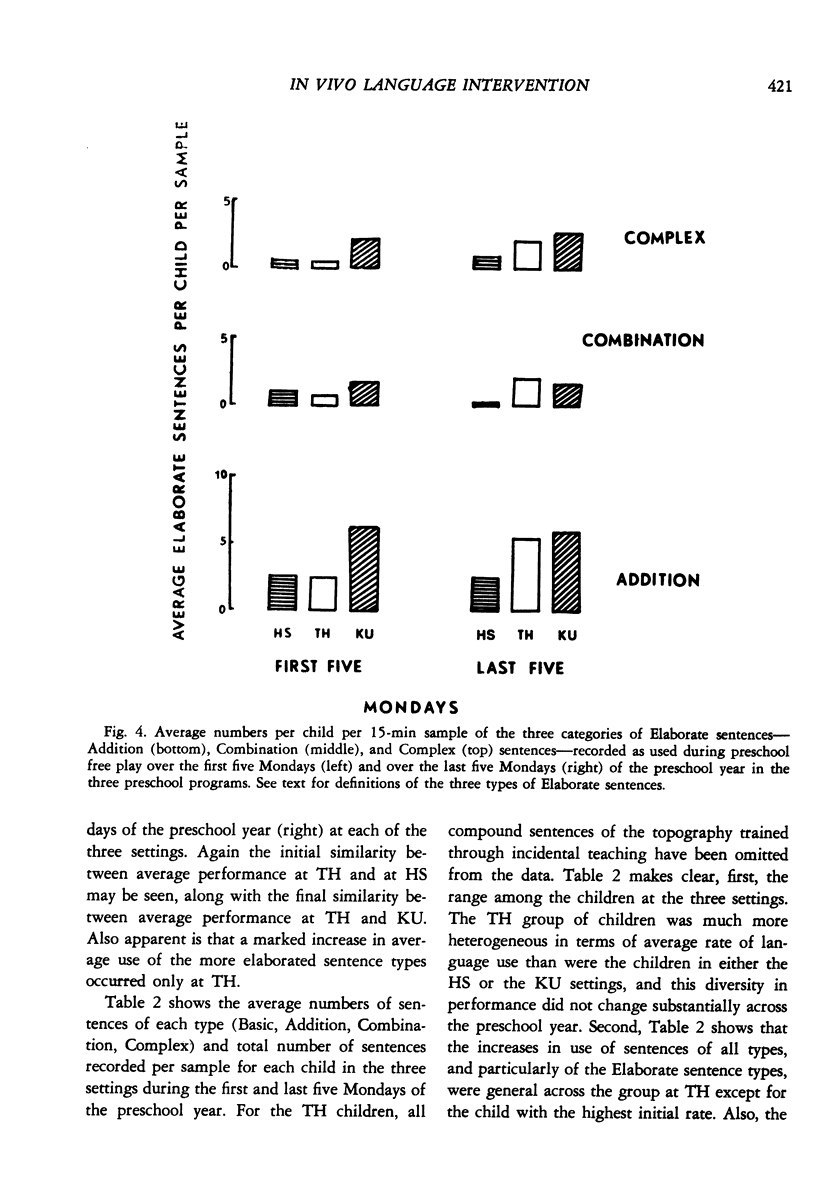
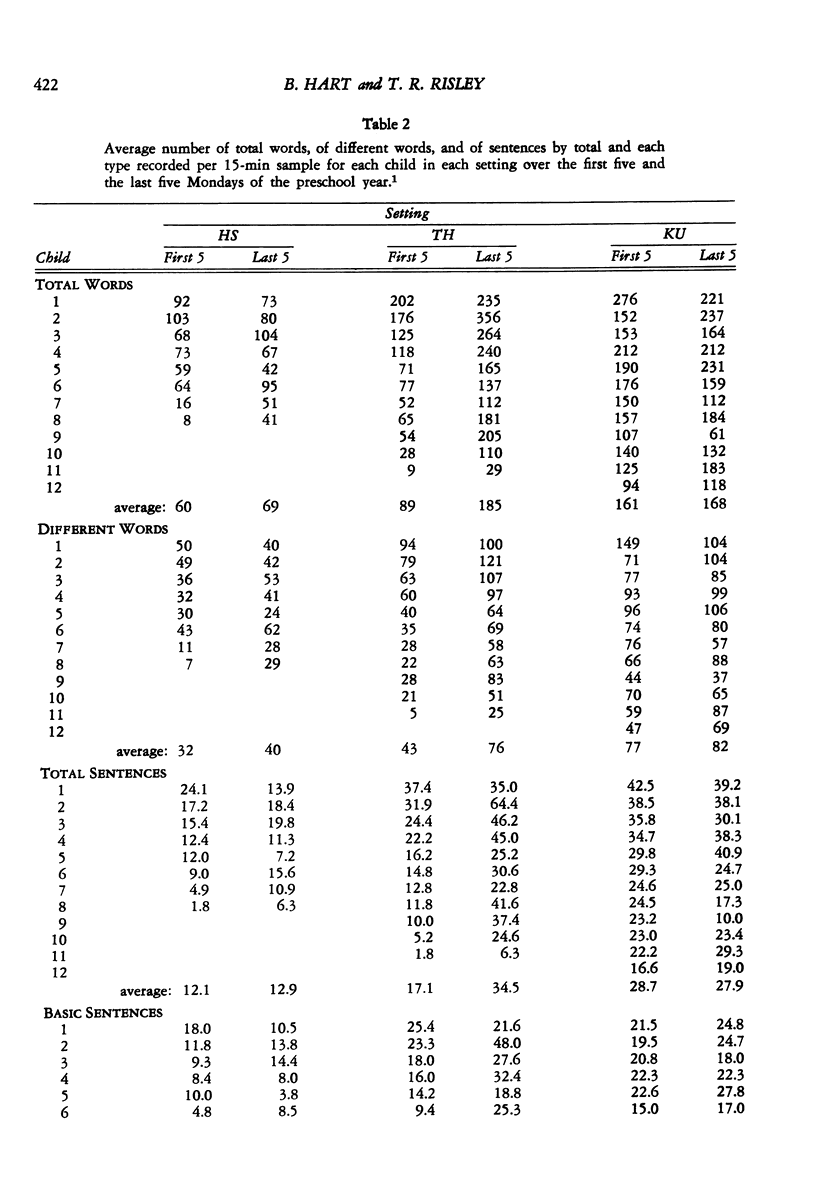
After observing the lack of generalization of language trained in highly structured training sessions using established behavior modification techniques, "incidental teaching" procedures were developed to change the use of specified language behaviors in the natural environment. This paper reports an analysis of the general changes in the language, other than that specifically targeted by the incidental teaching procedures, used by disadvantaged preschool children. The daily language samples of disadvantaged children involved in a previously reported experiment to increase compound sentence usage were reexamined and compared to comparable records of other disadvantaged children and of middle-class children of college parents in order to assess possible general effects of the intervention program. Whereas the language that both groups of comparison children used changed little across the preschool year, the amount of talking by the children in the experimental program increased markedly. Their use of more elaborate vocabulary and more elaborate sentences also increased in direct proportion to the increases in overall language use, such that both language use and language elaboration in the experimental group of children changed from a pattern simlar to the comparison group of disadvantaged children to a pattern similar to the comparison group of middleclass children. It is argued that some general features of the incidental teaching procedure--differentially attending to child overtures and responding relative to the child's selected topic (reinforcer)--contributed to the increase in overall language use beyond the specific language behavior targeted, and that this increase in the probability of children's talking itself resulted in the substantial increases in elaboration seen in the children's spontaneous language. Because, at least in children with fairly well-developed language repertoires, language use is contextually controlled, talking more involves talking in more varied and complex contexts, which inevitably produces the use of more elaborate language.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYLLON T., MICHAEL J. The psychiatric nurse as a behavioral engineer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Oct;2:323–334. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. M., Risley T. R. Establishing use of descriptive adjectives in the spontaneous speech of disadvantaged preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):109–120. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B., Risley T. R. Incidental teaching of language in the preschool. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):411–420. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B., Risley T. R. Using preschool materials to modify the language of disadvantaged children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Summer;7(2):243–256. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS W., THOMAS J., GOLDIAMOND I. Application of operant conditioning to reinstate verbal behavior in psychotics. J Speech Hear Disord. 1960 Feb;25:8–12. doi: 10.1044/jshd.2501.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelaurin K., Risley T. R. The organization of day-care environments: "zone" versus "man-to-man" staff assignments. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Fall;5(3):225–232. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Berberich J. P., Perloff B. F., Schaeffer B. Acquisition of imitative speech by schizophrenic children. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T. R., Reynolds N. J. Emphasis as a prompt for verbal imitation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Fall;3(3):185–190. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN J. A. REINSTATEMENT OF VERBAL BEHAVIOR IN A PSYCHOTIC BY REINFORCEMENT METHODS. J Speech Hear Disord. 1963 Nov;28:398–401. doi: 10.1044/jshd.2804.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. F., Baer D. M. An implicit technology of generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):349–367. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


