Abstract
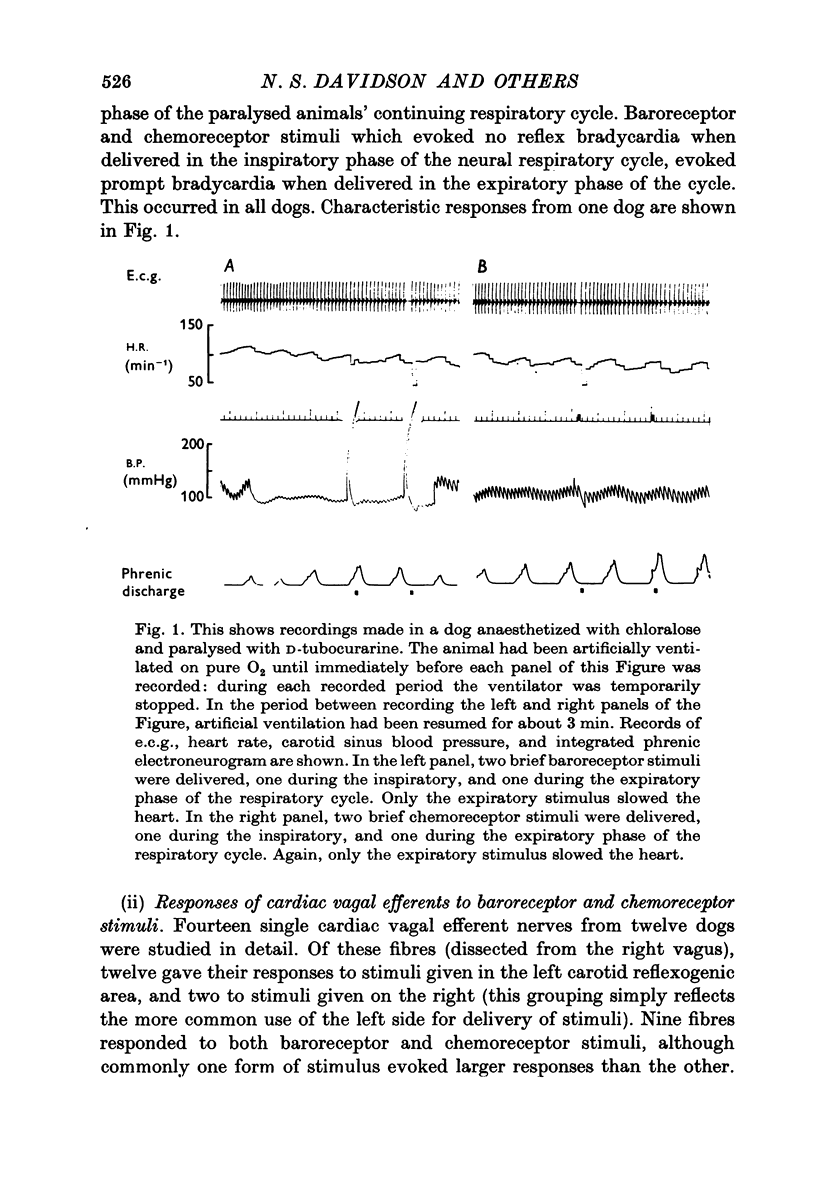
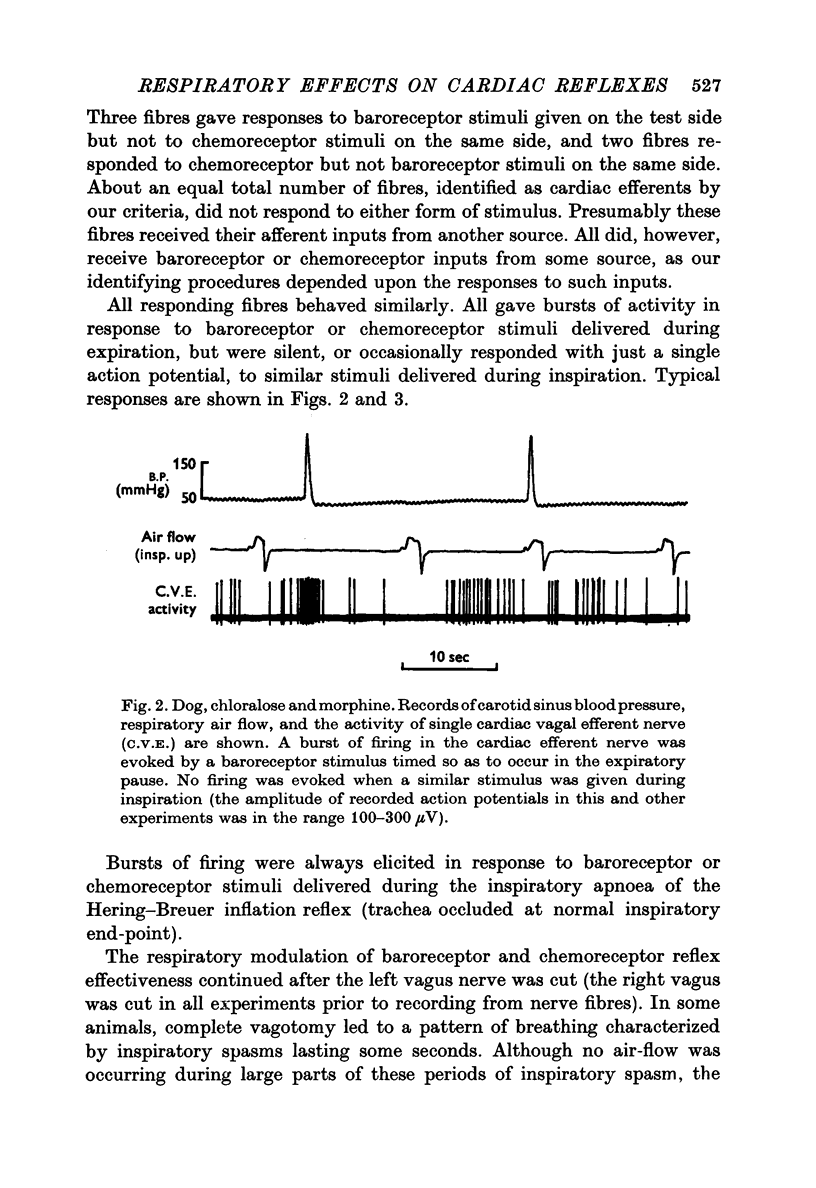
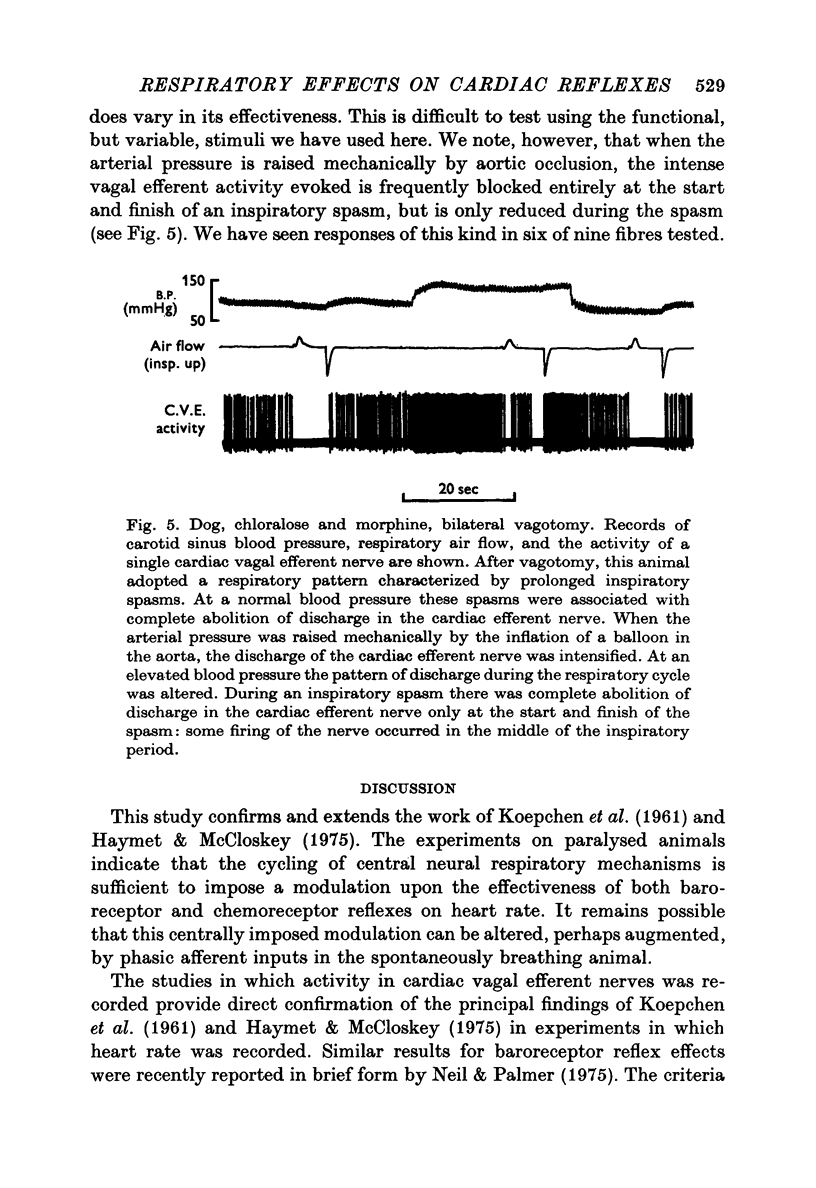
1. Brief stimuli were delivered to the carotid chemoreceptors or baroreceptors in dogs anaesthetized with chloralose. Chemoreceptor stimulation was achieved by rapid retrograde injection of 0.2-0.5 ml. CO2 equilibrated saline through a cannula in the external carotid artery. Baroreceptor stimulation was achieved by forceful retrograde injection of 2-5 ml. air-equilibrated saline into the external carotid artery after first clamping the common carotid artery. 2. prompt decreases in heart rate were elicited by brief sudden chemoreceptor or baroreceptor stimuli when these were delivered during the expiratory phase of respiration. The stimuli did not modify the control heart rate pattern when delivered in the inspiratory phase of respiration. This respiratory modulation of reflex effectiveness persisted when the animals were completely paralysed and the phase of the respiratory cycle was monitored through a phrenic electroneurogram. 3. single cardiac vagal efferent nerve fibres were dissected from the cut central end of the right cervical vagus nerve. They were classified as cardiac efferents by their cardiac and respiratory rhythmicity, and by their increased activity in response to stimulation of a carotid sinus nerve or to mechanical elevation of the systemic arterial pressure. These efferent fibres increased their activity in response to brief chemoreceptor or baroreceptor stimuli delivered in expiration, but did not respond to stimuli delivered in inspiration. This respiratory modulation of both reflexes persisted after bilateral cervical vagotomy.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Haymet B. T., McCloskey D. I. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor influences on heart rate during the respiratory cycle in the dog. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):699–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRIUCHIJIMA J., KUMADA M. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE VAGAL FIBERS EFFERENT TO THE HEART. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Oct 15;14:479–487. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEWETT D. L. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE EFFERENT FIBRES IN THE CERVICAL VAGUS NERVE OF THE DOG, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO POSSIBLE CARDIO-INHIBITORY FIBRES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:321–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPCHEN H. P., LUX H. D., WAGNER P. H. [Studies on time requirement and central development of the pressor receptor heart reflex]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1961;273:413–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil E., Palmer J. F. Effects of spontaneous respiration on the latency of reflex cardiac chronotropic responses to baroreceptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):16P–16P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


