Abstract
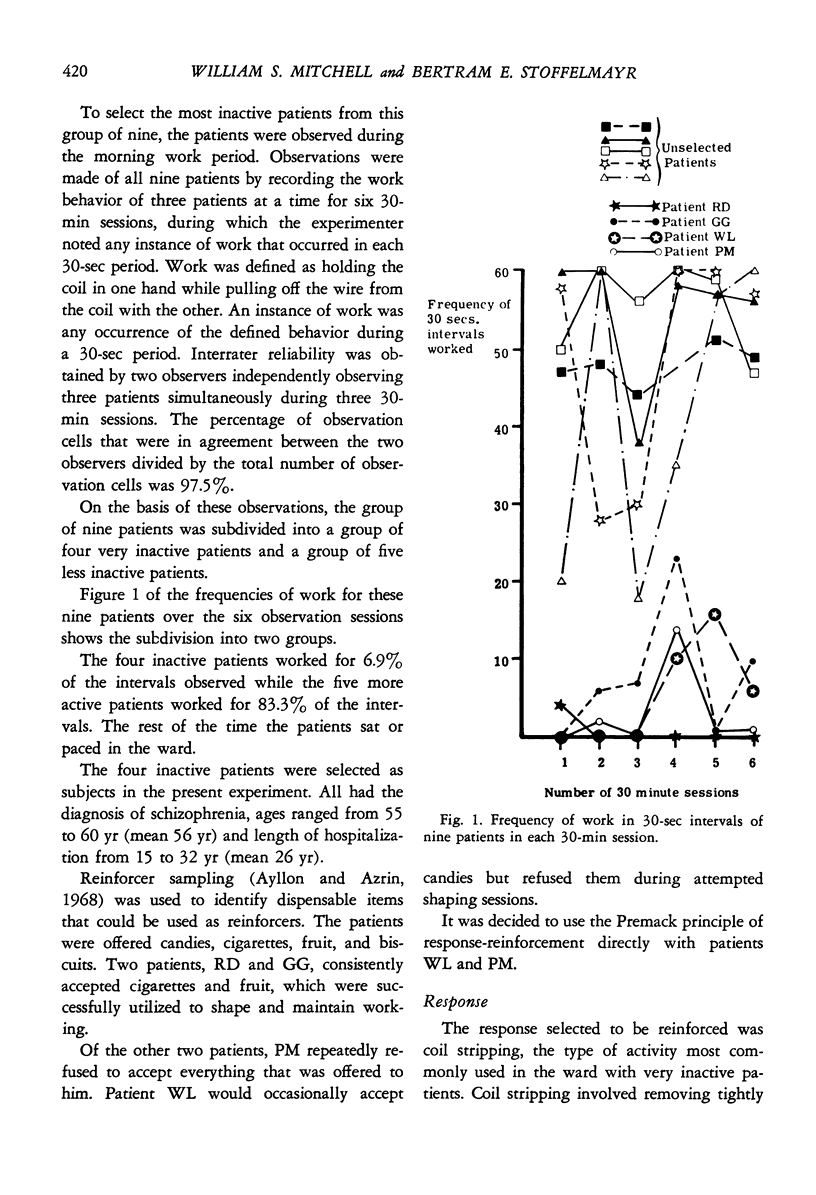
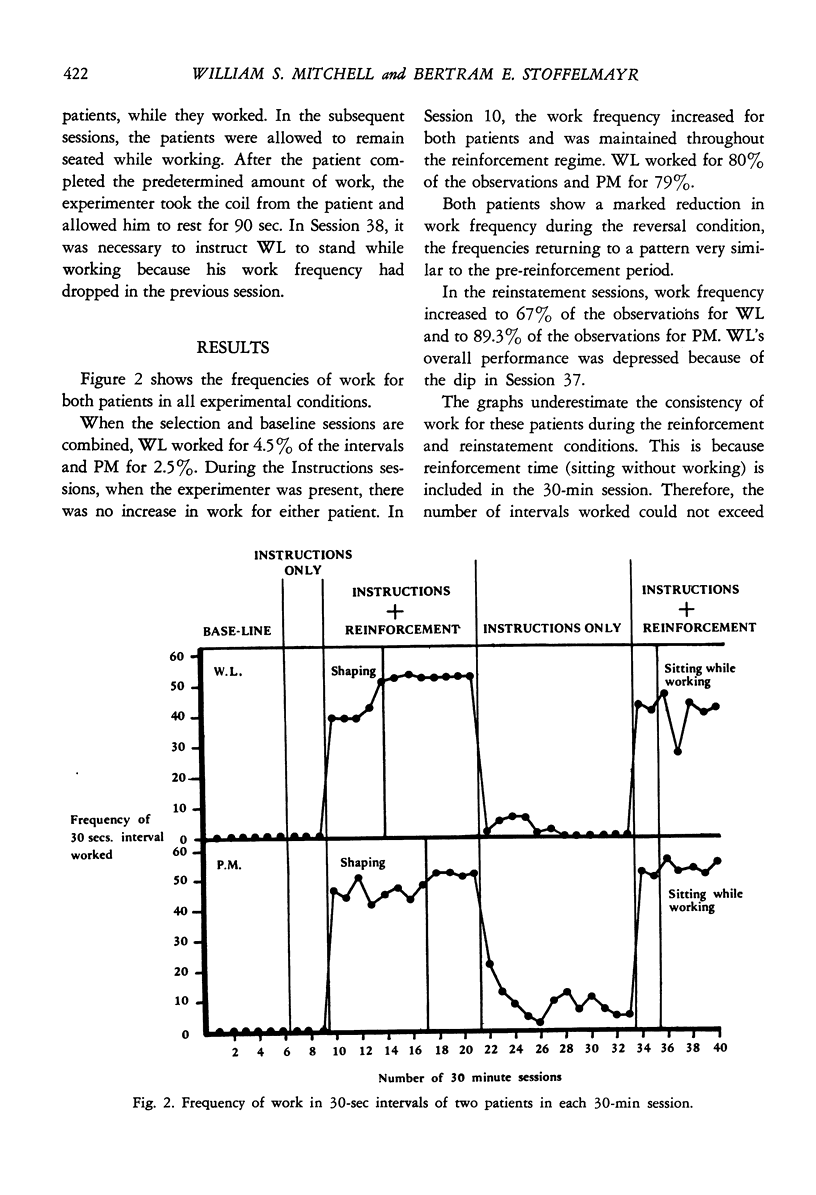
The four most inactive schizophrenic patients were selected by an observational technique from a ward of severely ill chronic patients. Of the four, two patients repeatedly refused to accept any dispensable rewards. Applying Premack's principle of reinforcement, consistent work behavior was shaped and maintained, using sitting as the reinforcer. The results indicate that the strict application of Premack's principle may have considerable therapeutic potential for those patients who, by refusing all tangible rewards, fail to respond to a reinforcement regime.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atthowe J. M., Jr, Krasner L. Preliminary report on the application of contingent reinforcement procedures (token economy) on a "chronic" psychiatric ward. J Abnorm Psychol. 1968 Feb;73(1):37–43. doi: 10.1037/h0025439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayllon T., Azrin N. H. The measurement and reinforcement of behavior of psychotics. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Nov;8(6):357–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSS A. H., LANG P. J. PSYCHOLOGICAL DEFICIT IN SCHIZOPHRENIA: I. AFFECT, REINFORCEMENT, AND CONCEPT ATTAINMENT. J Abnorm Psychol. 1965 Feb;70:2–24. doi: 10.1037/h0021685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinder B. J., Freeman D. M., Stunkard A. J. Behavior therapy of anorexia nervosa: effectiveness of activity as a reinforcer of weight gain. Am J Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;126(8):1093–1098. doi: 10.1176/ajp.126.8.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMME L. E., DEBACA P. C., DEVINE J. V., STEINHORST R., RICKERT E. J. USE OF THE PREMACK PRINCIPLE IN CONTROLLING THE BEHAVIOR OF NURSERY SCHOOL CHILDREN. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:544–544. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. E., Garlington W. K. Weekly variations in performance on a token economy psychiatric ward. Behav Res Ther. 1968 Nov;6(4):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(68)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREMACK D. Toward empirical behavior laws. I. positive reinforcement. Psychol Rev. 1959 Jul;66(4):219–233. doi: 10.1037/h0040891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer H. H., Martin P. L. Behavioral therapy for "apathy" of hospitalized schizophrenics. Psychol Rep. 1966 Dec;19(3):1147–1158. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1966.19.3f.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler R. C. Management of chronic psychiatric patients by a token reinforcement system. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Spring;3(1):47–55. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


