Abstract
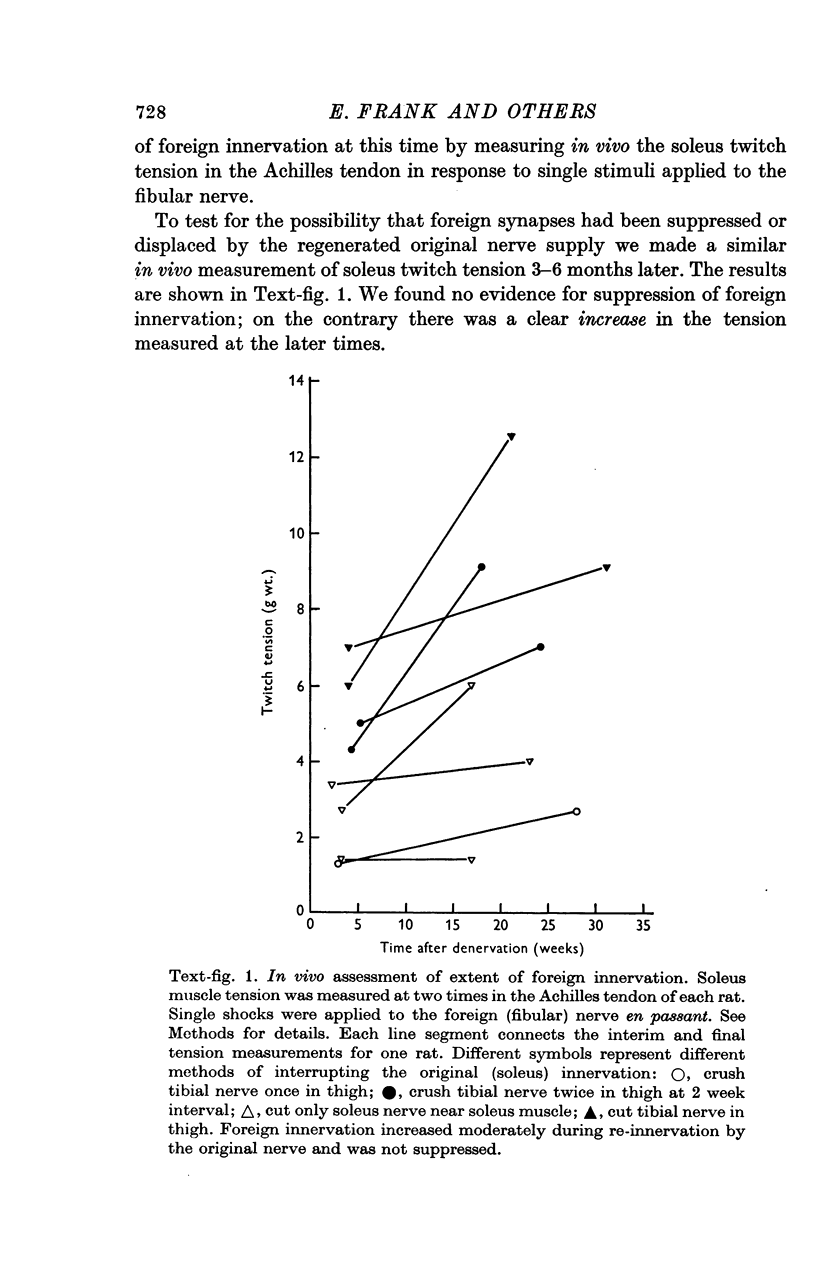
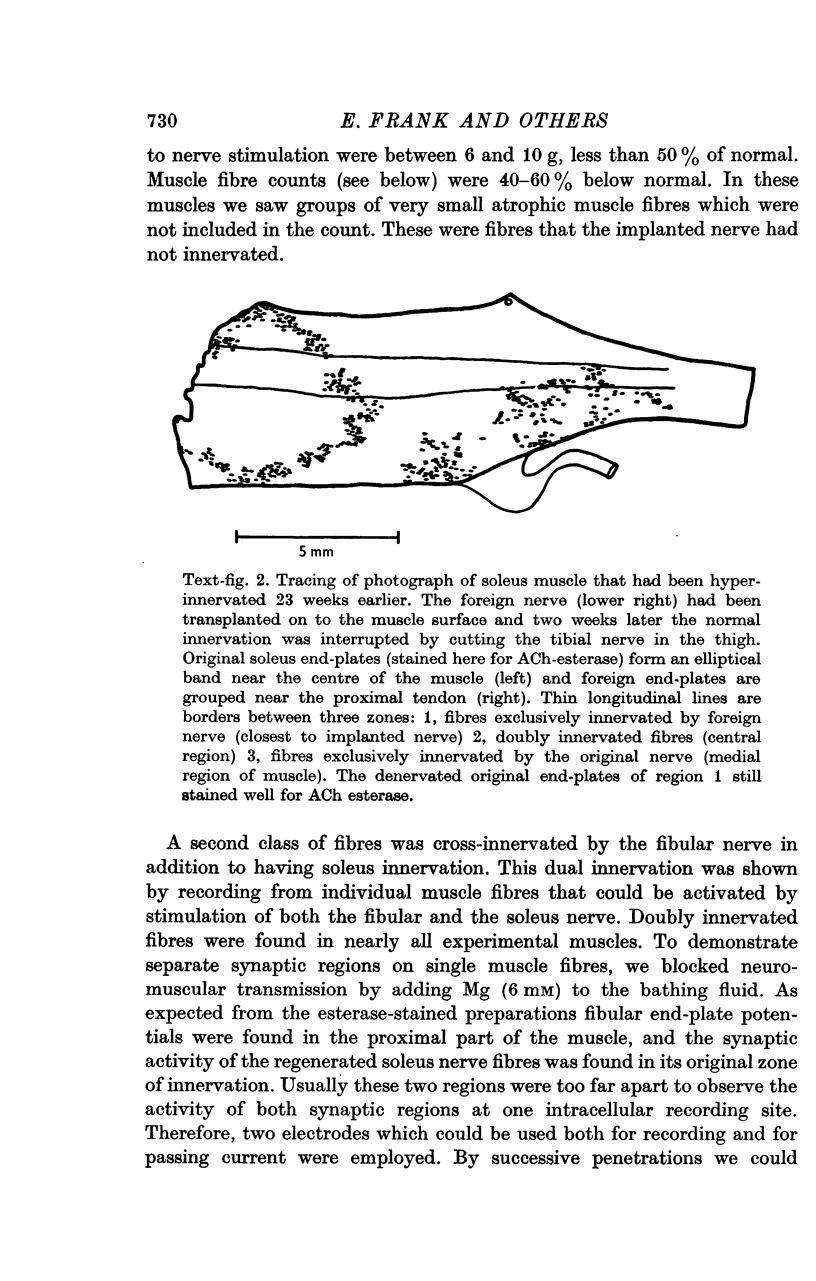
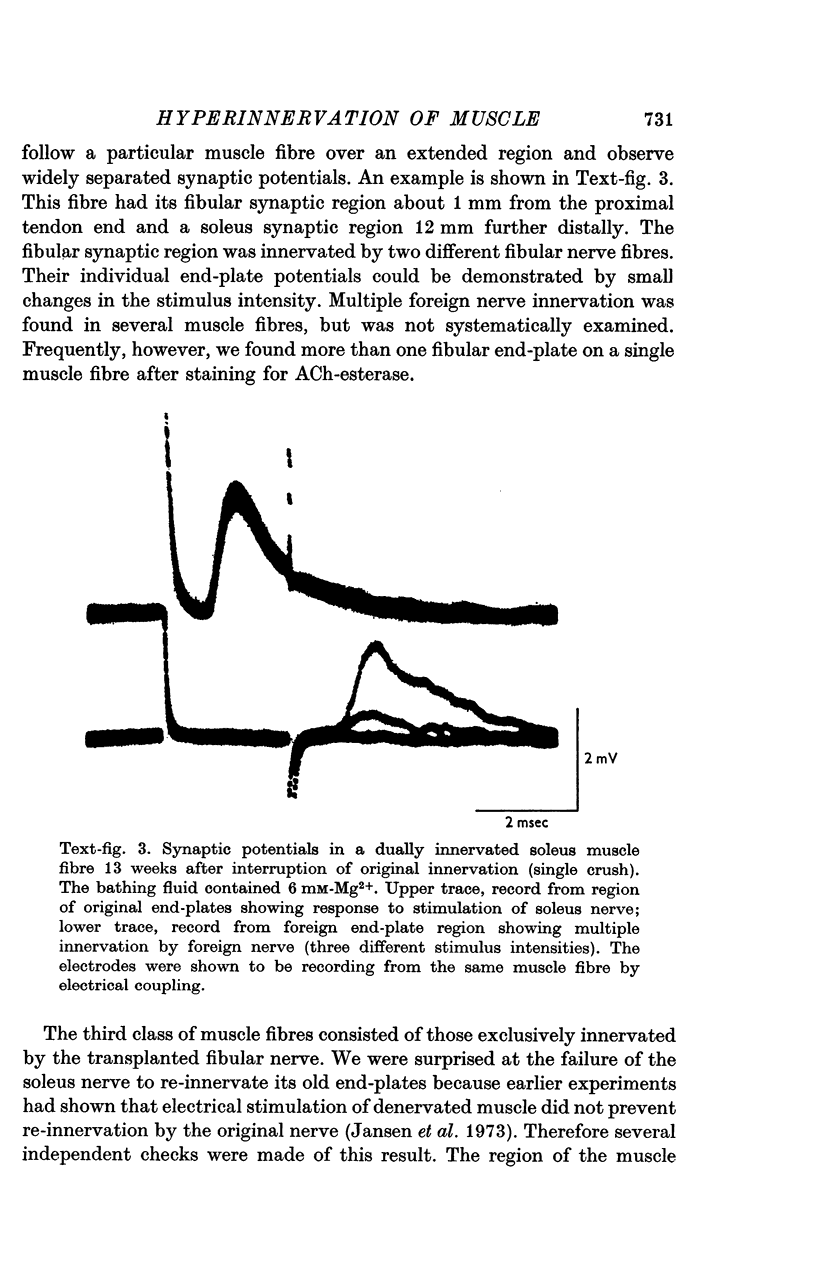
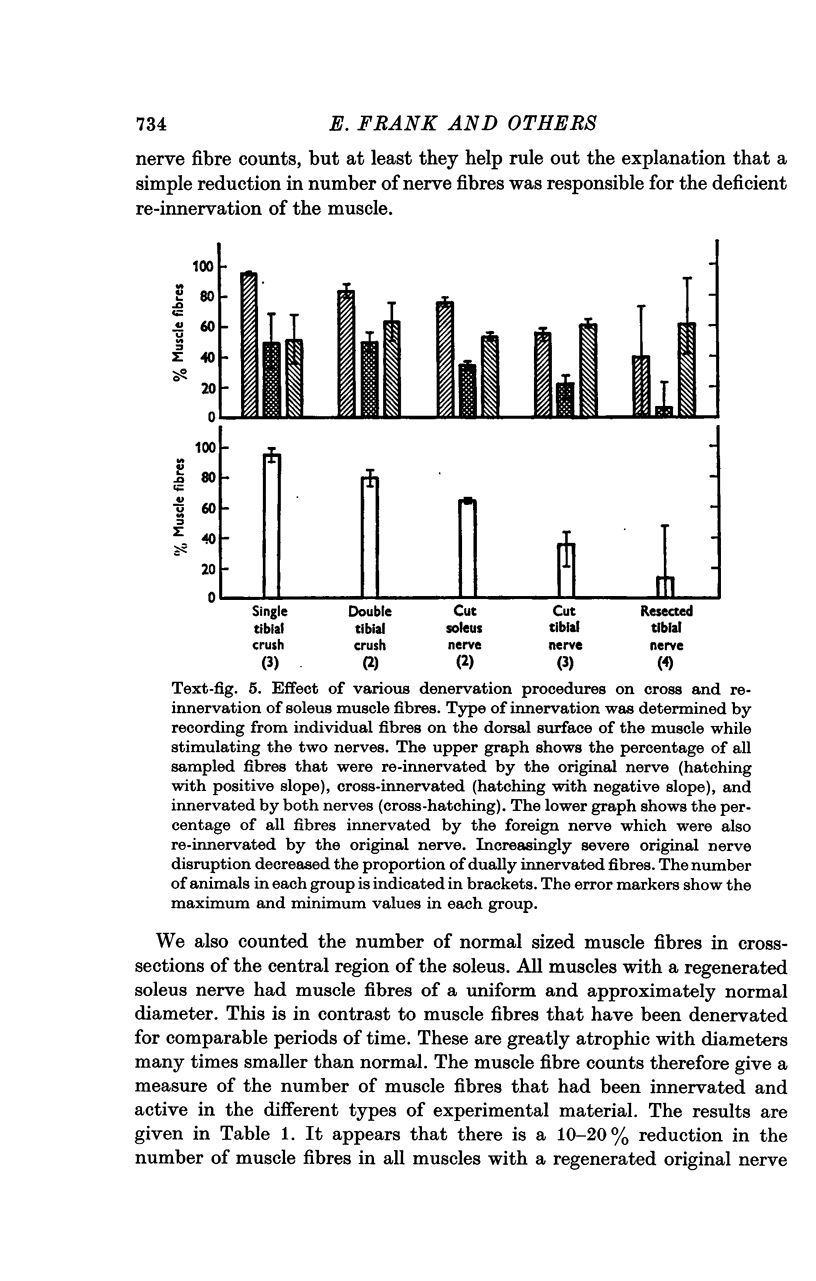
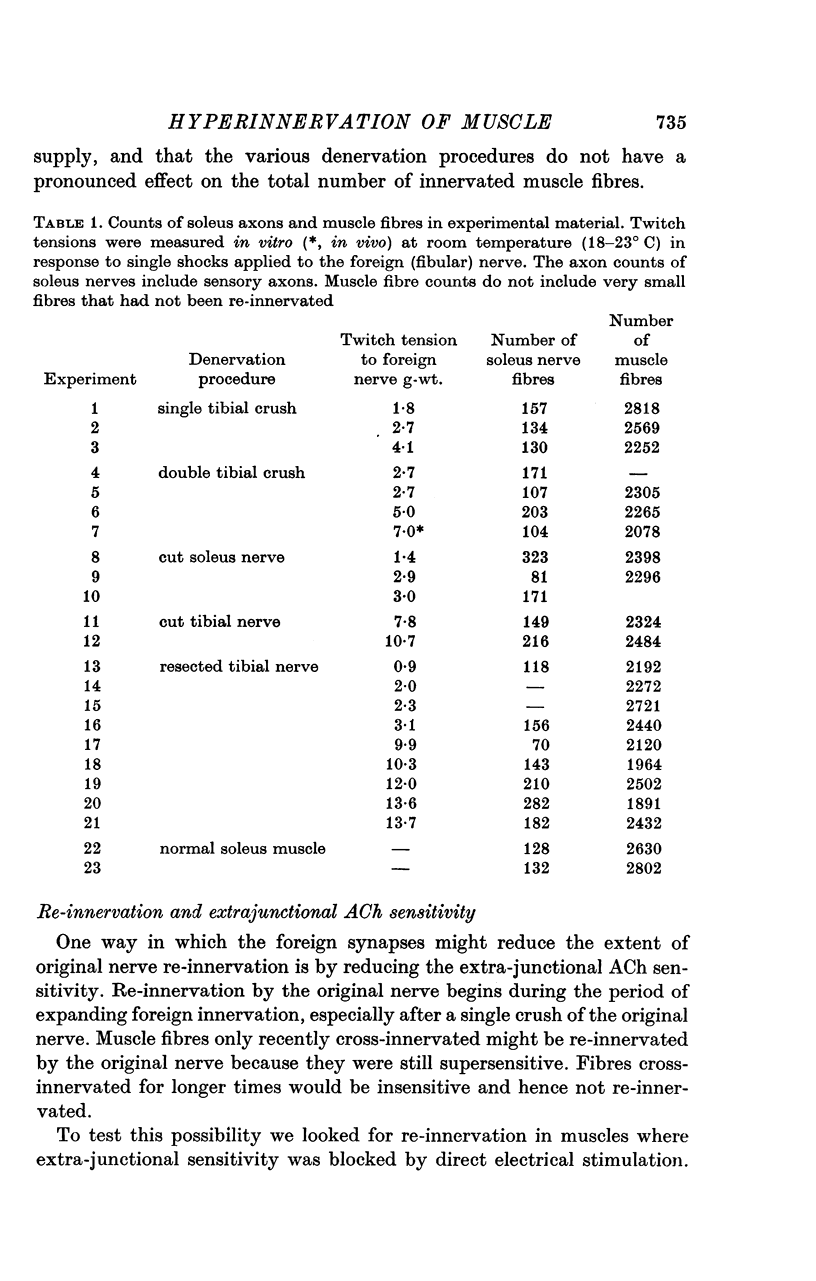
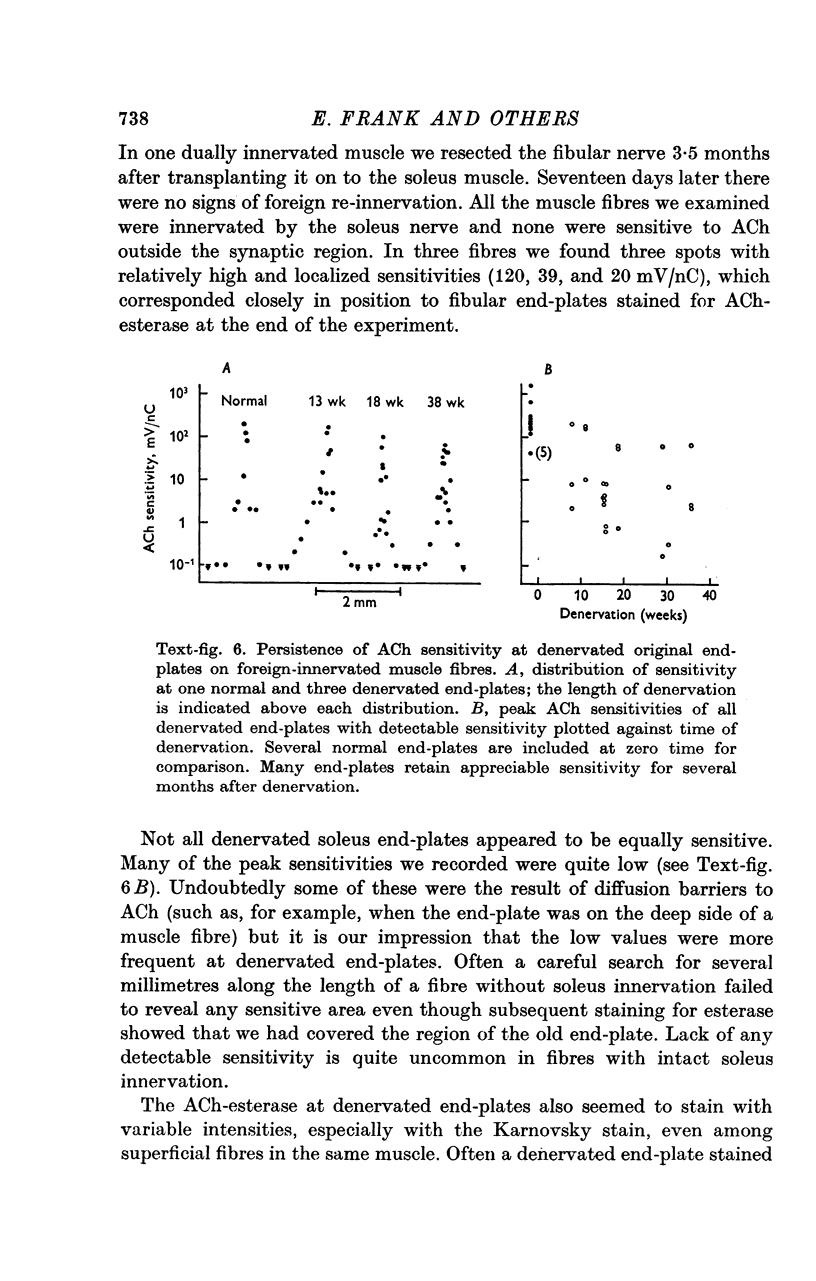
1. The fibular nerve was transplanted on to the soleus muscle of the rats. Interruption of the original soleus nerve then permitted cross-innervation, and subsequently, over a period of weeks, re-innervation by the original nerve. 2. Individual muscle fibres were often innervated by both the original and the foreign nerve. The original and foreign end-plates were located in separate regions of the muscle. There were no indications that the original nerve could displace or repress the foreign innervation. 3. The extent of re-innervation by the original nerve depended upon the method of denervation. A single crush of the nerve was followed by virtually complete re-innervation, even of muscle fibres already innervated by the foreign nerve. When re-innervation was delayed by resection of a segment of the nerve only muscle fibres without foreign nerve innervation were re-innervated. Denervation by a simple nerve cut gave an intermediate result. 4. Re-innervation by the original nerve can take place without measurable extrajunctional sensitivity to ACh. 5. The original end-plate region could retain high and localized sensitivity to ACh for several months despite degeneration of its motor nerve terminal and activity of the muscle fibre. 6. Established foreign end-plates were re-innervated by the foreign nerve on muscle fibres with intact original innervation. 7. The factors controlling synapse formation in skeletal muscles are discussed.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagust J., Lewis D. M., Westerman R. A. Polyneuronal innervation of kitten skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):241–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley G. A., Heaton J. A quantitative study of cholinesterase in myoneural junctions from rat and guinea-pig extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(3):743–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass D. T., Sutton T. J., Mark R. F. Competition between nerves for functional connexions with axolotl muscles. Nature. 1973 May 25;243(5404):201–203. doi: 10.1038/243201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsberg C. A. EXPERIMENTS ON MOTOR NERVE REGENERATION AND THE DIRECT NEUROTIZATION OF PARALYZED MUSCLES BY THEIR OWN AND BY FOREIGN NERVES. Science. 1917 Mar 30;45(1161):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.45.1161.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Sonesson B., Thesleff S., Zelená J. Nerve implants in botulinum poisoned mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):872–882. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Westgaard R. H. Proceedings: Effect of foreign innervation on the reinnervation of muscle by its original nerve. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):24P–25P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Westgaard R. Maintained function of foreign synapses on hyperinnervated skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. Nature. 1974 Feb 8;247(5440):375–376. doi: 10.1038/247375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm L. M. An evaluation of myotypic respecification in axolotls. J Exp Zool. 1971 Dec;178(4):479–496. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401780406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E., Hanzlíková V. Effects of accessory nerve supply to muscle achieved by implantation into muscle during regeneration of its nerve. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1967;16(3):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Volk R. J. Oxygen uptake by illuminated maize leaves. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):269–271. doi: 10.1038/222269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Lomo T., Nicolaysen K., Westgaard R. H. Hyperinnervation of skeletal muscle fibers: dependence on muscle activity. Science. 1973 Aug 10;181(4099):559–561. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4099.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. THE LOCALIZATION OF CHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY IN RAT CARDIAC MUSCLE BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACETYLCHOLINE SENSITIVITY IN NERVE-FREE SEGMENTS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:389–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Rosenthal J. Control of ACh sensitivity by muscle activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):493–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H., Dahl H. A. Contractile properties of muscle: control by pattern of muscle activity in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 27;187(1086):99–103. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. The acetylcholine sensitivity of frog muscle fibres after complete or partial devervation. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark R. F. Selective innervation of muscle. Br Med Bull. 1974 May;30(2):122–126. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotte L. R., Mark R. F. The mechanism of selective reinnervation of fish eye muscle. I. Evidence from muscle function during recovery. Brain Res. 1970 Apr 1;19(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P. A. Neuromuscular transmission in new-born rats. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):701–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Essen D., Jansen J. K. Reinnervation of the rat diaphragm during perfusion with alpha-bungarotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):571–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]