Abstract
1. Water and saline intake was measured in rats depleted of Na by I.P. dialysis. Na intake was prevented 180 min but not 60-90 min after bilateral nephrectomy. Unilateral nephrectomy as well as ureteral ligature had no effect on Na intake. 2. Renin (3u.) injected I.P. re-established the Na appetite abolished by nephrectomy. 3. Angiotensin I (5 ng) or II (5-40 ng) injected into the 3rd ventricle, also restored the Na intake and this effect was dose-dependent. 4. The angiotensin converting-enzyme inhibitor Sq 20,881 (1 mg/kg) inhibited the effect of AI but not that of AII in restoring Na intake. 5. It is concluded that the kidneys might play a role in the regulation of Na intake through the renin-angiotensin system.
Full text
PDF



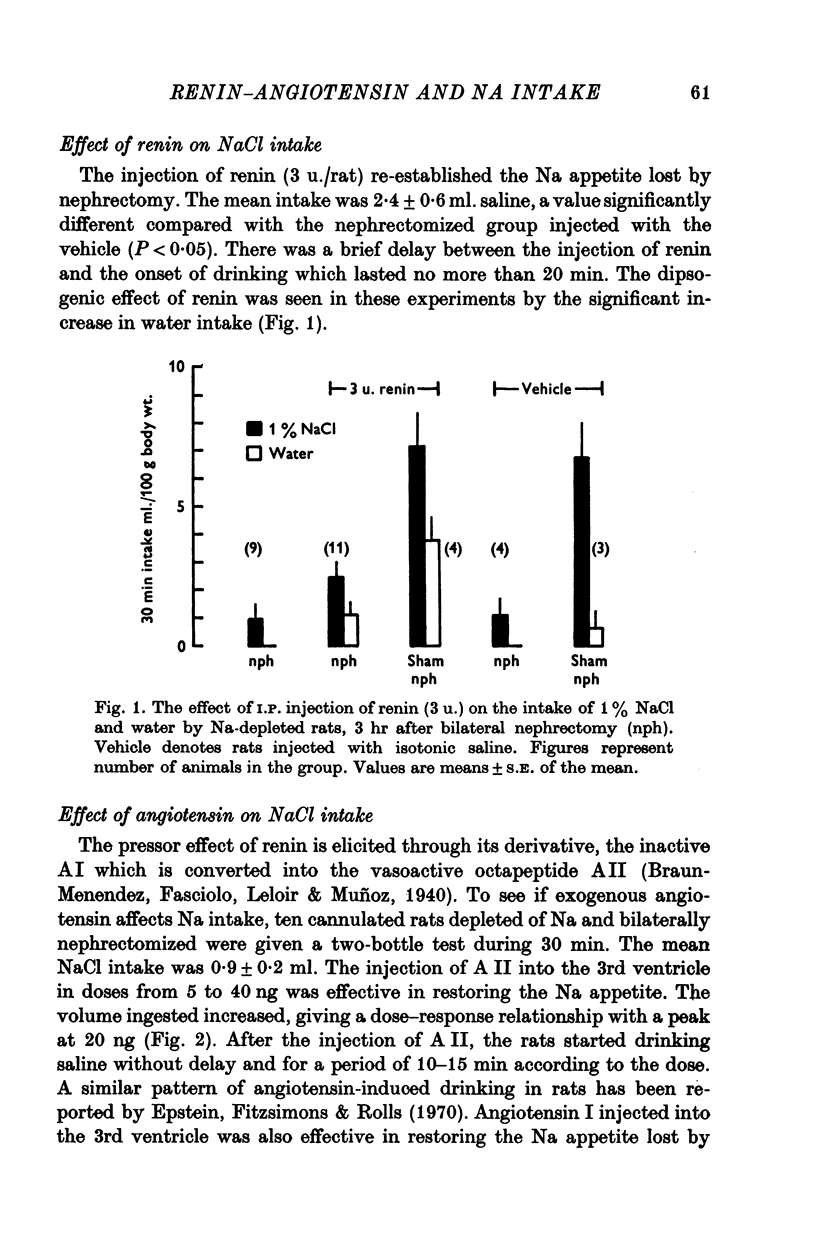
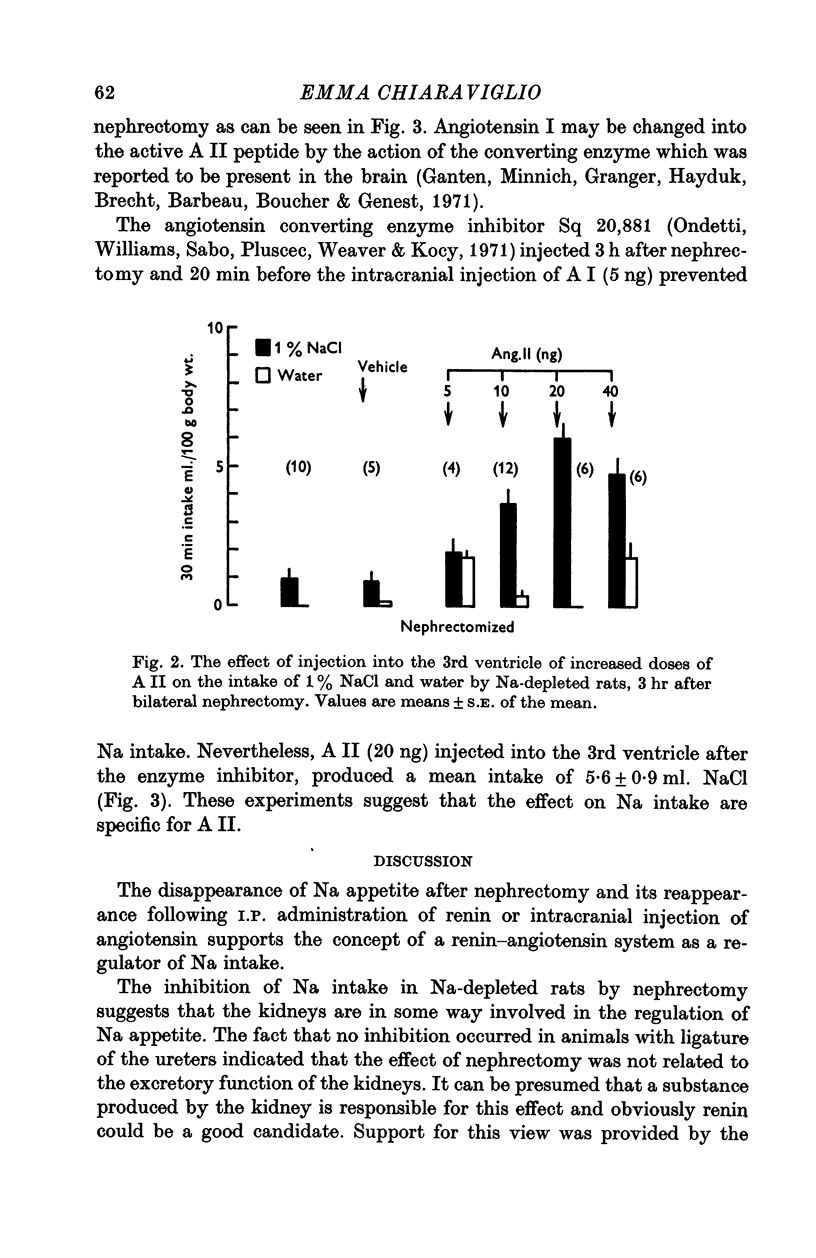
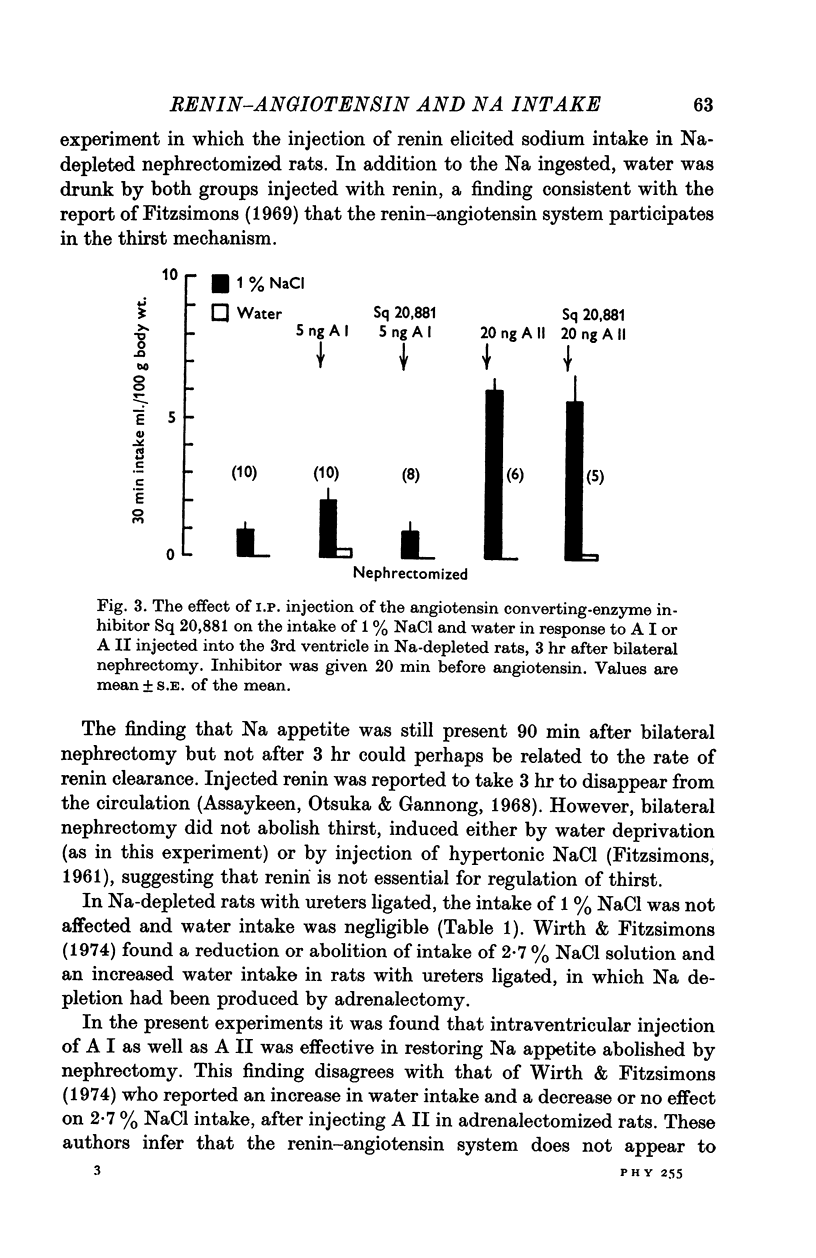



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaykeen T. A., Otsuka K., Ganong W. F. Rate of disappearance of exogenous dog renin from the plasma of nephrectomized dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):306–310. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. INFLUENCE OF SODIUM DEPRIVATION AND LOADING ON THE PLASMA-RENIN IN MAN. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;173:408–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Menendez E., Fasciolo J. C., Leloir L. F., Muñoz J. M. The substance causing renal hypertension. J Physiol. 1940 Jul 24;98(3):283–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiaraviglio E., Taleisnik S. Water and salt intake induced by hypothalamic implants of cholinergic and adrenergic agents. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jun;216(6):1418–1422. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.6.1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covian M. R., Gentil C. G., Antunes-Rodrigues J. Water and sodium chloride intake following microinjections of angiotensin II into the septal area of the rat brain. Physiol Behav. 1972 Sep;9(3):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(72)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., CARPENTER C. C., AYERS C. R., HOLMAN J. E., BAHN R. C. Evidence for secretion of an aldosterone-stimulating hormone by the kidney. J Clin Invest. 1961 Apr;40:684–696. doi: 10.1172/JCI104301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. N., Fitzsimons J. T., Rolls B. J. Drinking induced by injection of angiotensin into the rain of the rat. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):457–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N., Fitzsimons J. T., Johnson A. K. Proceedings: Peptide antagonists of the renin-angiotensin system and the elucidation of the receptors for angiotensin-induced drinking. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):34P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FASCIOLO J. C., DEVITO E., ROMERO J. C., CUCCHI J. N. THE RENIN CONTENT OF THE BLOOD OF HUMANS AND DOGS UNDER SEVERAL CONDITIONS. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:206–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZSIMONS J. T. Drinking by nephrectomized rats injected with various substances. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:563–579. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons J. T., Stricker E. M. Sodium appetite and the renin-angiotensin system. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 12;231(19):58–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons J. T. The role of a renal thirst factor in drinking induced by extracellular stimuli. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):349–368. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons J. T. Thirst. Physiol Rev. 1972 Apr;52(2):468–561. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.2.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Minnich J. L., Granger P., Hayduk K., Brecht H. M., Barbeau A., Boucher R., Genest J. Angiotensin-forming enzyme in brain tissue. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janowsky D. S., Davis J. M., Fann W. E., Freeman J., Nixon R., Michelakis A. A. Angiotensin effect on uptake of norepinephrine by synaptosomes. Life Sci I. 1972 Jan 1;11(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H. Renin, angiotensin, aldosterone and hormonal regulation of arterial pressure and salt balance. Introductory remarks. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Williams N. J., Sabo E. F., Pluscec J., Weaver E. R., Kocy O. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Isolation, elucidation of structure, and synthesis. Biochemistry. 1971 Oct 26;10(22):4033–4039. doi: 10.1021/bi00798a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs W. B., Summy-Long J., Daniels-Severs A. Effect of a converting enzyme inhibitor (SQ 20,881) on angiotensin-induced drinking. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):203–204. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. B., Routtenberg A. Subfornical organ: site of drinking elicitation by angiotensin II. Science. 1973 Sep 21;181(4105):1172–1175. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4105.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian L. Renin release and its role in renal function and the control of salt balance and arterial pressure. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volicer L., Loew C. G. Penetration of angiotensin II into the brain. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Sep;10(5):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


