Abstract
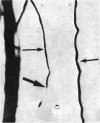
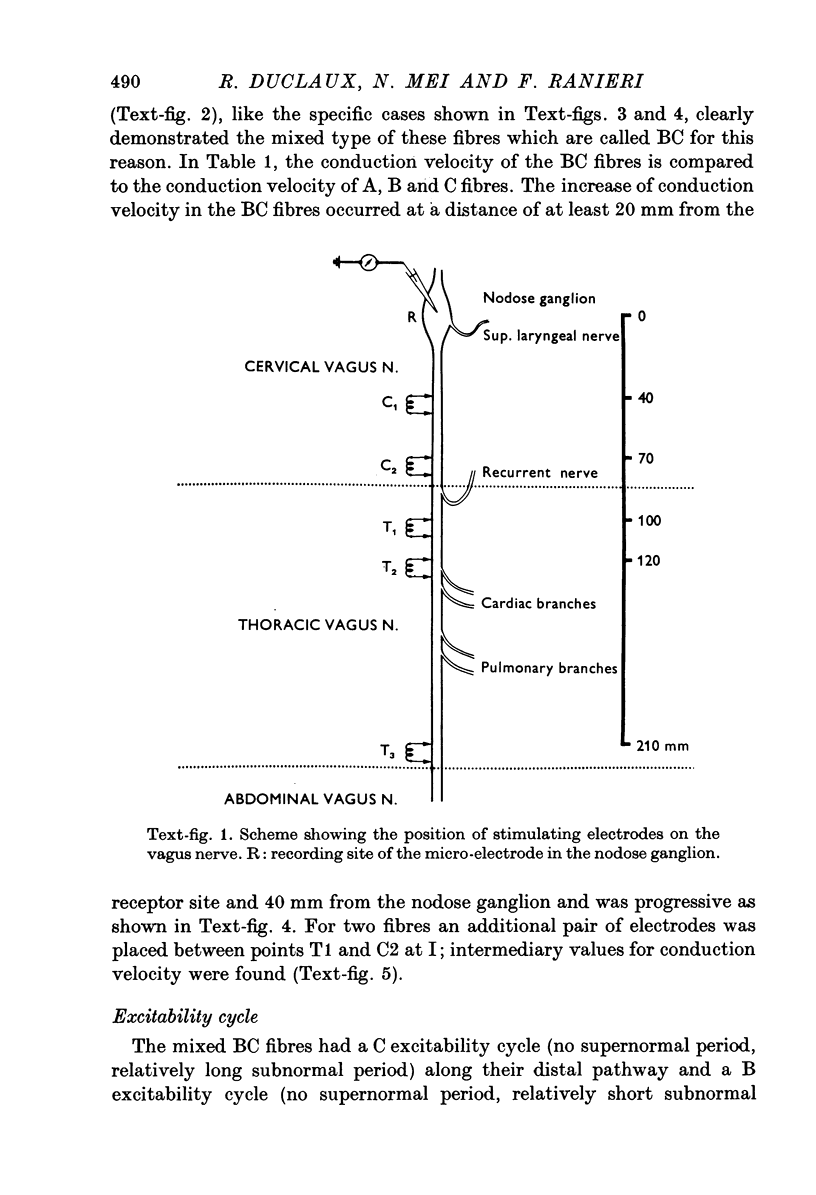
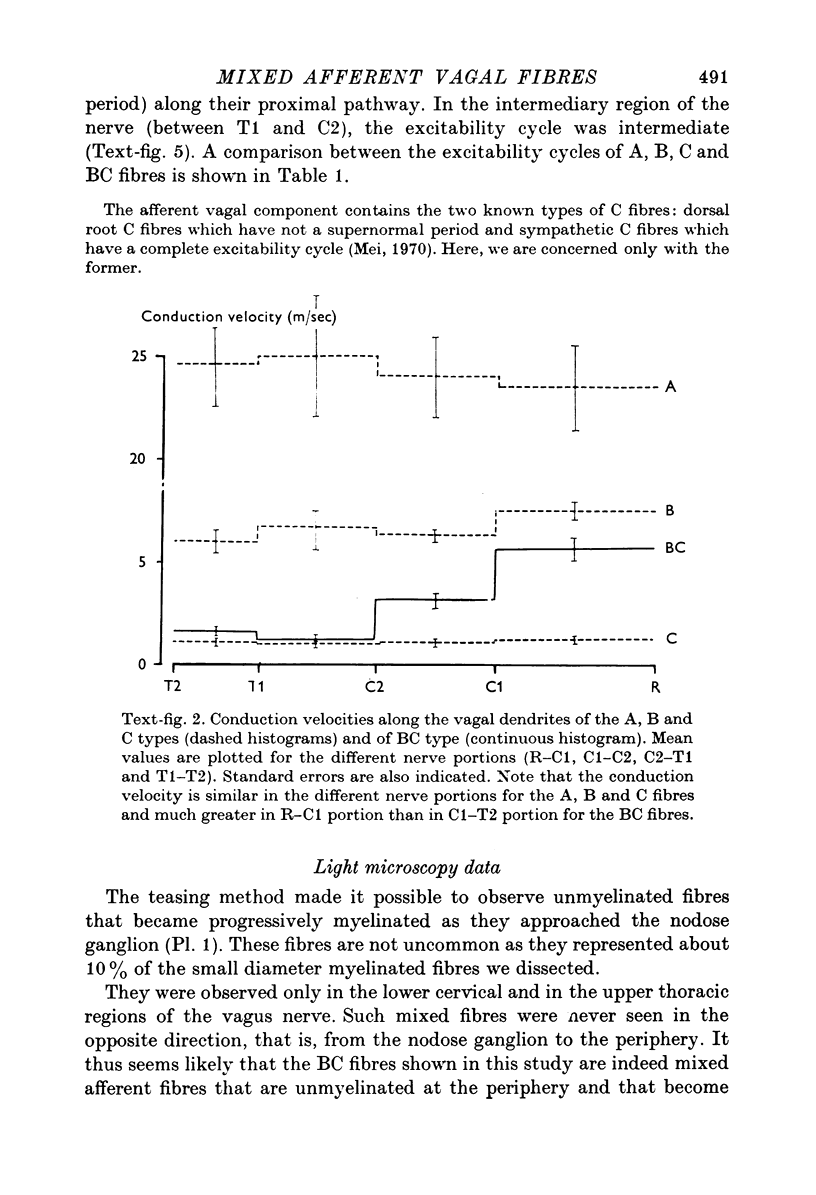
1. We systematically calculated the conduction velocity along the peripheral extensions of sensory vagal neurones in cats (the dendrites). In addition, a study of excitability cycle and light microscopic investigation were also conducted on these neurones. 2. The conduction velocity of the three known types of fibres (A, B and C) remains uniform along the dendrites. 3. Another mixed type of fibres exists with a C conduction velocity (mean value 1-5 m/sec) along its distal pathway and a B conduction velocity (mean value 6 m/sec) along its proximal pathway. The change in conduction velocity progressively occurs in the thoraco-cervical portion of the vagus nerve at least 20 mm from the receptor and at least 40 mm from the T cell. 4. The mixed fibres exhibited a C type excitability cycle in their peripheral pathway and a B type excitability cycle in their central pathway. 5. The histological study using the teasing method demonstrated the existence of unmyelinated fibres, in the thoraco-cervical region of the vagus nerve, becoming progressively myelinated from the periphery to the nodose ganglion. These fibres are likely to be the ones showing mixed electrophysiological properties. They represent (approximately) 10% of the vagal nerve population. 6. We propose to call the mixed fibres BC because they present electrophysiological and morphological properties of C fibres in their distal part and properties of B fibres in their proximal part.
Full text
PDF


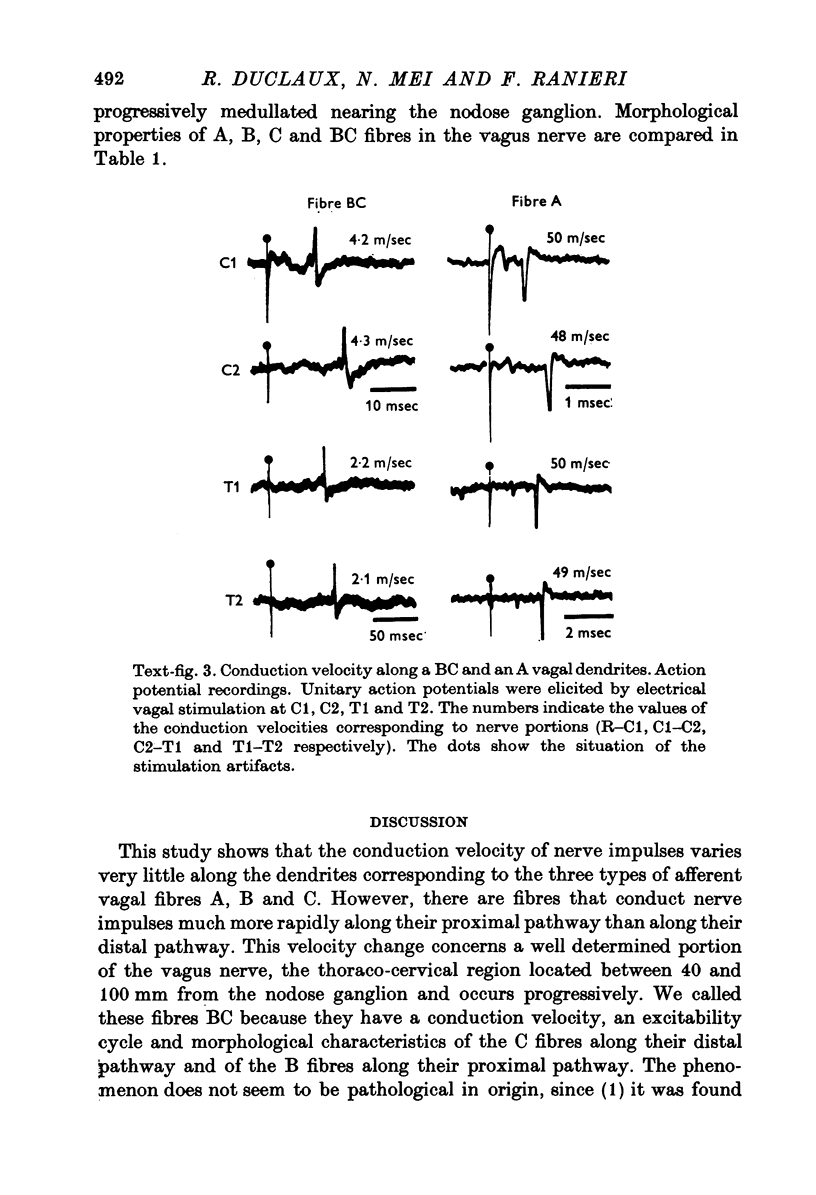
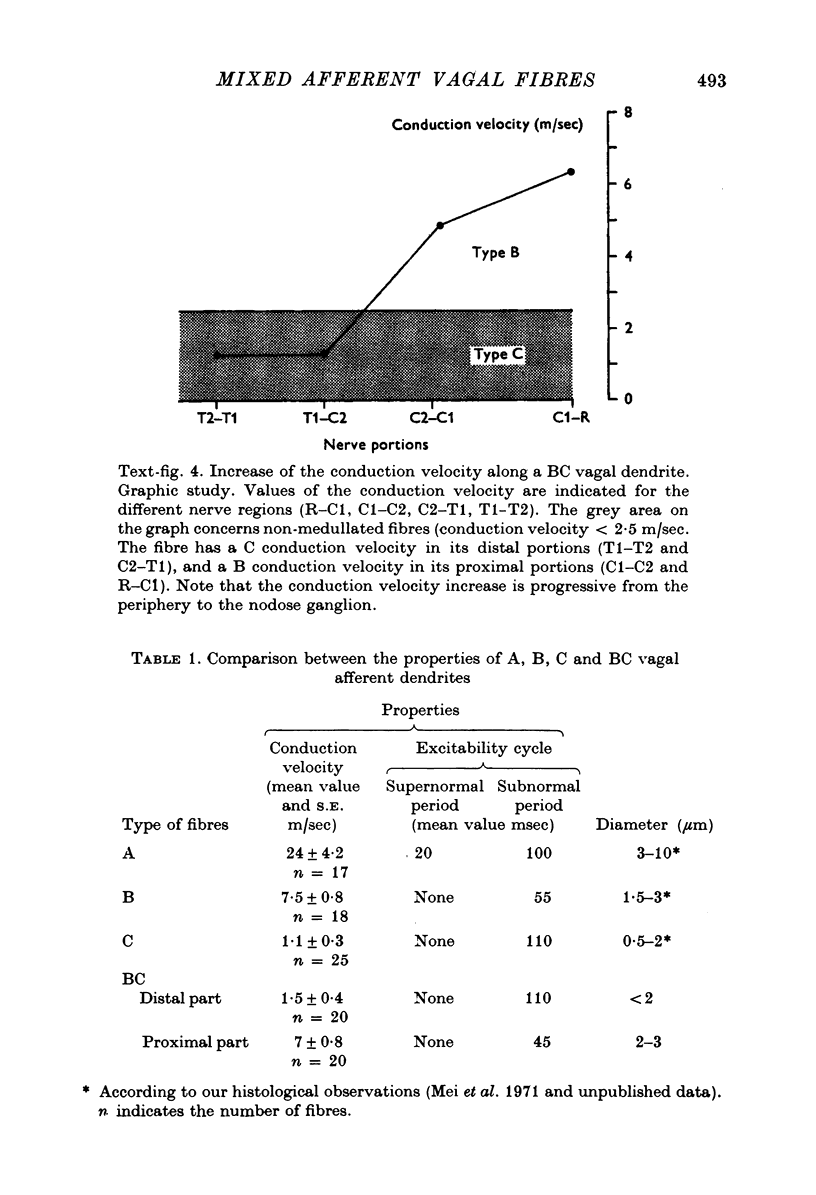
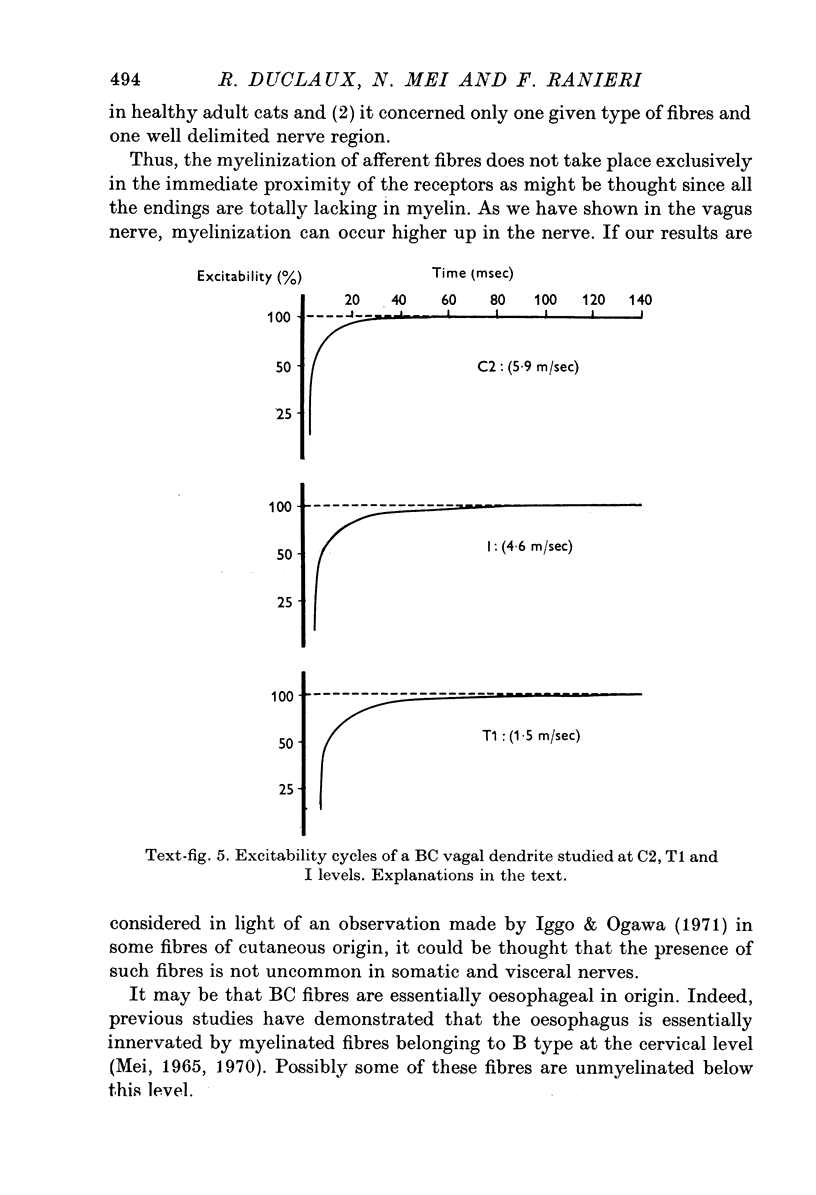


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Iggo A., Ogawa H. Primate cutaneous thermal nociceptors. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):77P–78P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei N., Boyer A., Condamin M. Etude comparée des deux prolongements de la cellule sensitive vagale. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1971;165(12):2371–2374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. VAGAL AFFERENT FIBRES. Ergeb Physiol. 1963;52:74–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri F., Crousillat J., Mei N. Etude électrophysiologique et histologique des fibres afférentes splanchniques. Arch Ital Biol. 1975 Dec;113(4):354–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizoso A. D., Young J. Z. Internode length and fibre diameter in developing and regenerating nerves. J Anat. 1948 Apr;82(Pt 1-2):110–134.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]