Abstract
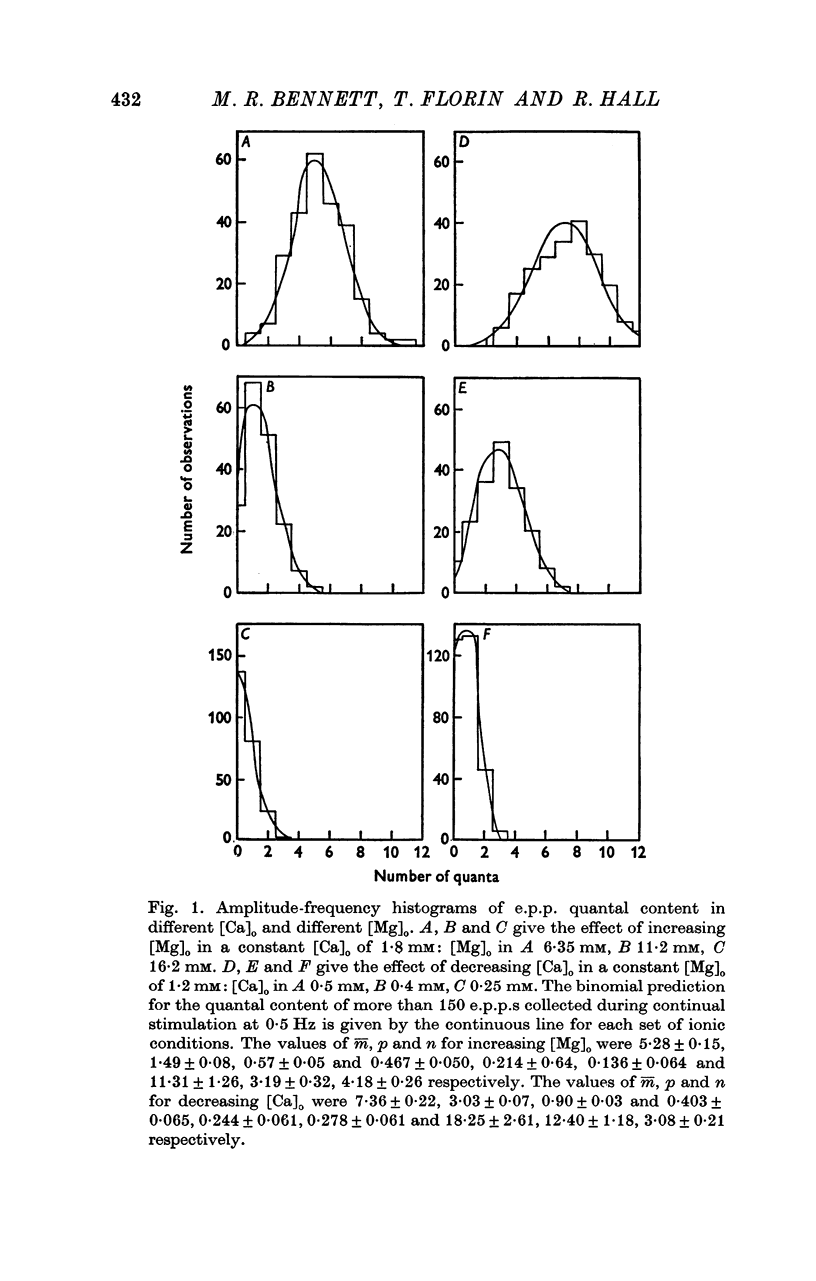
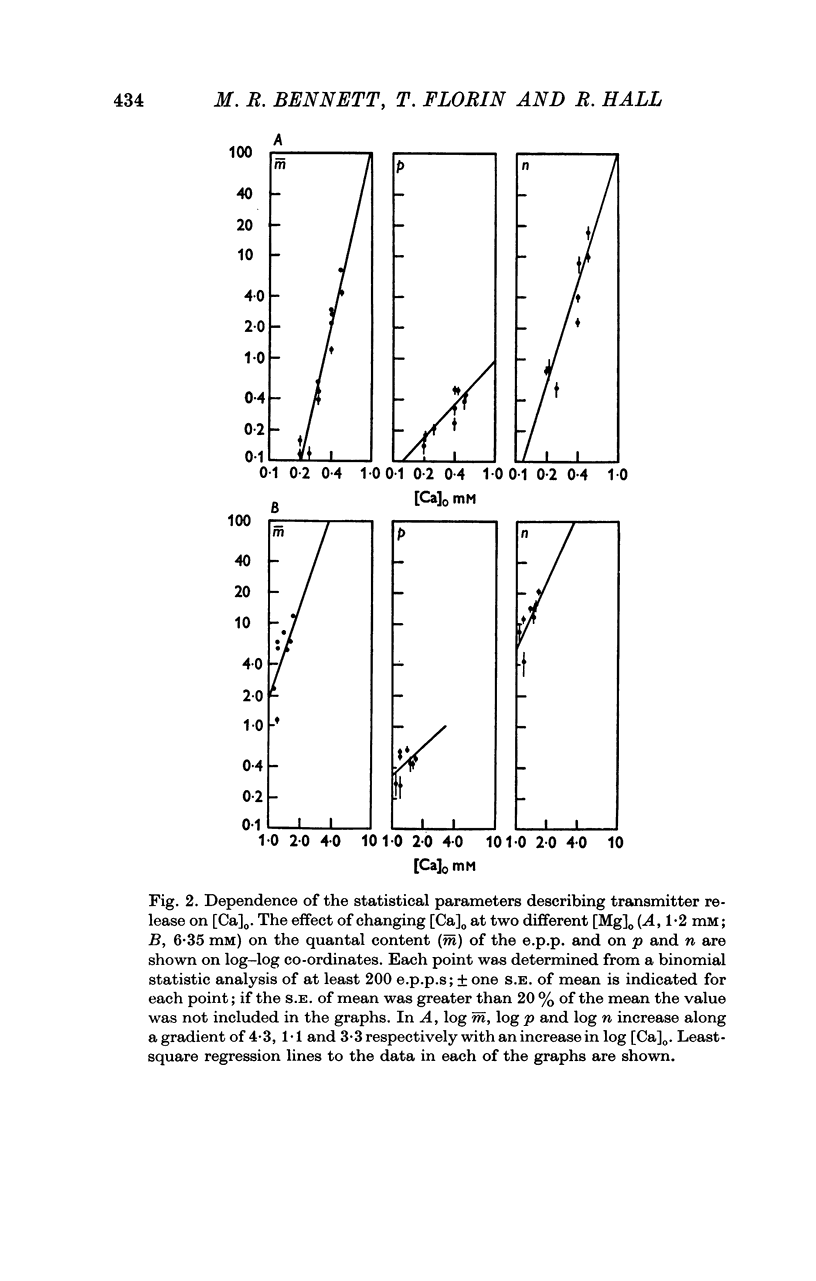
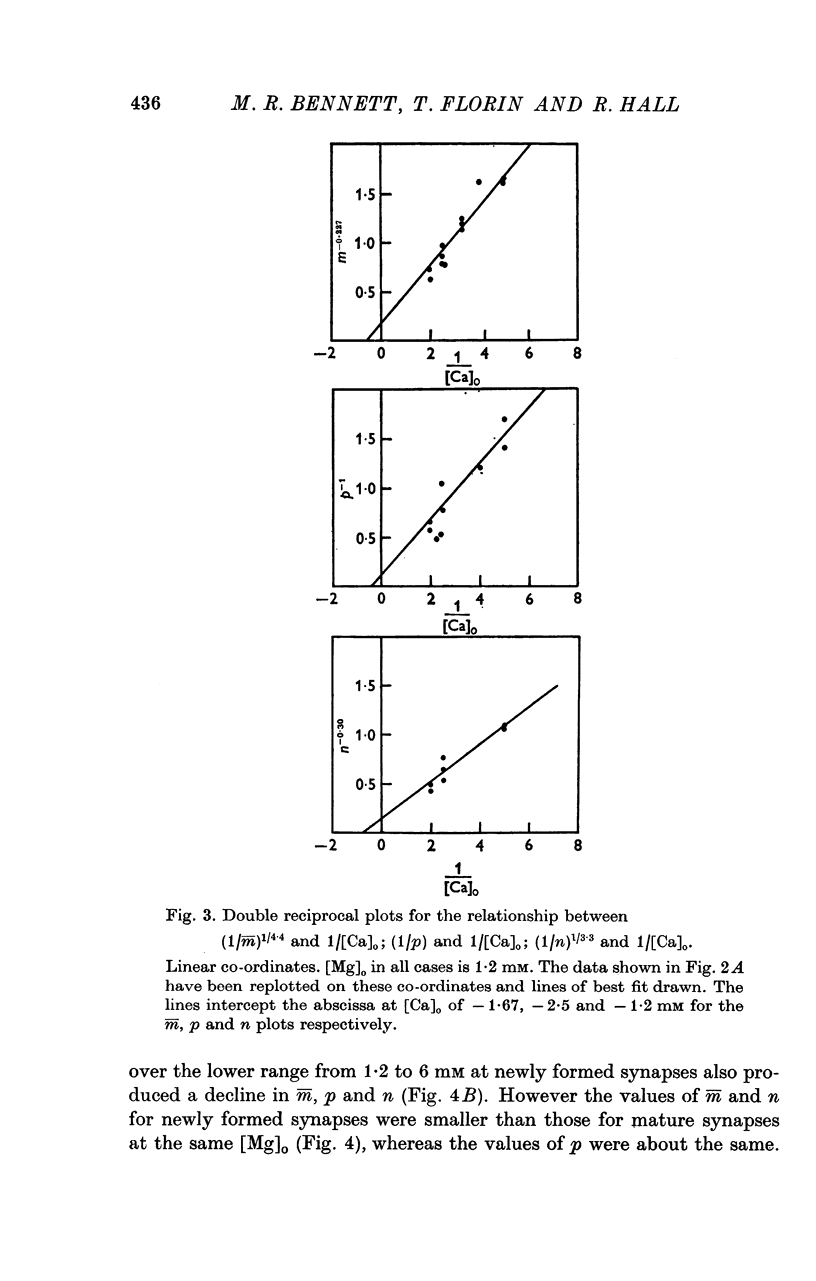
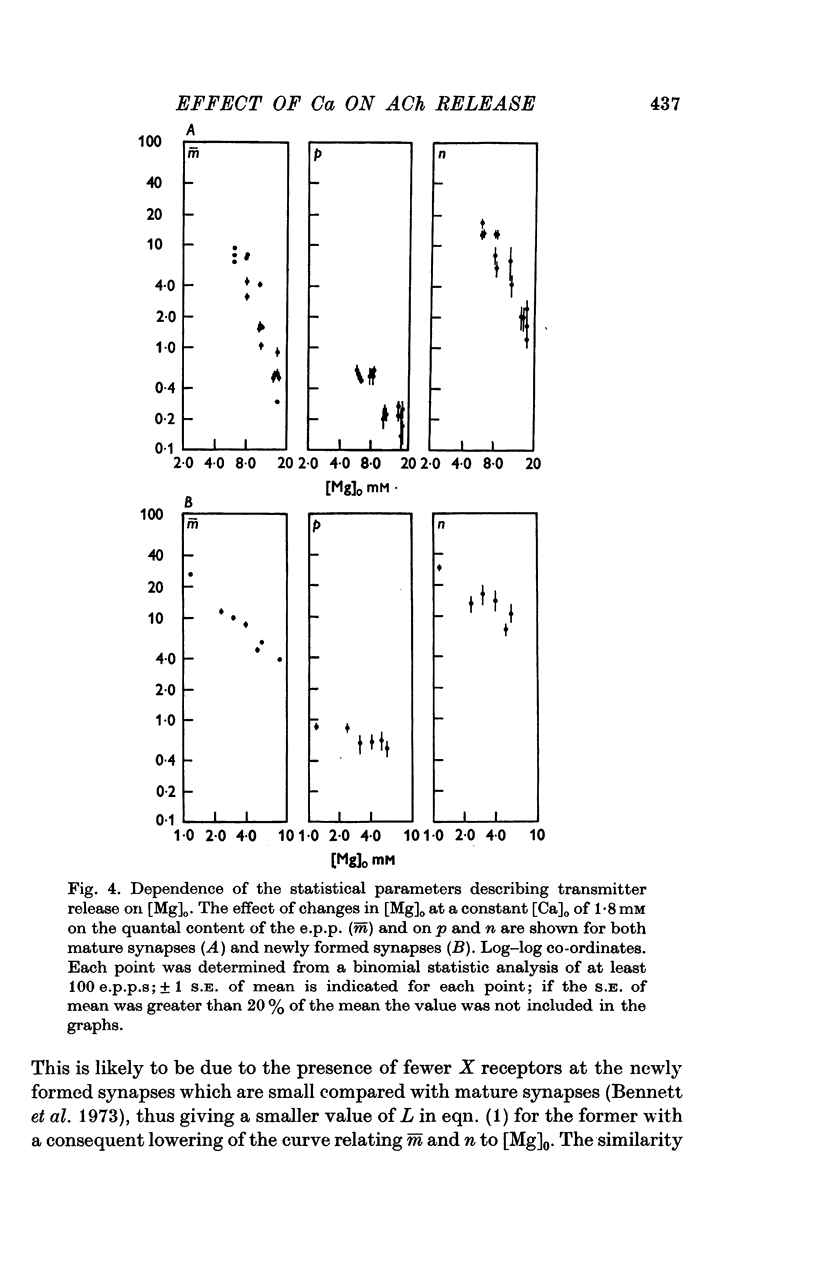
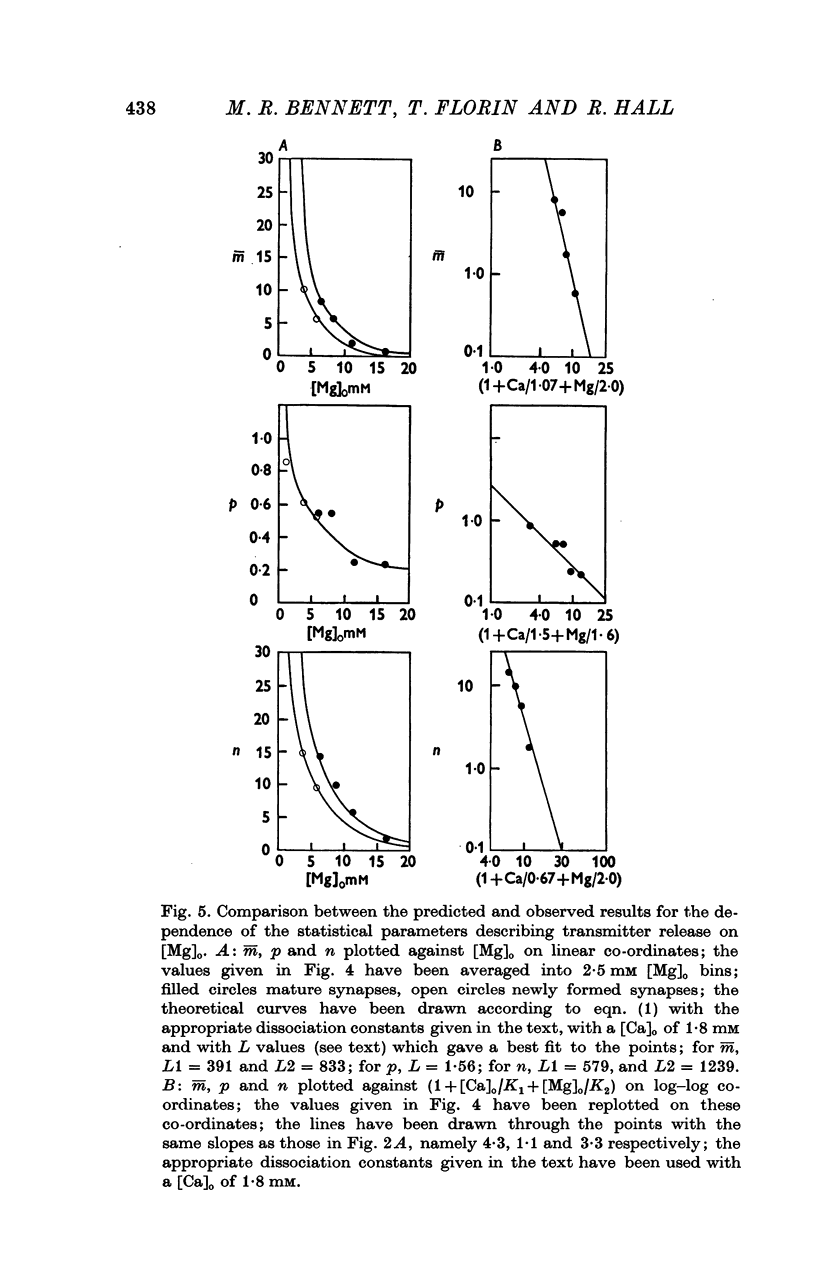
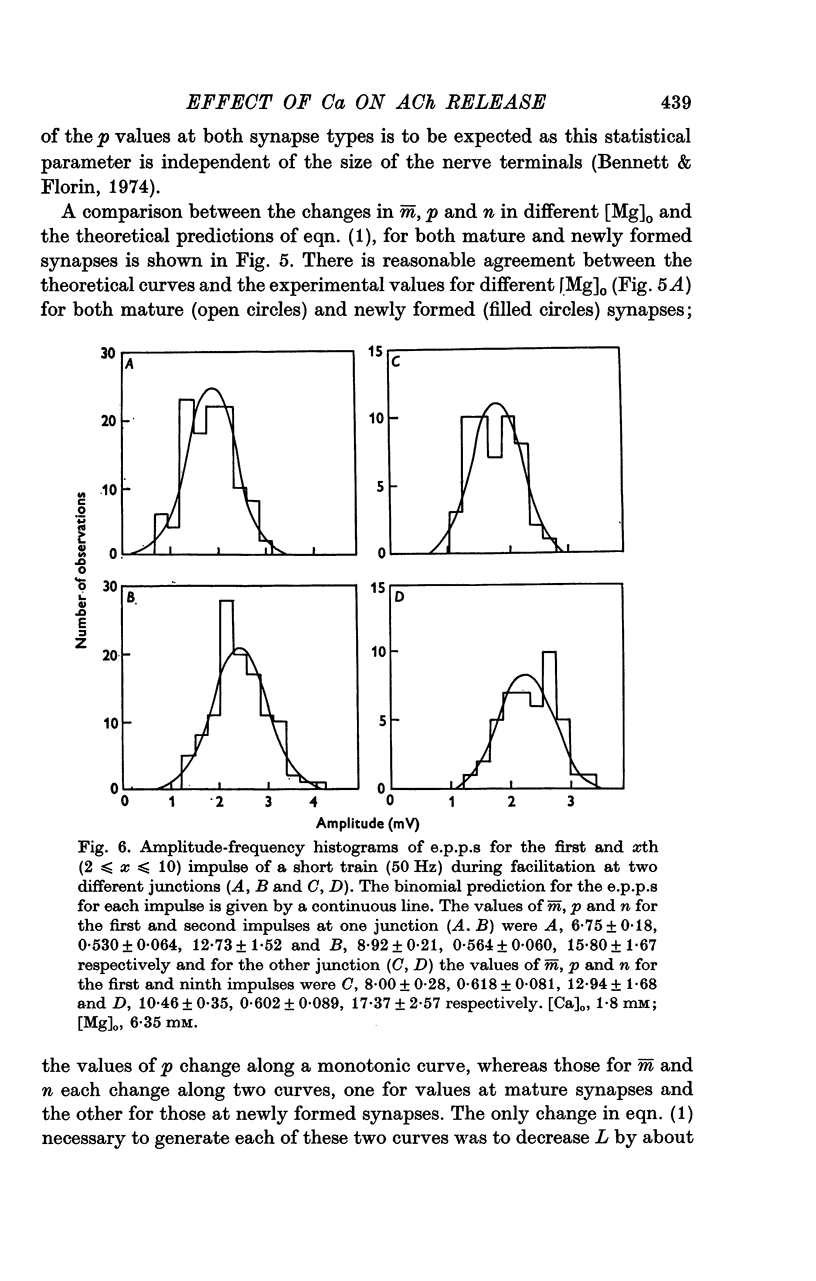
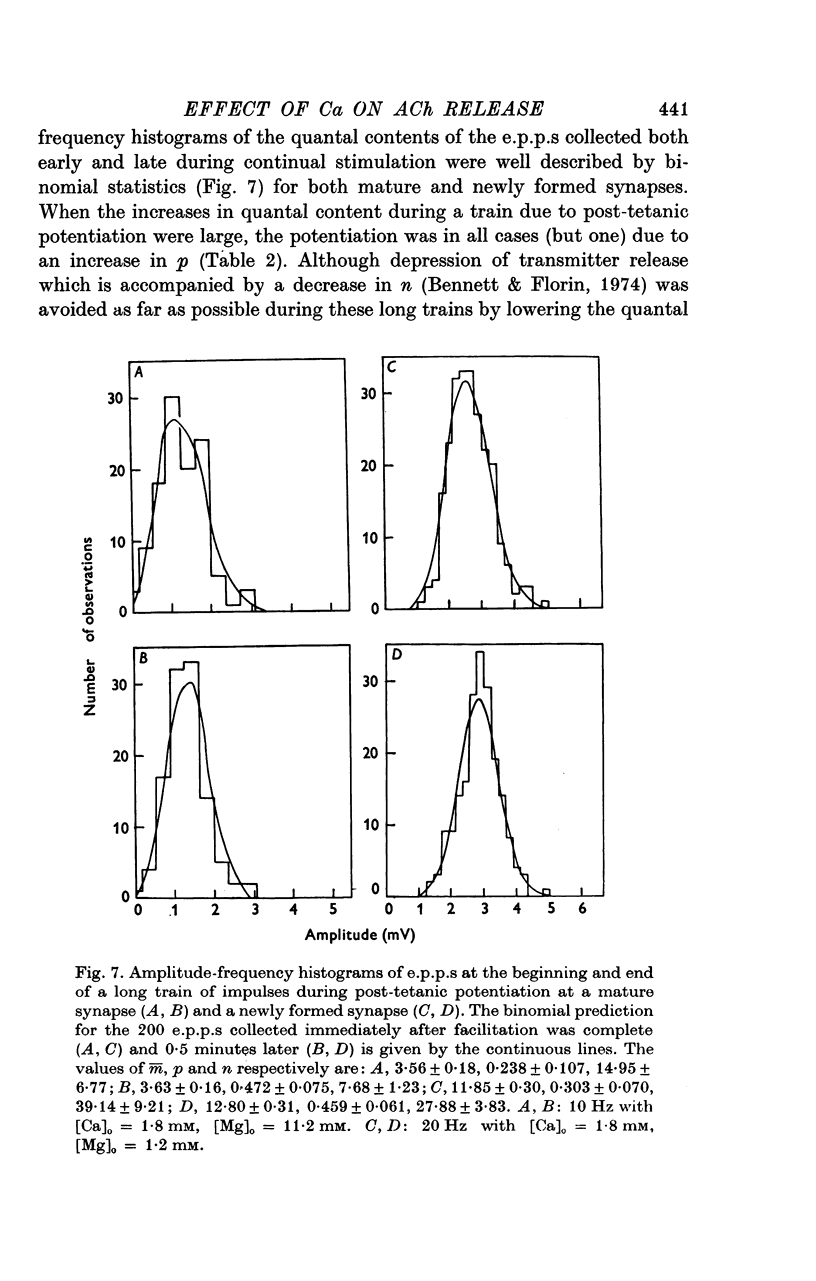
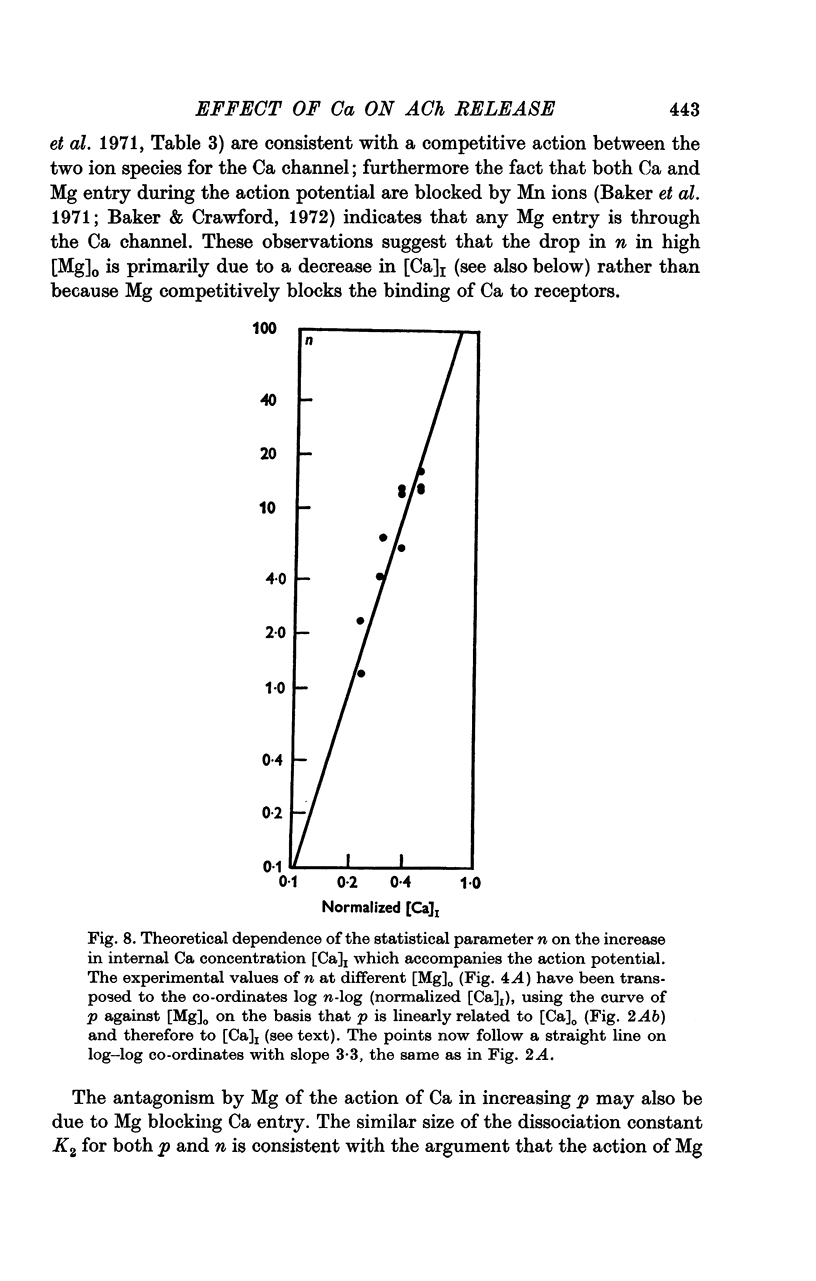
A study has been made of the effects of changing [Ca]O and [Mg]O on the binomial statistic parameters p and n which control the average quantal content (m) of the synaptic potential due to acetylcholine release. 2. When [Ca]O was varied in the range 0-1 to 1-0 mM, p increased as the first power of [Ca]O whereas n increased as the third power of [Ca]O. 3. Increasing [Mg]O depressed both p and n, however variations of [Ca]O in the presence of high [Mg]O did not significantly change the power relationship between either p and [Ca]O or between n and [Ca]O. 4. The facilitated increase in m during a short train was due to an increase in n, whereas the post-tetanic increase in m during a tetanus was due to an increase in p. These results are considered in terms of the role of Ca ions in facilitation and post-tetanic potentiation.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. Mobility and transport of magnesium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):855–874. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. A statistical analysis of the release of acetylcholine at newly formed synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):93–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T., Woog R. The formation of synapses in regenerating mammalian striated muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):79–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., McLachlan E. M., Taylor R. S. The formation of synapses in mammalian striated muscle reinnervated with autonomic preganglionic nerves. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):501–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. On the mechanism by which calcium and magnesium affect the release of transmitter by nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):75–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. W., Wernig A. The binomial nature of transmitter release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):757–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Blinks J. R., Nicholson C. Calcium transient in presynaptic terminal of squid giant synapse: detection with aequorin. Science. 1972 Jun 9;176(4039):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4039.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of repetitive stimulation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):327–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L. The effect of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation on facilitation of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. Tetanic and post-tetanic rise in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in low-calcium solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):245–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R. A dual effect of calcium ions on neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):471–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Yaari Y. Delayed release of transmitter at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):241–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Ionic mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. Changes in statistical parameters during facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):751–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A. The effects of calcium and magnesium on statistical release parameters at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):761–768. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younkin S. G. An analysis of the role of calcium in facilitation at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Changes in the statistics of transmitter release during facilitation. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):787–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


