Abstract
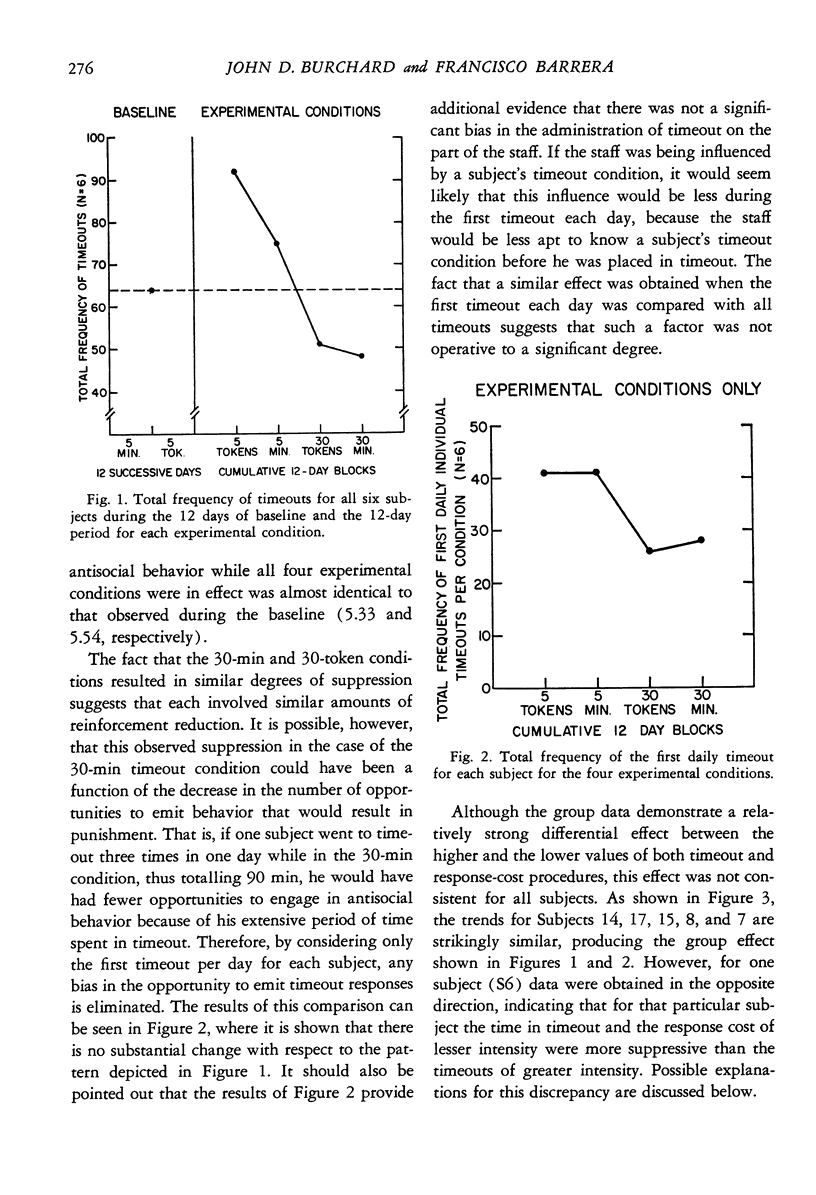
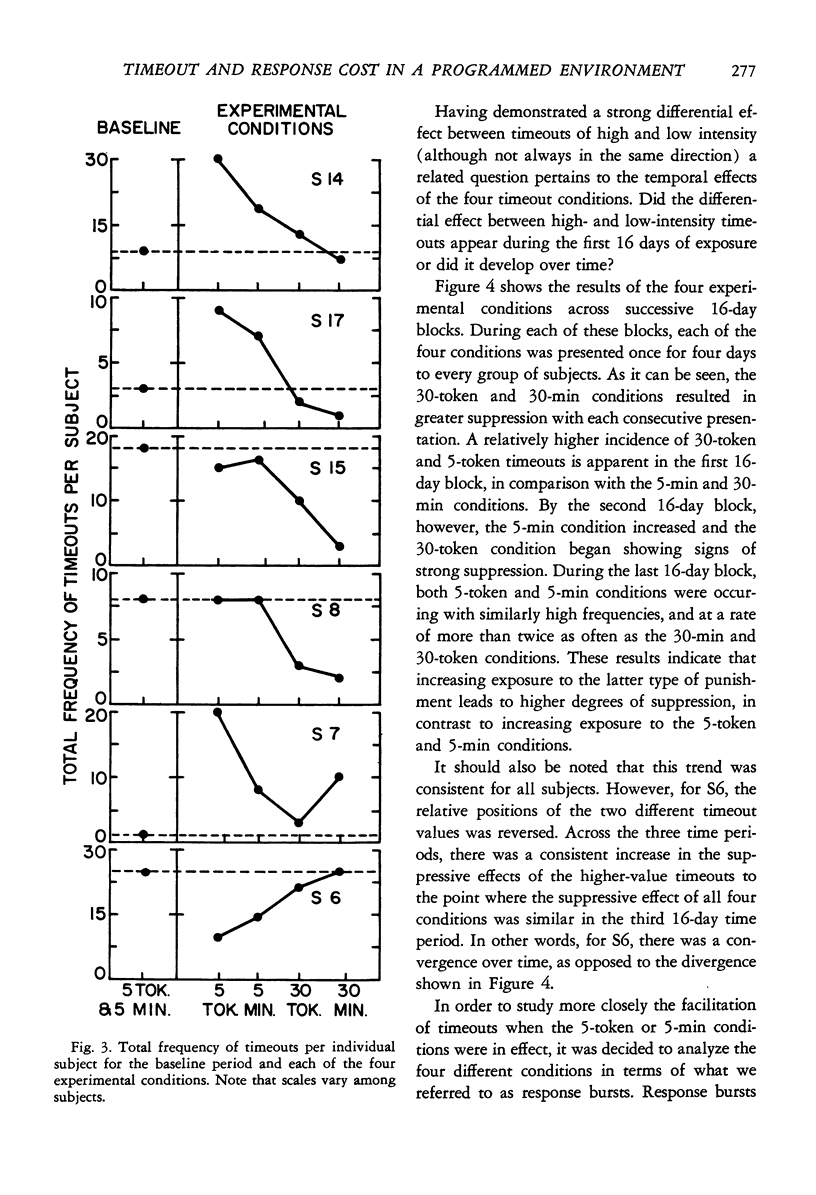
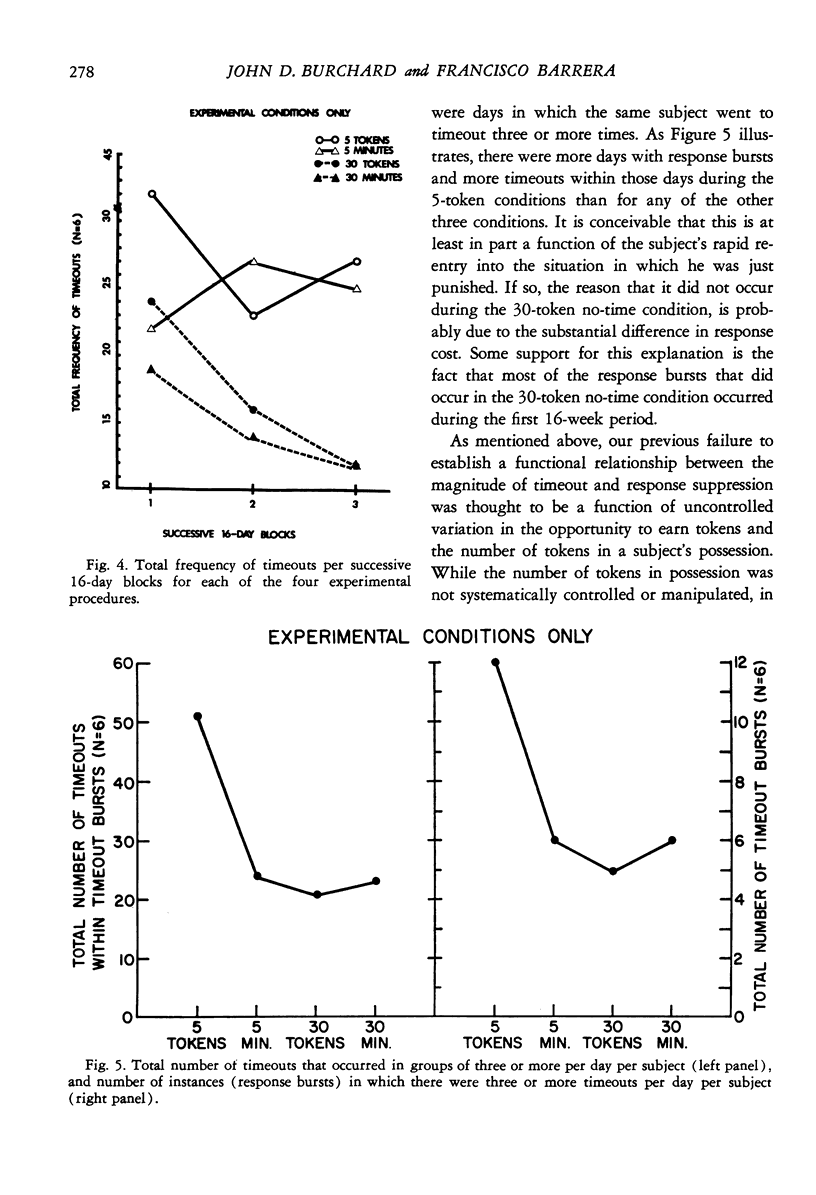
A group of mildly retarded adolescents with high rates of antisocial behavior was exposed to two parameters of timeout and response cost within the context of a programmed environment. For five of the six subjects, the two higher values (30 tokens response cost or 30 min timeout) were significantly more suppressive than the lower values (five tokens or 5 min). For the one remaining subject, there was a strong relationship in the opposite direction. Also, the timeout and response cost of higher value became increasingly more suppressive over time, whereas those of lower value did not. There were few appreciable differences between the timeout and response cost of similar magnitude. A discussion of these results is presented in support of the notion that the functional aversiveness of timeouts (and response costs) appears to be critically dependent upon interactions with the environmental conditions in which they are implemented and the reinforcement histories of the subjects.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURCHARD J., TYLER V., Jr THE MODIFICATION OF DELIQUENT BEHAVIOR THROUGH OPERANT CONDITIONING. Behav Res Ther. 1965 Apr;3:245–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(65)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton E. S., Guess D., Garcia E., Baer D. M. Improvement of retardates' mealtime behaviors by timeout procedures using multiple baseline techniques. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Summer;3(2):77–84. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., APPEL J. B. Punishment of S delta responding in matching to sample by time out from positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:45–56. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H., AYLLON T. Elimination of behavior of mental patients by response-produced extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:407–412. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. Interactions between the discriminative and aversive properties of punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:229–234. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman A., Baron A. Suppression of behavior by timeout punishment when suppression results in loss of positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):595–607. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitenberg H. Is time-out from positive reinforcement an aversive event? A review of the experimental evidence. Psychol Bull. 1965 Dec;64(6):428–441. doi: 10.1037/h0022657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan D. E. A comparison of the punishing effects of response-produced shock and response-produced time out. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):439–449. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L. V. Application of timeout from positive reinforcement for increasing the efficiency of speech training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):199–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T., Wolf M. Establishing functional speech in echolalic children. Behav Res Ther. 1967 May;5(2):73–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(67)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sailor W., Guess D., Rutherford G., Baer D. M. Control of tantrum behavior by operant techniques during experimental verbal training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):237–243. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel G. M., Lenske J., Broen P. Suppression of normal speech disfluencies through response cost. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Winter;2(4):265–276. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. Some effects of response cost upon human operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:201–208. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., FERSTER C. B. Intermittent punishment of Sdelta responding in matching to sample. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:349–356. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


