Abstract
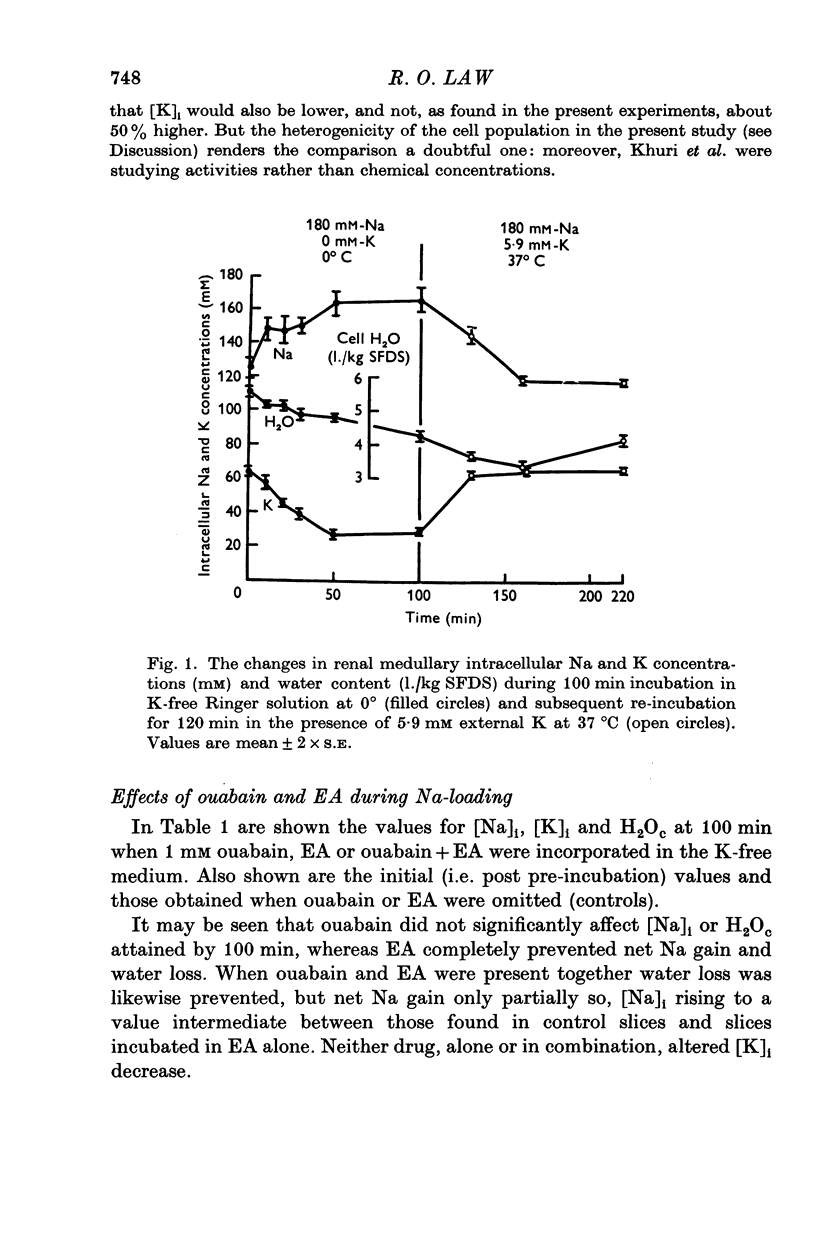
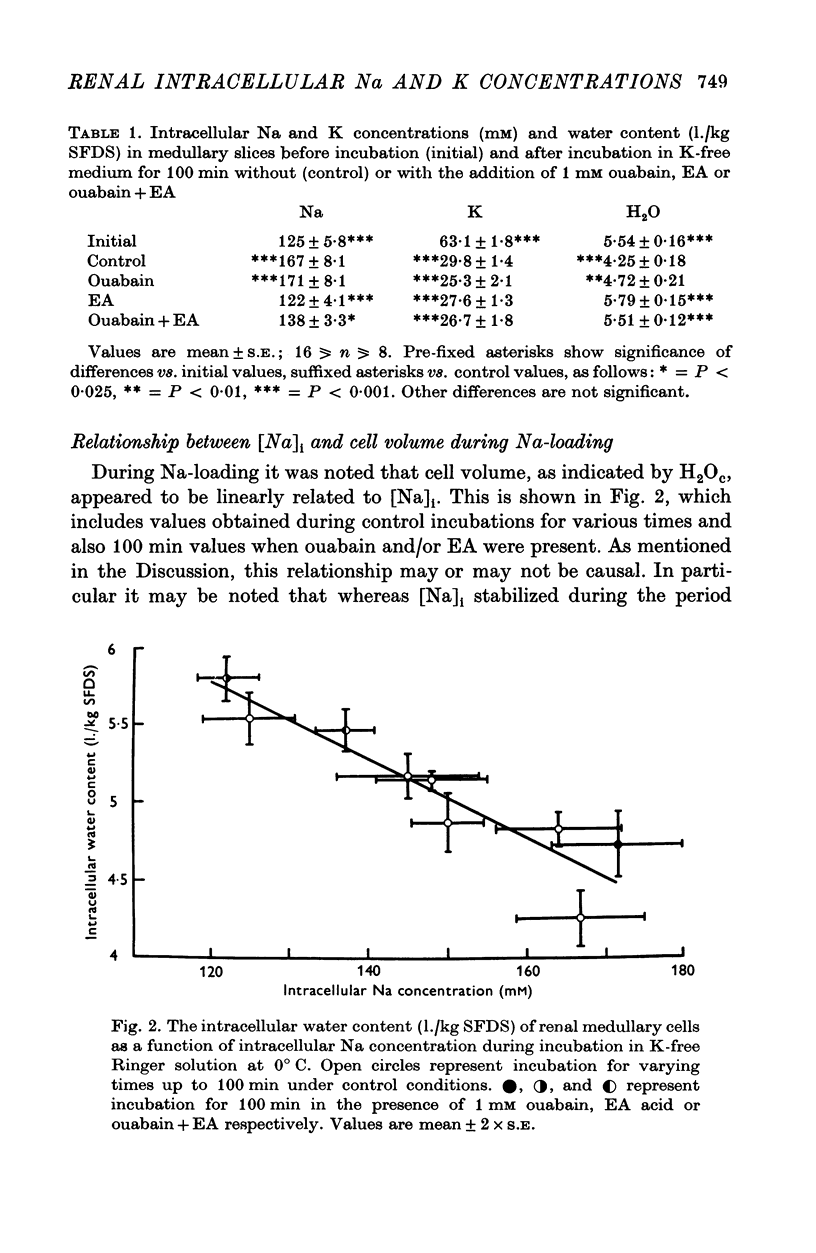
1. The cells in slices cut from the renal outer medulla of normally hydrated adult rats were loaded with Na and depleted of K by incubation for up to 100 min in cold iso-osmolal K-free Ringer containing 180 mM-Na. There was a continuous net cellular water loss during this time; an inverse linear relationship existed between water content and intracellular Na concentration. 2. The original intracellular Na and K concentration were restored following 60 min re-incubation in warm Ringer (37 degrees C) containing 5-9 mM-K. Restoration of cellular water content was incomplete after re-incubation for up to 120 min. 3. During incubation in cold K-free Ringer the presence of 1 mM ouabain did not affect cellular Na uptake or K and water loss. Ethacrynic acid, 1 mM, completely blocked cellular Na uptake and water loss, without affecting the intracellular K concentration at 100 min. When ouabain and ethacrynic acid were present together water loss was also prevented but intracellular Na concentration rose slightly by 100 min. 4. During re-incubation in warm K-containing Ringer 1 mM ouabain inhibited Na extrusion completely for up to 60 min while only partially preventing K uptake and further depressing the level of cellular hydration. Ouabain in the presence of 1 mM ethacrynic acid had similar effects on intracellular Na and K concentrations, but raised the level of intracellular water above that of cells in control slices. 5. Ethacrynic acid alone, 1 mM, did not interfere with Na extrusion or K uptake, but also raised intracellular water above control values. 6. The results obtained are discussed in relation to (a) the nature of the preparation used, (b) the possible membrane transport processes occurring and their known or suggested sensitivity to ouabain and ethacrynic acid, (c) the mechanisms which may be responsible for cell volume maintenance in the medulla.
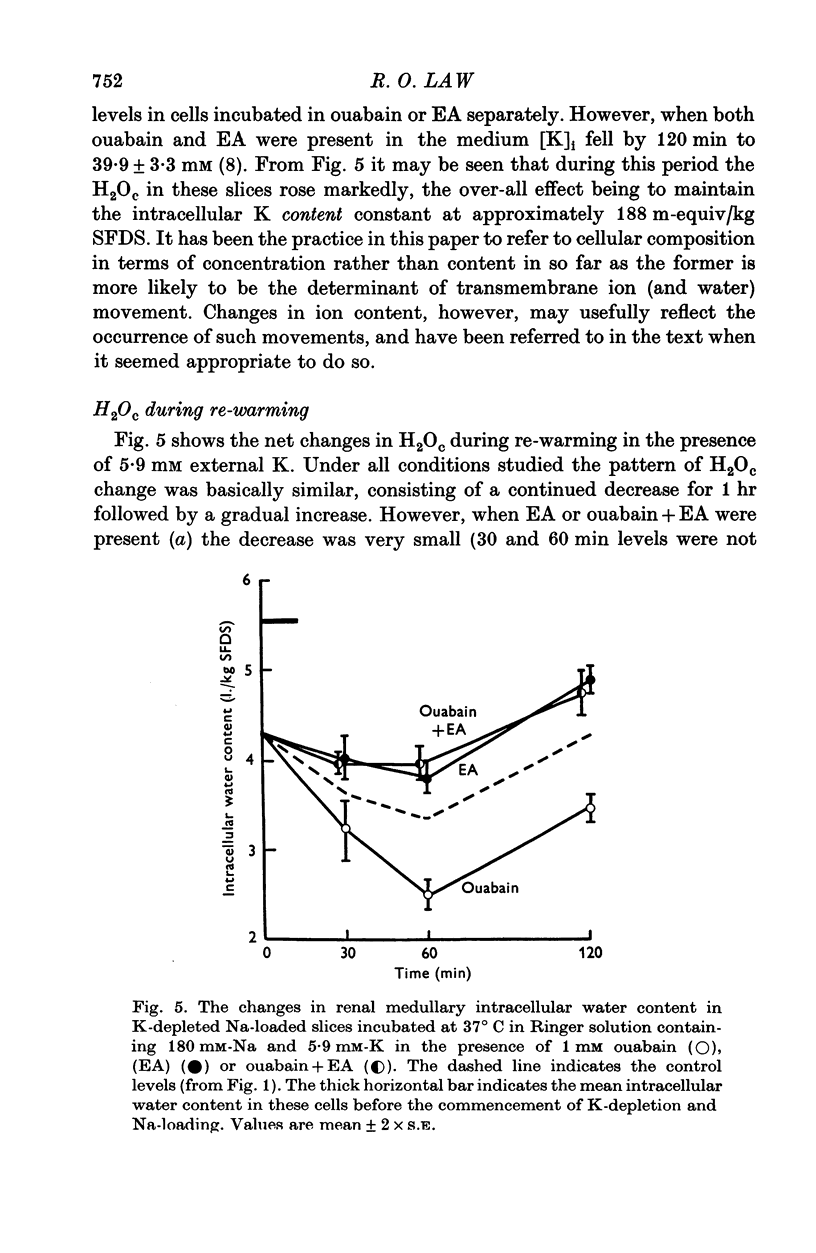
Full text
PDF




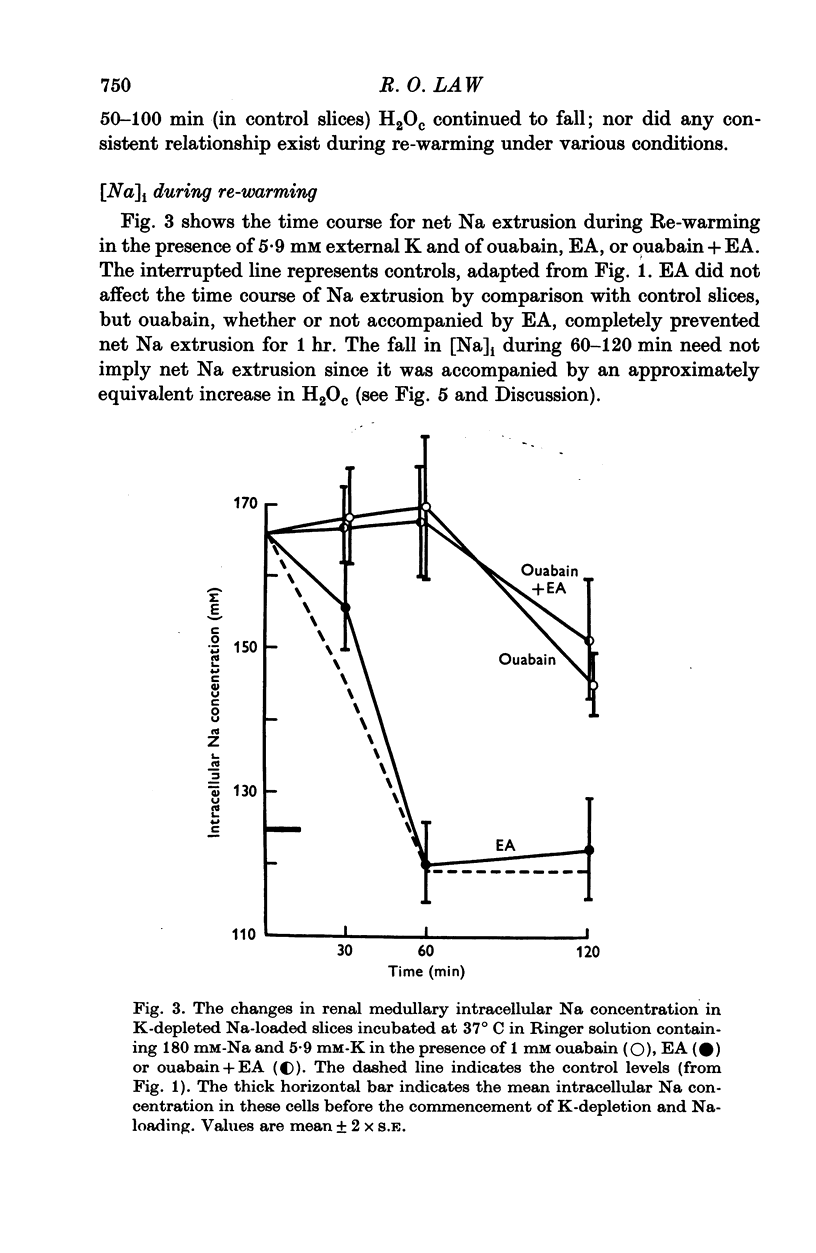
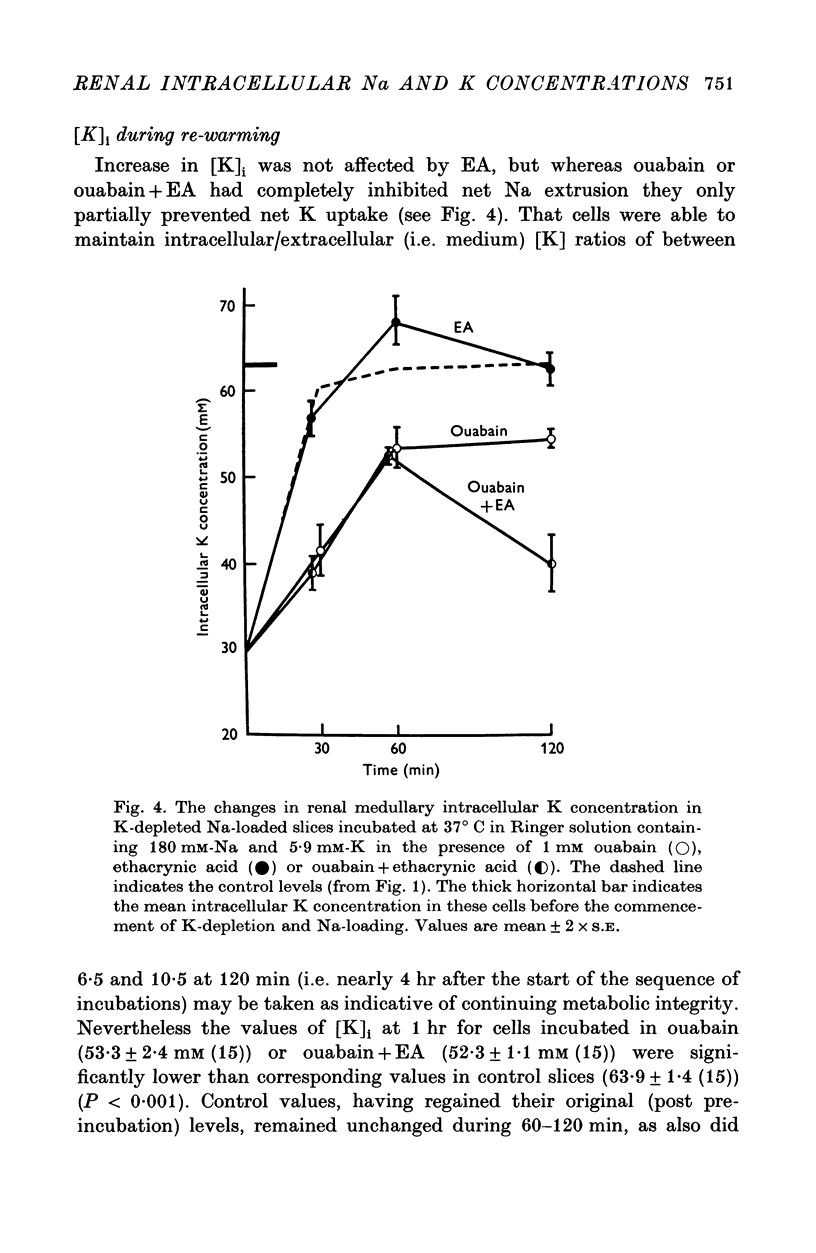






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. C., Martinez-Maldonado M., Eknoyan G., Suki W. N., Schwartz A. Relation between digitalis binding in vivo and inhibition of sodium, potassium-adenosine triphosphatase in canine kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;20(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90473-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. The time course of changes in renal tissue composition during mannitol diuresis in the rat. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):411–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aukland K., Johannesen J., Kiil F. In vivo measurements of local metabolic rate in the dog kidney. Effect of mersalyl, chlorothiazide, ethacrynic acid and furosemide. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Jun;23(4):317–330. doi: 10.3109/00365516909081697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. W. Inhibition of renal Na + ,K + -activated adenosine triphosphatase activity by ethacrynic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;19(6):1983–1989. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. G., Chomety F., Giebisch G. Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):632–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan D. E., Noll R. M. Effects of ethacrynic acid upon membrane ATPase of dog kidney in vivo and in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):762–767. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel H., Ehrich J., De Santo N. G., Doerken U. Plasma membranes of the kidney. 3. Influence of diuretics on ATPase activity. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00592159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. W. The effects of ethacrynic acid on active transport of sugars and ions and on other metabolic processes in rabbit kidney cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):128–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Boulpaep E. L., Whittembury G. Electrolyte transport in kidney tubule cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Aug 20;262(842):175–196. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. Ethacrynic acid: site and mode of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman Y., Wald H., Czazkes W. Differences in characteristics of ethacrynic acid accumulation in kidney cortex, medulla and papilla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Apr 1;24(7):775–778. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györy A. Z., Brendel U., Kinne R. Effect of cardiac glycosides and sodium ethacrynate on transepithelial sodium transport in in vivo micropuncture experiments and on isolated plasma membrane Na-K ATPase in vitro of the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00586219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki C., Martinez-Maldonado M., Schwartz A. Some in vivo and in vitro effects of ethacrynic acid on renal Na+,K+ -ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Sep;158(1):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90639-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Agulian S. K., Kalloghlian A. Intracellular potassium in cells of the distal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1972;335(4):297–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00586220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon E. J., Fitzpatrick D. F. Ethacrynic acid and kidney cell metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Jun 1;21(11):1561–1568. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H., Cannon P. J., Stason W. B., Heinemann H. O. Physiologic and clincical observations on furosemide and ethacrynic acid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):453–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R. O. Proceedings: Medullary cell Na and K concentrations, and water content, during K depletion at 0 degrees C and re-warming: effects of ouabain and ethacrynic acid. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R. O. The inulin space, solute concentrations, and weight changes in rat renal medullary slices incubated in iso-osmolal media, and their modification during anoxia and hypothermia. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):37–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law R. O. Volume adjustment by renal medullary cells in hypo- and hyperosmolal solutions containing permeant and impermeant solutes. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):55–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D., Civan M. M., Leaf A. Some effects of ouabain on cellular ions and water in epithelial cells of toad urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1975;20(3-4):387–401. doi: 10.1007/BF01870645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D. The effects of ethacrynic acid on the electrolyte and water contents of rat renal cortical slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 11;173(2):223–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Microperfusion study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transfer in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):548–559. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maldonado M., Tsaparas N., Inagaki C., Schwartz A. Interactions of digoxin and ethacrynic acid with renal sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Mar;188(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maude D. L. Effects of K and ouabain on fluid transport and cell Na in proximal tubule in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1969 May;216(5):1199–1206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.5.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIver D. J., Macknight A. D. Extracellular space in some isolated tissues. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):31–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nechay B. R., Contreras R. R. In vivo effect of ethacrynic acid on renal adenosine triphosphatase in dog and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Oct;183(1):127–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Nechay B. R. Effects of cardiac glycosides of renal adenosine triphosphatase activity and Na+ reabsorption in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Dec;175(3):727–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poat P. C., Poat J. A., Munday K. A. The site of action of the diuretic ethacrynic acid on rat kidney and liver tissue. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;1(4):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(70)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podevin R. A., Boumendil-Podevin E. F. Effects of temperature, medium K+, ouabain and ethacrynic acid on transport of electrolytes and water by separated renal tubules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):234–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. W. The inhibition of glycine and beta-methylglucoside transport in dog kidney cortex slices by ouabain and ethacrynic acid: contribution to the understanding of sodium-pumping mechanisms. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;3(10):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(72)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT-NIELSEN B., O'DELL R. Structure and concentrating mechanism in the mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1119–1124. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin D. W., Eknoyan G., Suki W. N., Rector F. C., Jr Localization of diuretic action from the pattern of water and electrolyte excretion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):328–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieder N., Khuri R., Wiederholt M., Giebisch G. Studies on the renal action of ouabain in the rat. Effects in the non-diuretic state. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Jun 11;349(2):91–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00586621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suki W. N., Eknoyan G., Martinez-Maldonado M. Tubular sites and mechanisms of diuretic action. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:91–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torretti J., Hendler E., Weinstein E., Longnecker R. E., Epstein F. H. Functional significance of Na- K-ATPase in the kidney: effects of ouabain inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1398–1405. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRZ H., HARGITAY B., KUHN W. Lokalisation des Konzentrierungsprozesses in der Niere durch direkte Kryoskopie. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1951 Jun;9(2):196–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald H., Gutman Y., Czaczkes W. Comparison of microsomal ATPase in the cortex, medulla and papilla of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(1):47–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01061949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittembury G., Proverbio F. Two modes of Na extrusion in cells from guinea pig kidney cortex slices. Pflugers Arch. 1970;316(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00587893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf K., Bieg A., Fülgraff G. On the mode of action of diuretics. II. Effects of ethacrynic acid on renal oxygen consumption and tubular sodium reabsorption in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;7(3):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mello-Aires M., Giebisch G., Malnic G. Kinetics of potassium transport across single distal tubules of rat kidney. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):47–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


