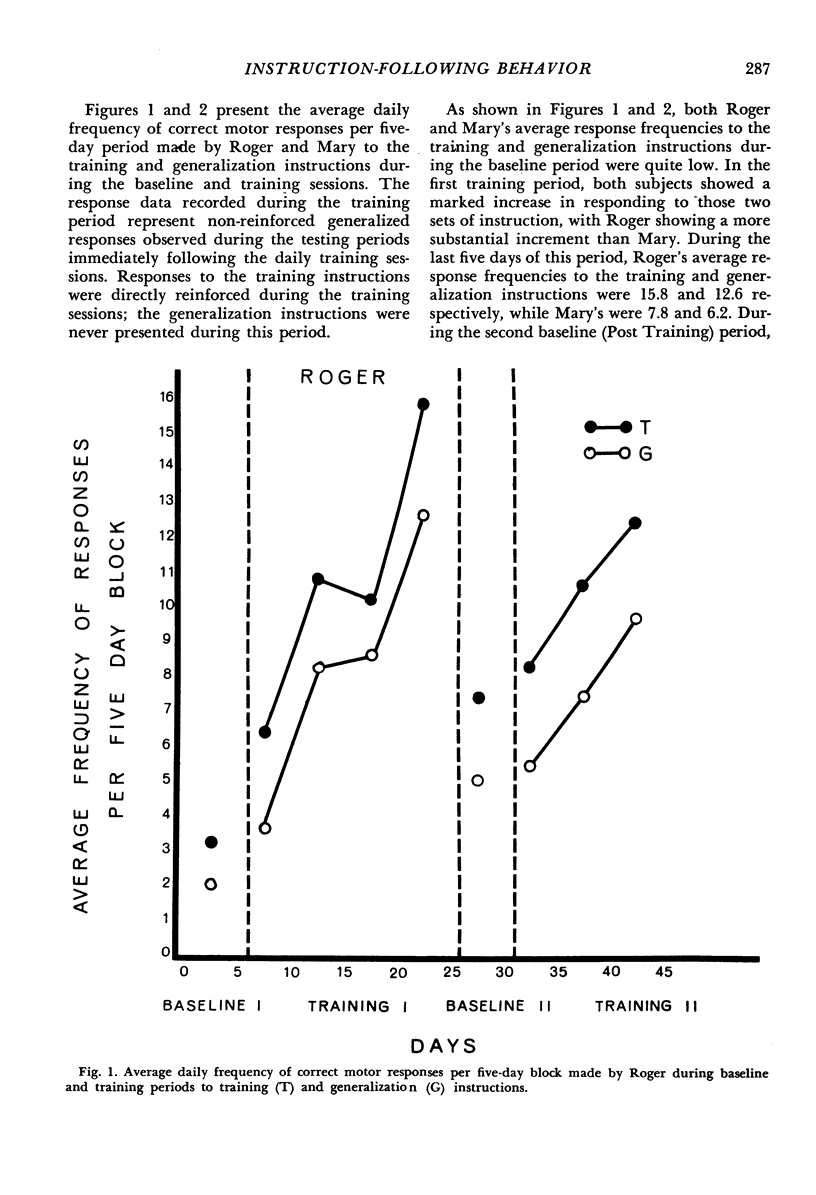
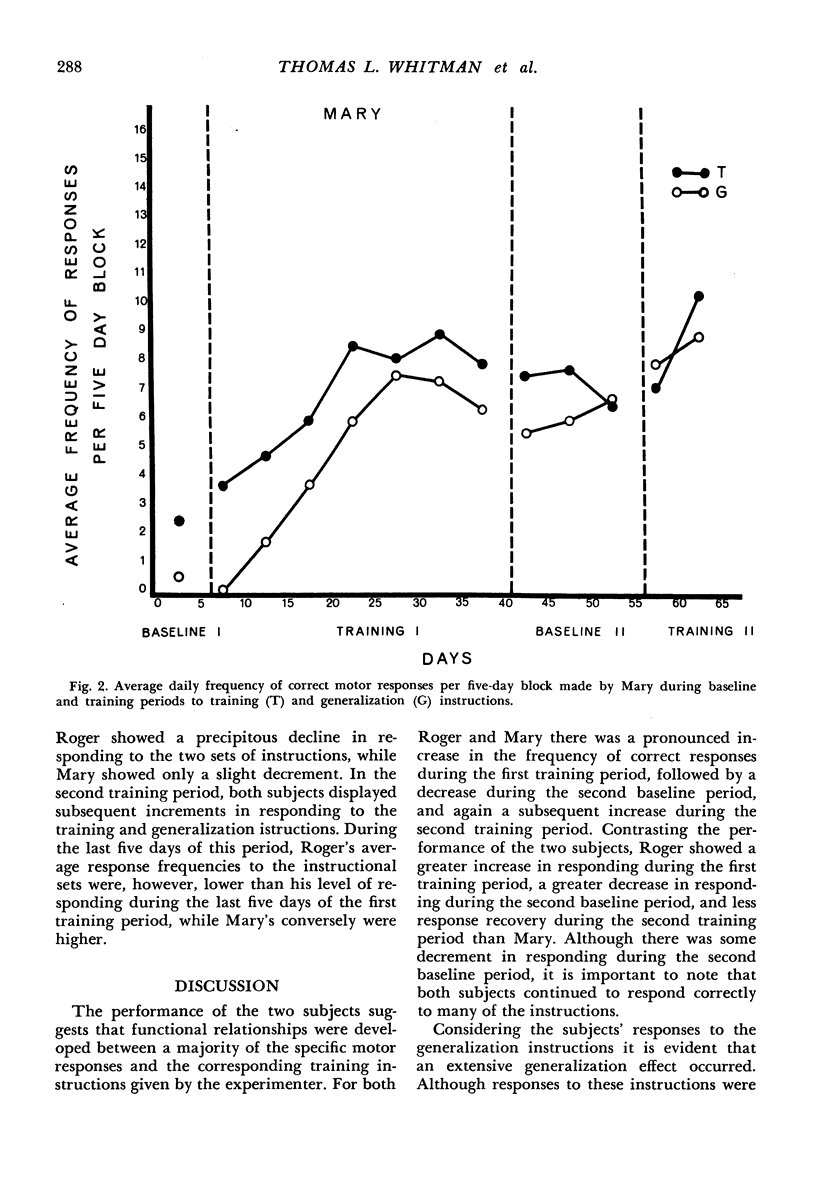
Abstract
Positive reinforcement, physical guidance, and fading procedures were used to teach two severely retarded children motor responses to a variety of verbal instructions. Subjects' responses to one set of instructions provided the focus for the training procedures. Their responses to a second set of instructions were used to assess the generalized effects of training. The frequency of responses to both sets of instructions was evaluated during Baseline 1, Training 1, Baseline 2, and Training 2 periods. During the training periods, this evaluation was made after the daily training sessions when no training procedures were in effect. Results indicated that the subjects showed pronounced increases in instruction-following behaviors (both trained and untrained) during training periods with decreases in such behavior occurring during the Baseline 2 period. The general findings demonstrate the applicability of the training procedures for producing and maintaining instruction-following behaviors in severely retarded children and for facilitating appropriate responding to instructions not directly involved in training.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYLLON T., AZRIN N. H. REINFORCEMENT AND INSTRUCTIONS WITH MENTAL PATIENTS. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jul;7:327–331. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Peterson R. F., Sherman J. A. The development of imitation by reinforcing behavioral similarity to a model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):405–416. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Kaufman A., Stauber K. A. Effects of instructions and reinforcement-feedback on human operant behavior maintained by fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):701–712. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKERSON D. J., GIRARDEAU F. L., SPRADLIN J. E. VERBAL PRETRAINING AND DISCRIMINATION LEARNING BY RETARDATES. Am J Ment Defic. 1964 Jan;68:476–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. Learning of a generalized response class in mentally retarded individuals. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 Jul;71(1):100–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MECHAM M. J. The development and application of procedures for measuring speech improvement in mentally defective children. Am J Ment Defic. 1955 Oct;60(2):301–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLANGER B. B., GOTTSLEBEN R. H. Analysis of speech defects among the institutionalized mentally retarded. J Speech Hear Disord. 1957 Mar;22(1):98–103. doi: 10.1044/jshd.2201.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLANGER B. B. Speech examination of a group of institutionalized mentally handicapped children. J Speech Hear Disord. 1953 Dec;18(4):339–349. doi: 10.1044/jshd.1804.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER B., VALLON J. The results of a speech therapy program for mentally retarded children. Am J Ment Defic. 1954 Jan;59(3):417–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman E. H., Zimmerman J., Russell C. D. Differential effects of token reinforcement on instruction-following behavior in retarded students instructed as a group. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):101–112. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


