Abstract
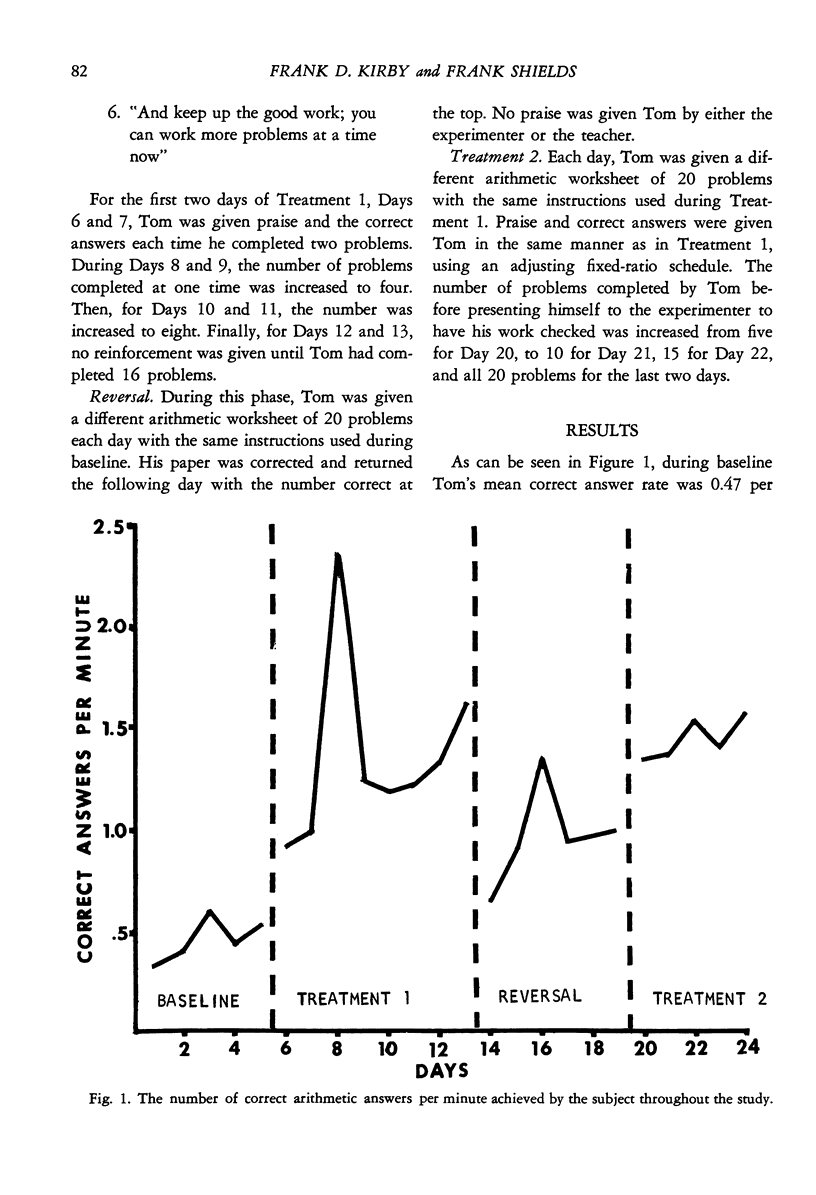
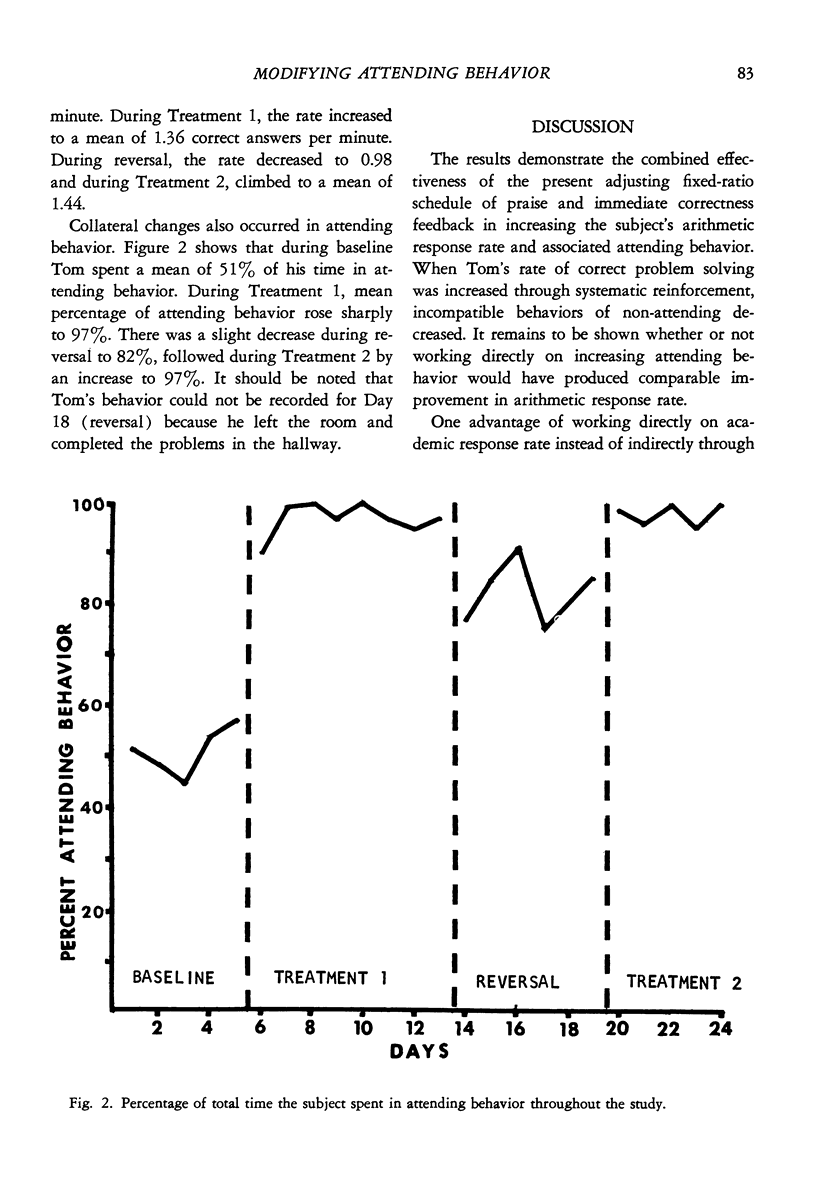
An adjusting fixed-ratio schedule of praise and immediate correctness feedback produced increases in a seventh-grade student's arithemic response rate. Percentage of time spent in attending behavior also increased collaterally. Removal of the treatment led to decreases in both arithmetic response rate and collateral attending behavior. Reinstatements of the procedure again produced increases in both types of behavior. It was suggested that the present procedure of directly modifying arithmetic response rate requires less time and effort than working indirectly through modifying attending behavior.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bushell D., Wrobel P. A., Michaelis M. L. Applying "group" contingencies to the classroom study behavior of preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):55–61. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. V., Lund D., Jackson D. Effects of teacher attention on study behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovitt T. C., Curtiss K. A. Effects of manipulating an antecedent event on mathematics response rate. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):329–333. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt P. R., Ulrich R. E., Hawkins R. P. An elementary student as a behavioral engineer. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):85–92. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker H. M., Buckley N. K. The use of positive reinforcement in conditioning attending behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):245–250. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


