Abstract
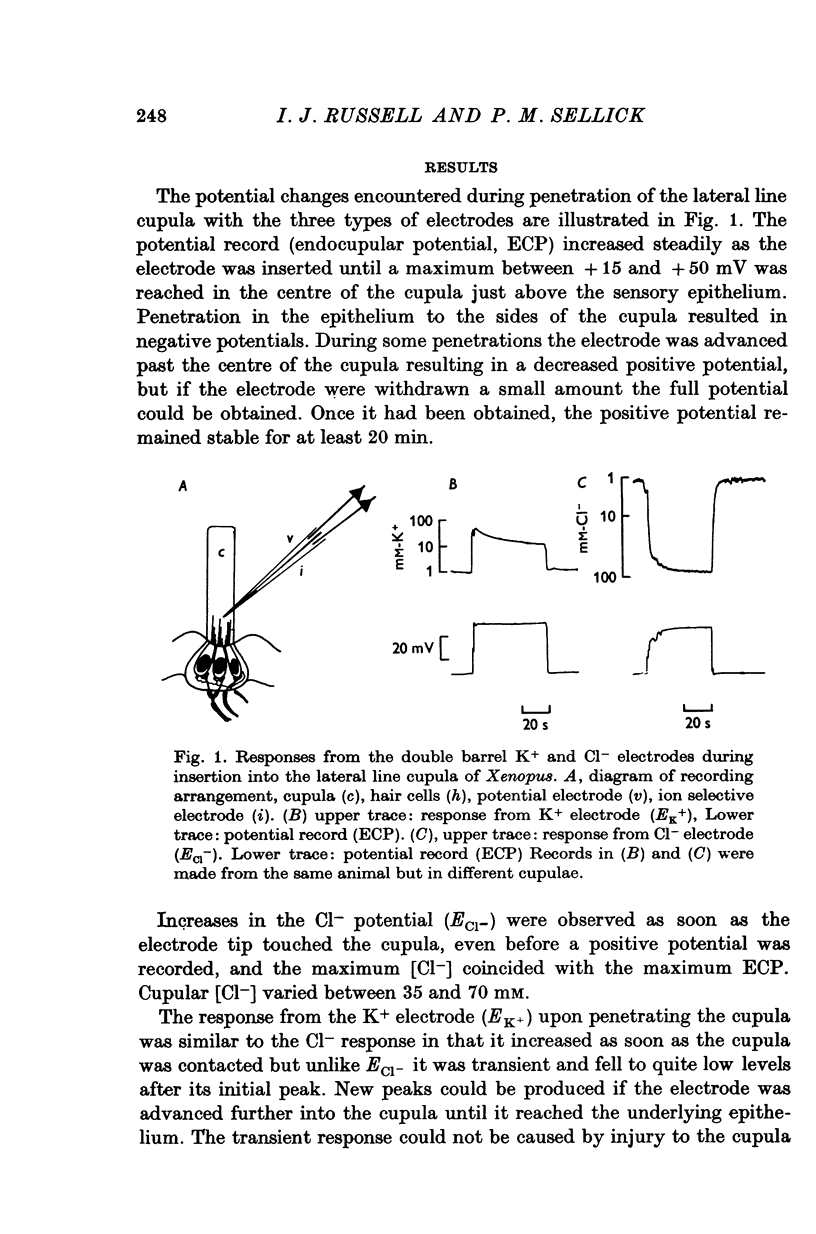
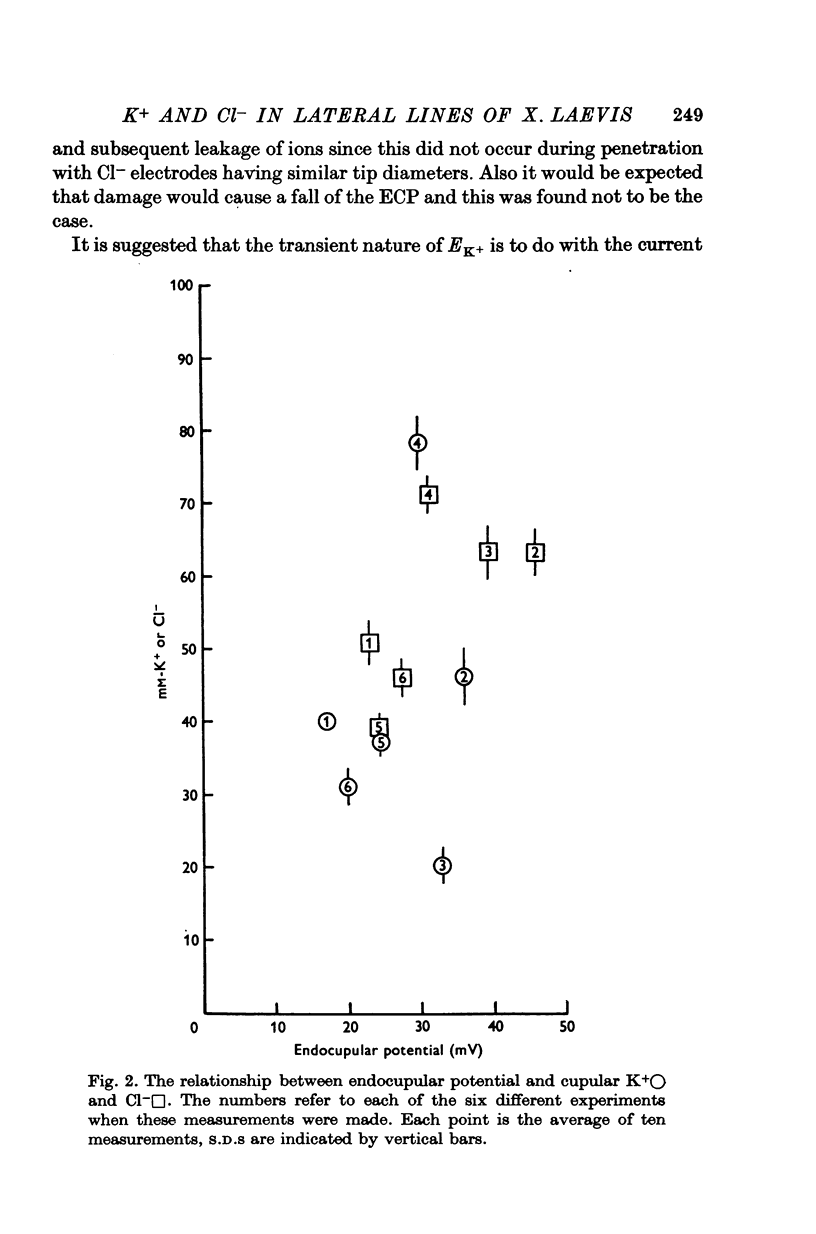
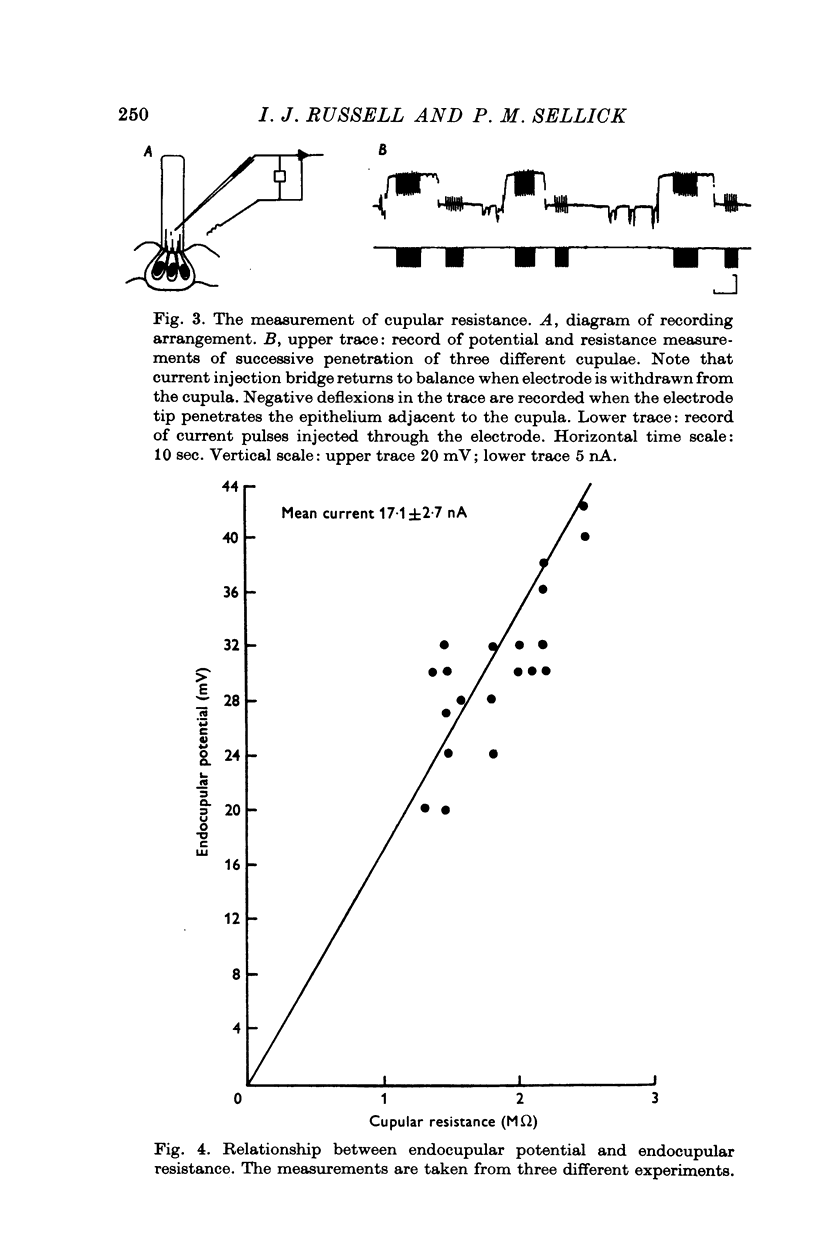
1. Potential measurements were made with double barrel ion selective electrodes from the cupulae of lateral line organs in the aquatic toad Xenopus laevis. 2. A positive endocupular potential (ECP) of 15-50 mV was recorded within the cupula, immediately above the hair cells. 3. Increases in the Cl- and K+ potentials were recorded when the ion selective electrodes touched the cupula. Cupular Cl- and K+ varied between 35 and 70 mM and 24 and 100 mM respectively. This variation existed between, rather than within, different animals. 4. Subcutaneous injections of 0-4 ml. 2 mM ouabain greatly reduced the ECP and cupular K+, whereas 0-4 ml. of Xenopus Ringer had no effect. 5. Changing the bath Cl- a hundredfold had no effect on the ECP. It was concluded that the ECP was produced by an electrogenic K+ pump which maintained high K+ levels within the cupula.
Full text
PDF


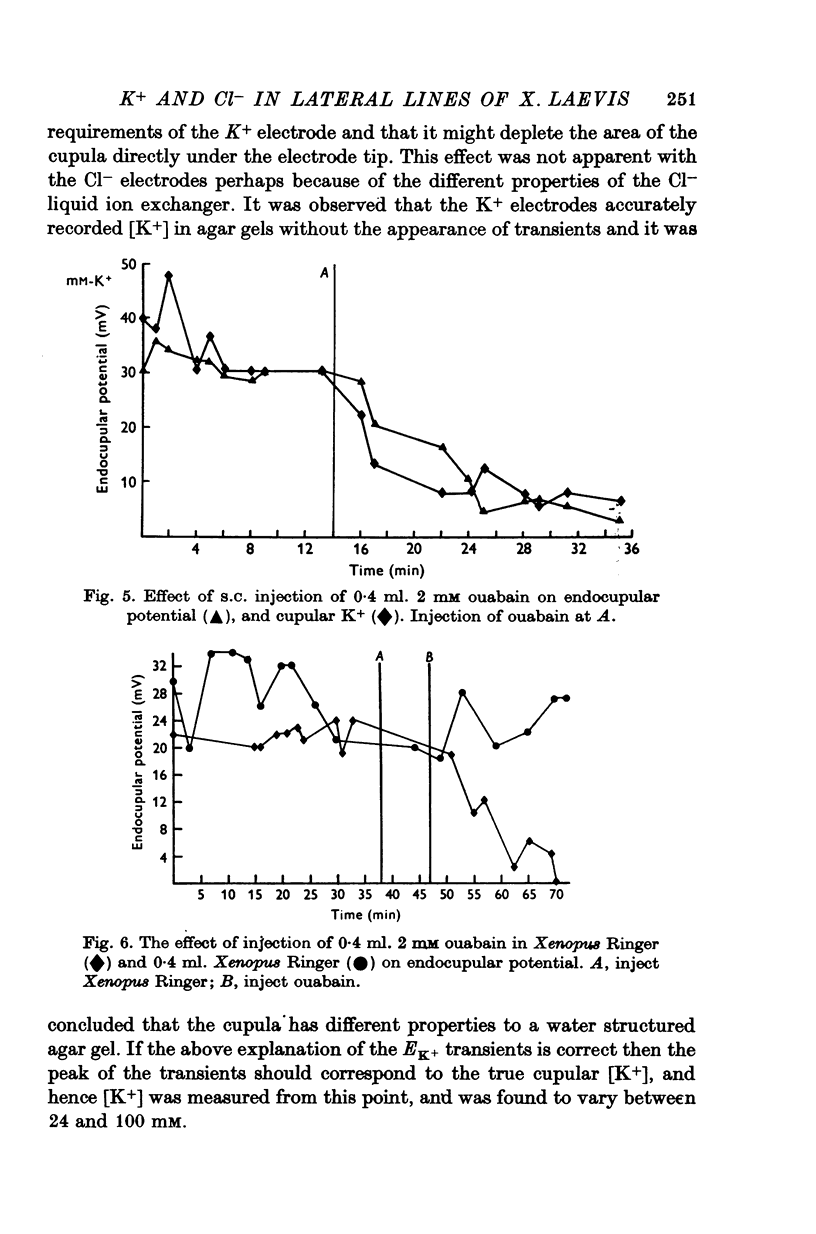



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clusin W., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Activation of a voltage-insensitive conductance by inward calcium current. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):425–427. doi: 10.1038/256425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. Biophysics and physiology of the inner ear. Physiol Rev. 1957 Jan;37(1):1–49. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIELOF R., SPOOR A., DE VRIES H. The microphonic activity of the lateral line. J Physiol. 1952 Feb;116(2):137–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone B. M., Sellick P. M. The peripheral auditory apparatus. Q Rev Biophys. 1972 Feb;5(1):1–57. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. M., Flock A. The ultrastructure of lateral line sense organs in the adult salamander Ambystoma mexicanum. J Neurocytol. 1973 Jun;2(2):133–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01474715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Hajjar J. J., Agulian S. K. Measurement of intracellular potassium with liquid ion-exchange microelectrodes. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Mar;32(3):419–422. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell I. J. Influence of efferent fibres on a receptor. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):177–178. doi: 10.1038/219177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellick P. M., Johnstone B. M. Production and role of inner ear fluid. Prog Neurobiol. 1975;5(4):337–362. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(75)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


