Abstract
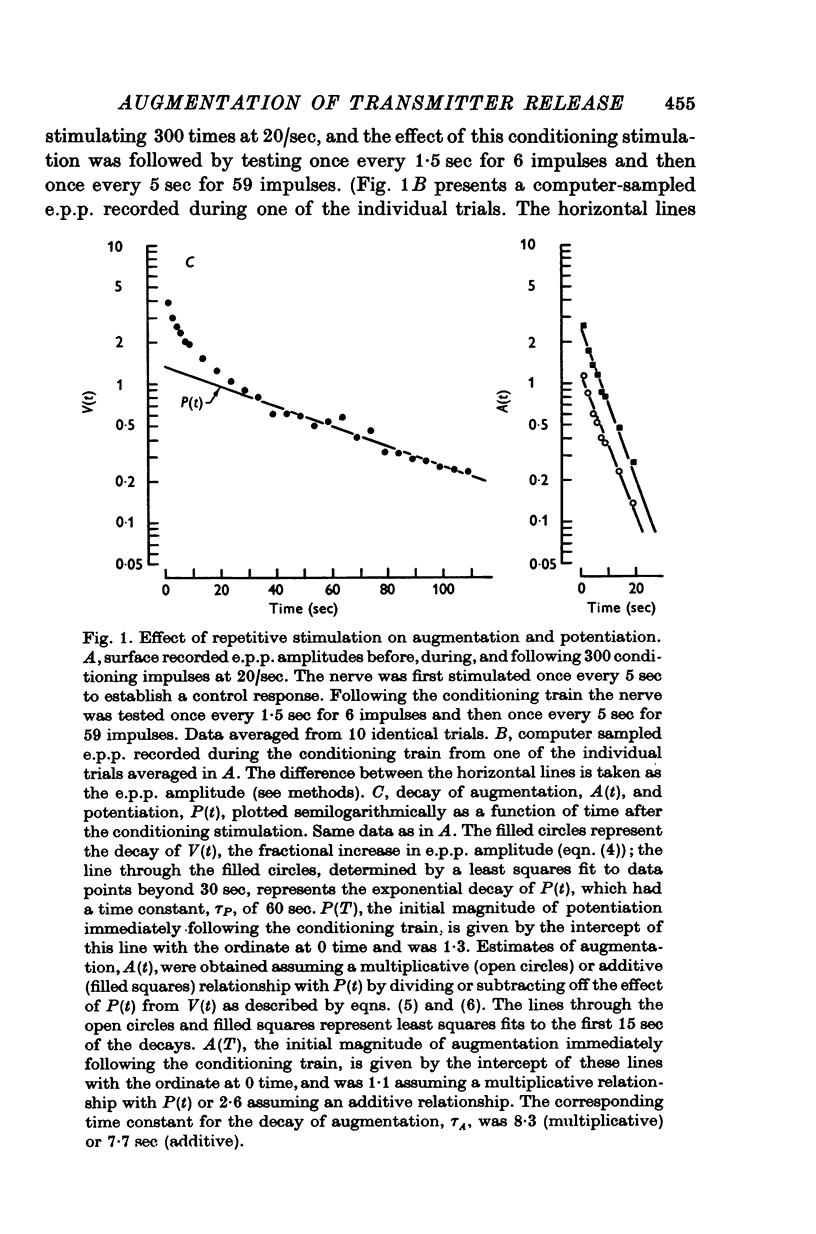
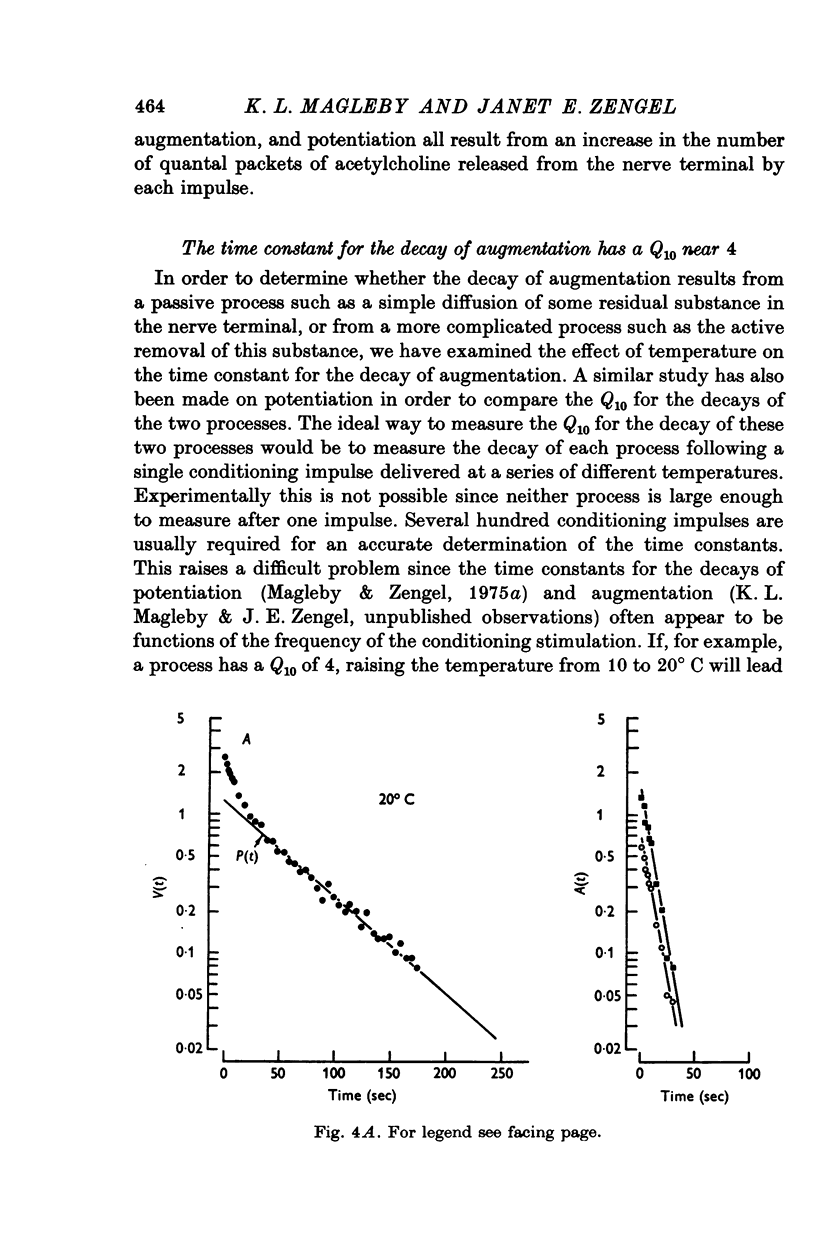
1. End-plate potentials (e.p.p.s) were recorded from frog neuromuscular junctions bathed in Ringer solution containing increased Mg and decreased Ca to reduce transmitter release. Conditioning and testing stimulation was applied to the nerve to study a previously uncharacterized process which acts to increase e.p.p. amplitudes. We will refer to this process as augmentation. 2. Following repetitive stimulation augmentation decayed approximately exponentially over most of its time course with a mean time constant of about 7 sec (range 4-10 sec) which is intermediate in duration between the time constants for the decay of facilitation and potentiation. 3 . The magnitude of agumentation increased with the duration of the conditioning stimulation. Assuming a multiplicative relationship between augmentation and potentiation, values of the magnitude of augmentation ranged from 0-3 to 0-6 following 50 impulses at 20/sec to 0-5-7-8 following 600 impulses at 20/sec. (An augmentation of 0-3 and 7-8 would increase e.p.p. amplitudes 1-3 and 8-8 times, respectively.) 4. The time constant characterizing the decay of augmentation remained relatively constant as the duration of the conditioning stimulation was increased. 5. Augmentation as well as facilitation and potentiation resulted from an increase in the number of quanta of transmitter released from the nerve terminal. 6. Augmentation decayed faster at higher temperatures with a mean temperature coefficient, Q10, of about 3-8. The corresponding Q10 for the decay of potentiation was found to be about 2-4. 7. It is concluded that augmentation can be a significant factor in increasing transmitter release and will therefore have to be accounted for when studying the effects of repetitive stimulation on the function of the nerve terminal or when formulating models of transmitter release.
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balnave R. J., Gage P. W. On facilitation of transmitter release at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):657–675. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T., Hall R. The effect of calcium ions on the binomial statistic parameters which control acetylcholine release at synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):429–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Schmidt R. F., Zimmermann M. Facilitation at the frog neuromuscular junction during and after repetitive stimulation. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;287(1):41–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00362453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDEL J., KUFFLER S. W. Mechanism of facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:530–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., QUASTEL D. M. PRESYNAPTIC ACTION OF HEMICHOLINIUM AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Quastel D. M. A quantitative study of end-plate potentials in isolated human muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Jun;178(3):505–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Hubbard J. I. An investigation of the post-tetanic potentiation of end-plate potentials at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):353–375. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F. Post-tetanic restoration of neuromuscular transmission blocked by D-tubocurarine. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):216–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. The effect of temperature change upon transmitter release, facilitation and post-tetanic potentiation. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):591–609. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I. Microphysiology of vertebrate neuromuscular transmission. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):674–723. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. F., Kwanbunbumpen S. Some effects of nerve stimulation andhemicholinium on quantal transmitter release at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):51–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The quantal components of the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):571–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M., Smolinsky A., Lass Y. Post-tetanic potentiation and facilitation do not share a common calcium-dependent mechanism. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio244155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C. Neuromuscular facilitation with low-frequency stimulation and effects of some drugs. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;32(5):785–792. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.5.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. A dual effect of repetitive stimulation on post-tetanic potentiation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):163–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. A quantitative description of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):183–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Zengel J. E. Long term changes in augmentation, potentiation, and depression of transmitter release as a function of repeated synaptic activity at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):471–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. Post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):121–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


