Abstract
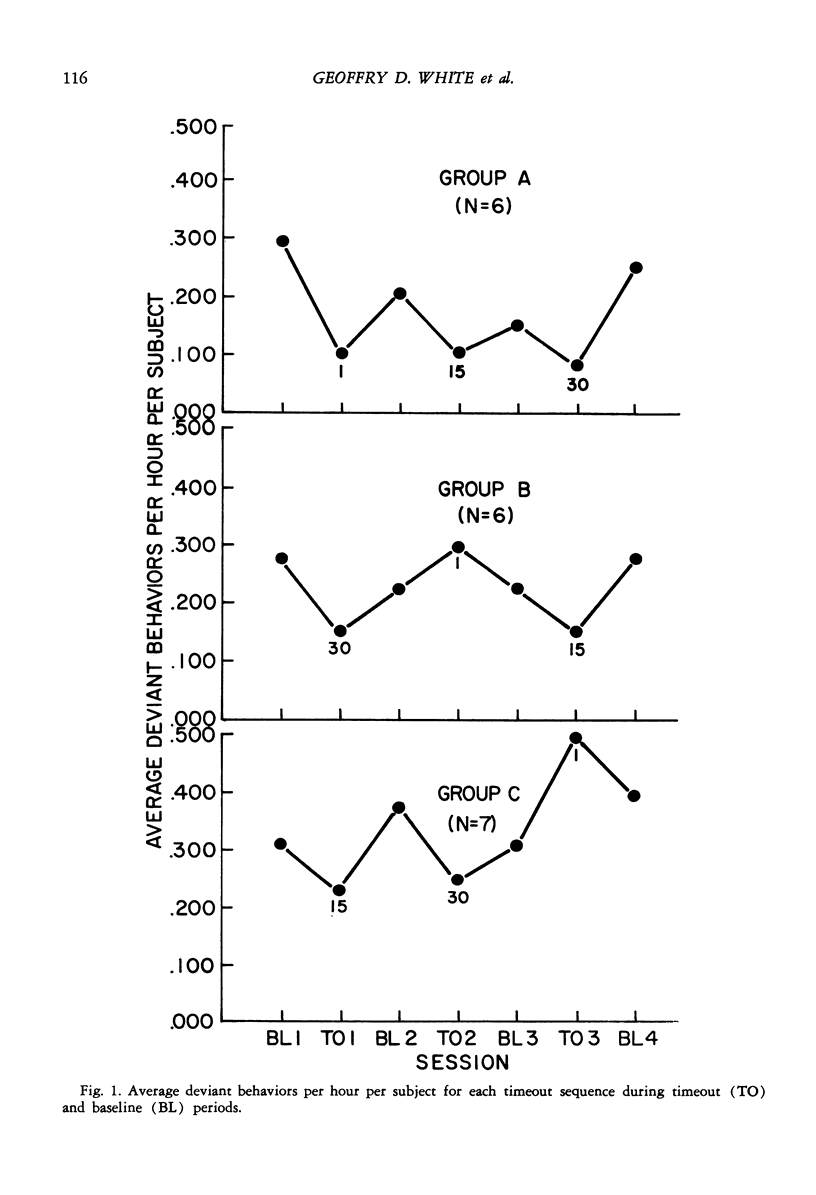
The effects of three different timeout durations were investigated in a group of 20 retarded, institutionalized subjects. Each subject received 1, 15, and 30 min of timeout in a design that was counterbalanced in terms of the order in which timeout durations were presented. Displays of deviant behavior—such as aggression, tantrums, and self-destruction—were followed by periods of isolation in a timeout room. A reversal design was employed such that return-to-baseline periods were instituted after each timeout period. The overall effect of timeout was to reduce significantly the rate of deviant behavior. On the average, 15 and 30 min produced a 35% decrease in deviant behavior with little difference between the effectiveness of 15 and 30 min. The range of effects in all timeout conditions varied widely. The sequence in which the 1-min duration was presented effected the direction of its effect. When it preceded the use of longer durations, 1 min was most effective. As it came later in the sequence, its suppressive characteristics became less reliable.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEVAN W., ADAMSON R. Reinforcers and reinforcement: their relation to maze performance. J Exp Psychol. 1960 Apr;59:226–232. doi: 10.1037/h0045962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURCHARD J., TYLER V., Jr THE MODIFICATION OF DELIQUENT BEHAVIOR THROUGH OPERANT CONDITIONING. Behav Res Ther. 1965 Apr;3:245–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(65)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan W. The contextual basis of behavior. Am Psychol. 1968 Oct;23(10):701–714. doi: 10.1037/h0026697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostow D. E., Bailey J. B. Modification of severe disruptive and aggressive behavior using brief timeout and reinforcement procedures. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Spring;2(1):31–37. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., APPEL J. B. Punishment of S delta responding in matching to sample by time out from positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:45–56. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles D. K., Wolf M. M. Toilet training institutionalized, severe retardates: an application of operant behavior modification techniques. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 Mar;70(5):766–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. P., Peterson R. F., Schweid E., Bijou S. W. Behavior therapy in the home: amelioration of problem parent-child relations with the parent in a therapeutic role. J Exp Child Psychol. 1966 Sep;4(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(66)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitenberg H. Is time-out from positive reinforcement an aversive event? A review of the experimental evidence. Psychol Bull. 1965 Dec;64(6):428–441. doi: 10.1037/h0022657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T. R. The effects and side effects of punishing the autistic behaviors of a deviant child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):21–34. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sailor W., Guess D., Rutherford G., Baer D. M. Control of tantrum behavior by operant techniques during experimental verbal training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):237–243. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS C. D. The elimination of tantrum behavior by extinction procedures. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1959 Sep;59:269–269. doi: 10.1037/h0046688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G., Winkel G. H., Peterson R. F., Morrison D. C. Mothers as behavior therapists for their own children. Behav Res Ther. 1965 Sep;3(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(65)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., BAYDAN N. T. PUNISHMENT OF S-DELTA RESPONDING OF HUMANS IN CONDITIONAL MATCHING TO SAMPLE BY TIME-OUT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:589–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., FERSTER C. B. Intermittent punishment of Sdelta responding in matching to sample. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:349–356. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


