Abstract
1. Electrophysiological and micro-electrophoretic studies were carried out in anaesthetized cats on spinal interneurones which were monosynaptically activated from group 1 muscle afferents and recurrently inhibited by Renshaw cells. 2. The recurrent inhibition was blocked by the iontophoretic administration of strychnine, which also blocked the action of glycine. 3. The time course of the block of synaptic inhibition by strychnine was slower than the block of glycine evoked inhibition. The significance of this observation in terms of the location of the inhibitory synapses is discussed. 4. The observation that recurrent inhibition of motoneurones and of interneurones is blocked by strychnine whereas the mutual inhibition of Renshaw cells is not is discussed in relation to the proposal that the nature of the post-synaptic inhibitory receptor is not determined solely by the innervating neurone, which is the Renshaw cell in all three instances. 5. The recurrent inhibition of the interneurones was not blocked by the iontophoretic administration of bicuculline, but difficulties were encountered in demonstrating that this agent consistently antagonized the inhibitory effects of GABA.
Full text
PDF

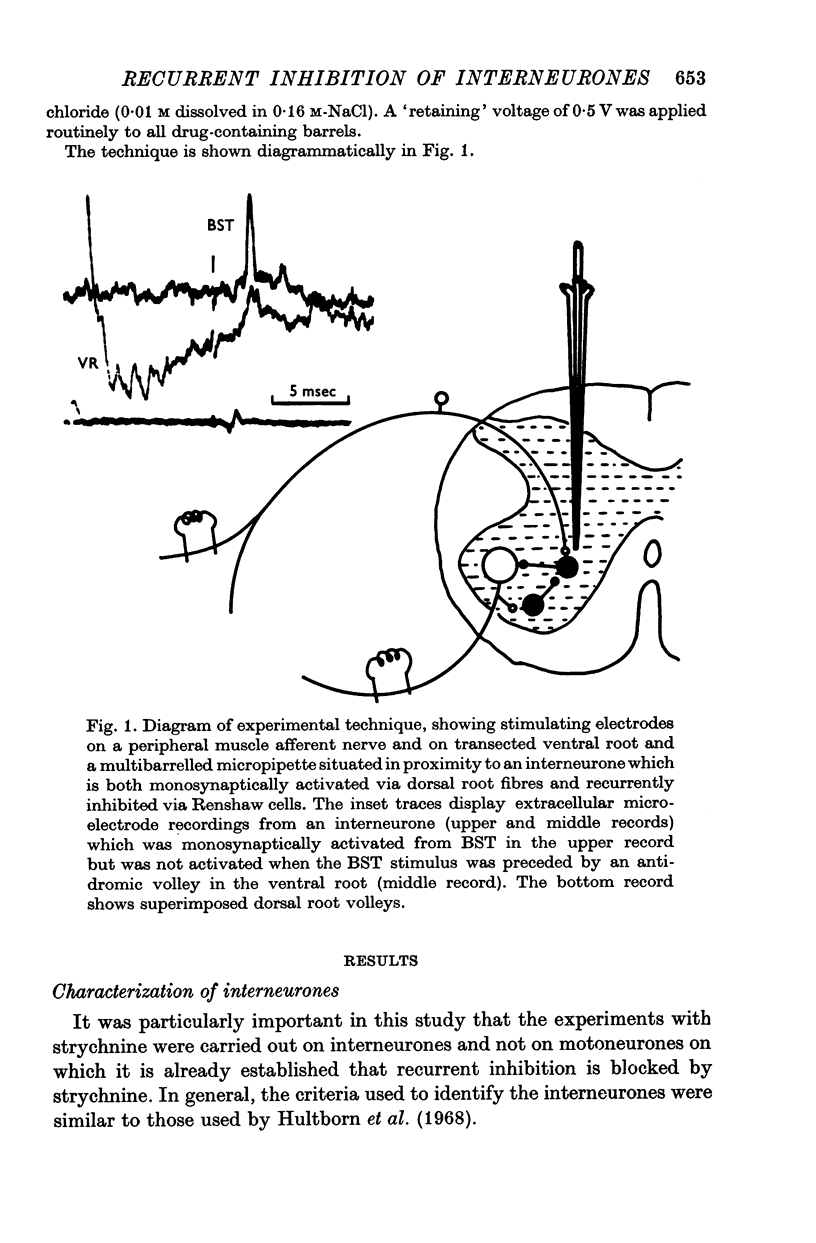


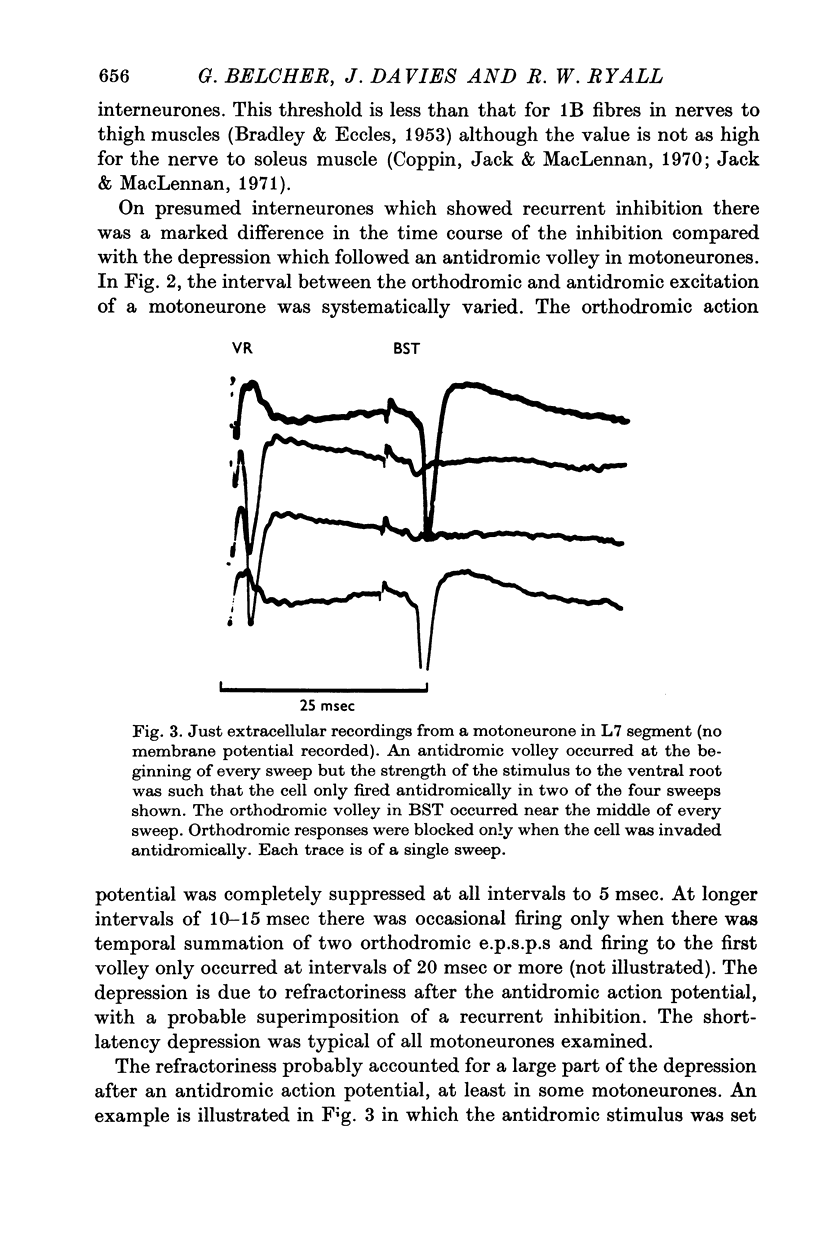
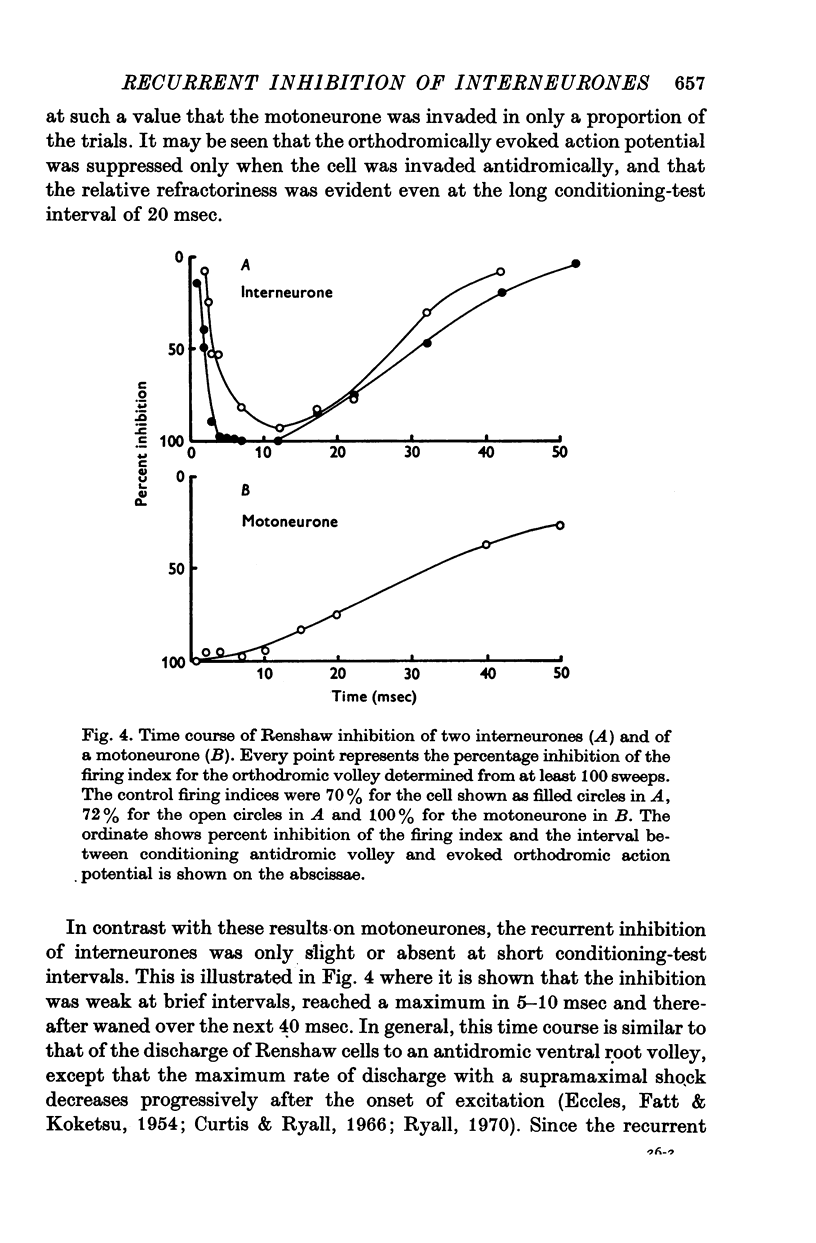
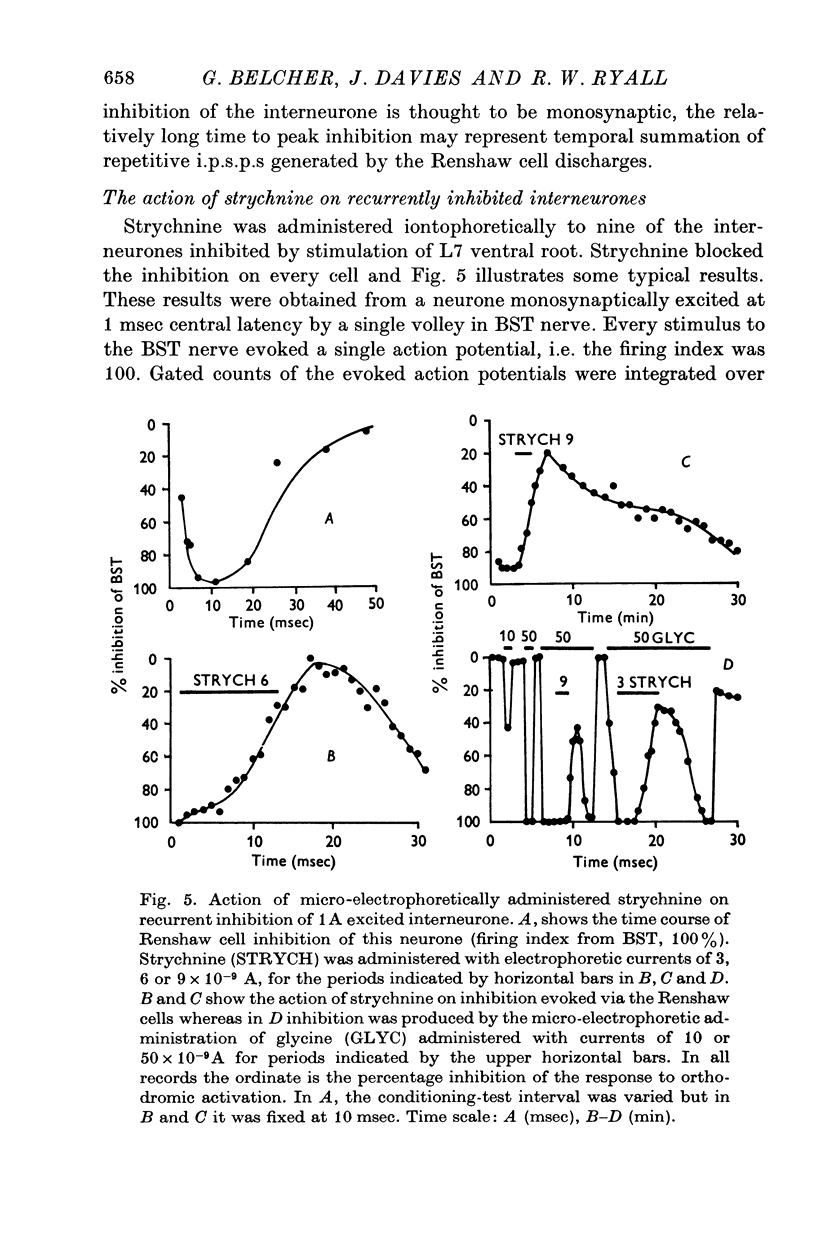



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY K., EASTON D. M., ECCLES J. C. An investigation of primary or direct inhibition. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):474–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., MacLennan C. R. A method for the selective electrical activation of tendon organ afferent fibres from the cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):18P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Felix D., Johnston G. A. Bicuculline, an antagonist of GABA and synaptic inhibition in the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):69–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Ryall R. W. The synaptic excitation of Renshaw cells. Exp Brain Res. 1966;2(1):81–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00234362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decandia M., Provini L., Taborikova H. Mechanisms of the reflex discharge depression in the spinal motoneurone during repetitive orthodromic stimulation. Brain Res. 1967 Mar;4(2):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S. Recurrent inhibition from motor axon collatersls in interneurones monosynaptically activated rom la afferents. Brain Res. 1968 Jul;9(2):367–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., MacLennan C. R. The lack of an electrical threshold discrimination between group Ia and group Ib fibres in the nerve to the cat peroneus longus muscle. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):35P–36P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. Monosynaptic reflex response of individual motoneurons as a function of frequency. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jan 20;40(3):435–450. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W., Piercey M. F., Polosa C. Strychnine-resistant mutual inhibition of Renshaw cells. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90620-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W. Renshaw cell mediated inhibition of Renshaw cells: patterns of excitation and inhibition from impulses in motor axon collaterals. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):257–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


