Abstract
The effect of contingent nonverbal teacher approval on student attentive behavior was examined in a classroom with 12 retarded children. After baseline data were gathered on contingent verbal and nonverbal teacher approval and student attentive behavior, the teacher was instructed to increase her use of contingent nonverbal approval (smiles and physical contact) and to maintain her baseline level of verbal approval. After a reversal phase, the nonverbal approval phase was reinstated. Nonverbal teacher behaviors increased during the experimental phases, whereas verbal teacher approval (alone or in conjunction with nonverbal behaviors) did not increase. Attentive behavior increased for 11 of 12 students during the phases in which contingent nonverbal teacher approval increased. Correlational data suggested that nonverbal teacher approval accounted for behavior change of the students to a greater extent than did changes in the amount of teacher approval per se or in the teacher's use of verbal approval.
Full text
PDF




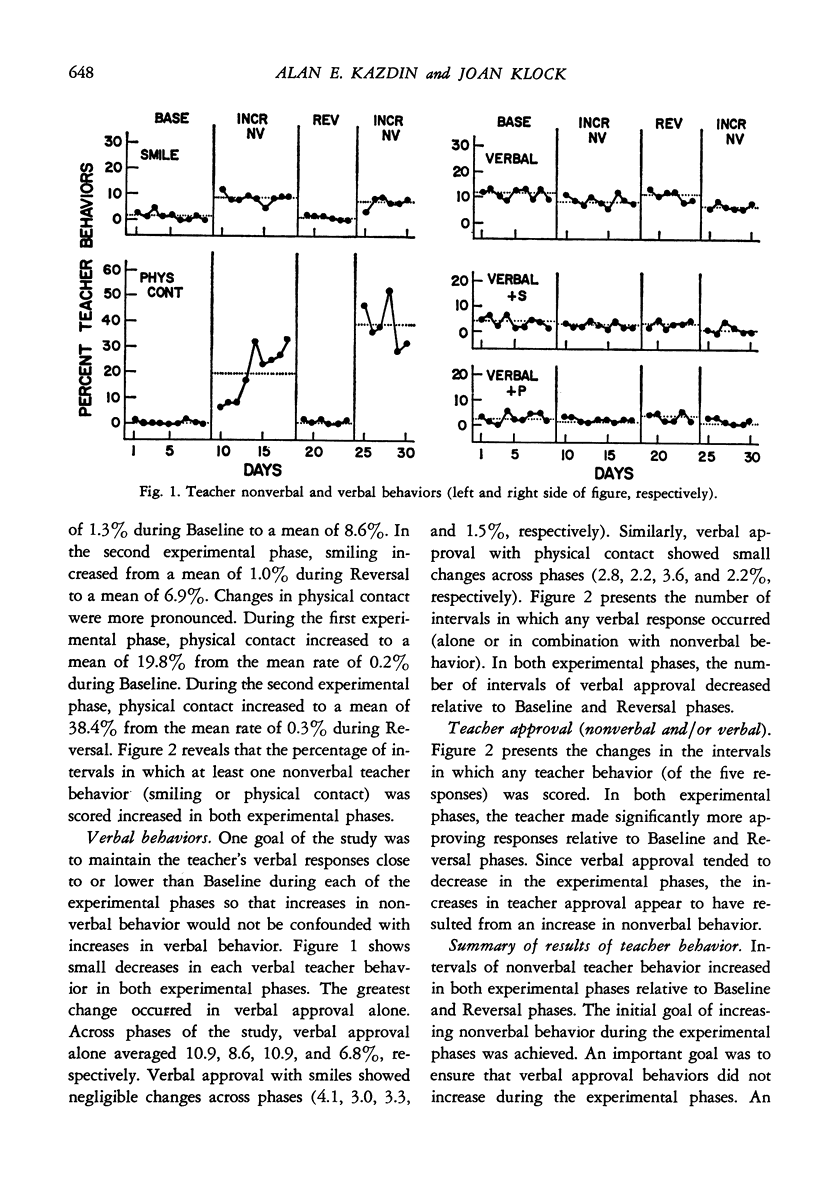
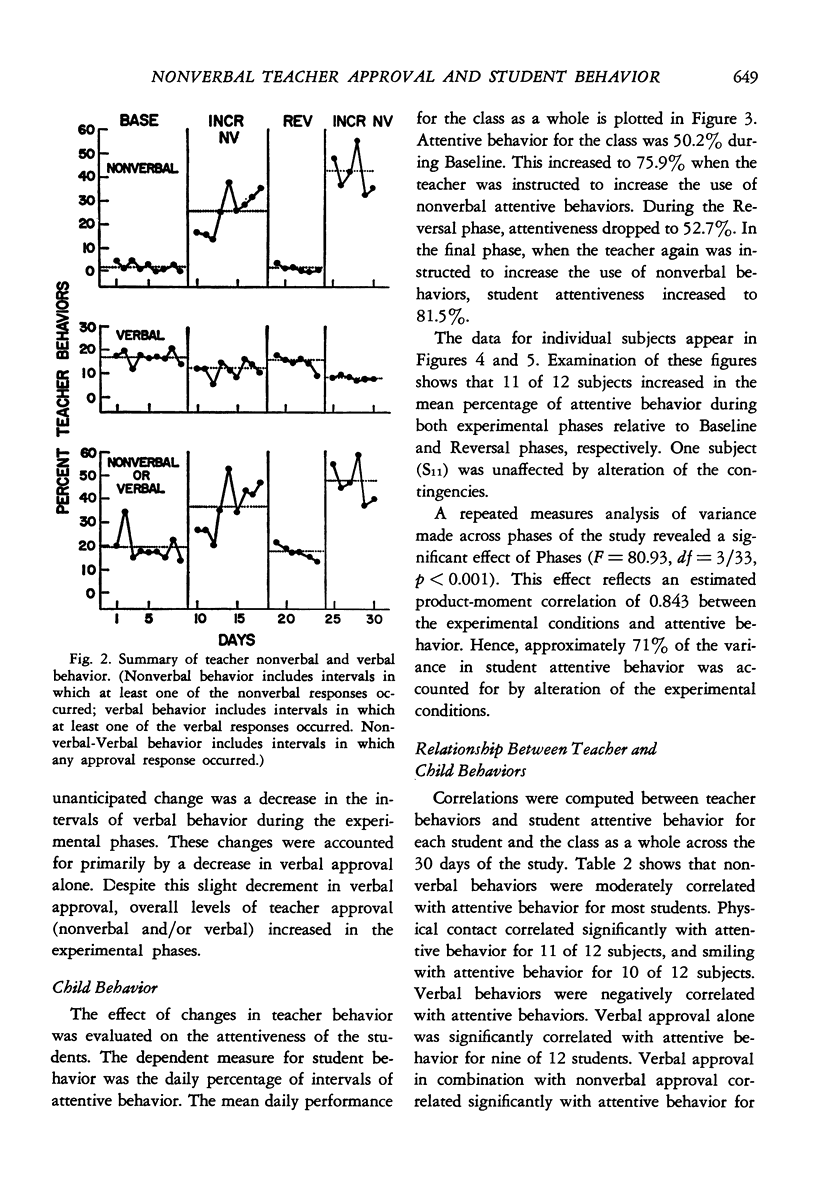
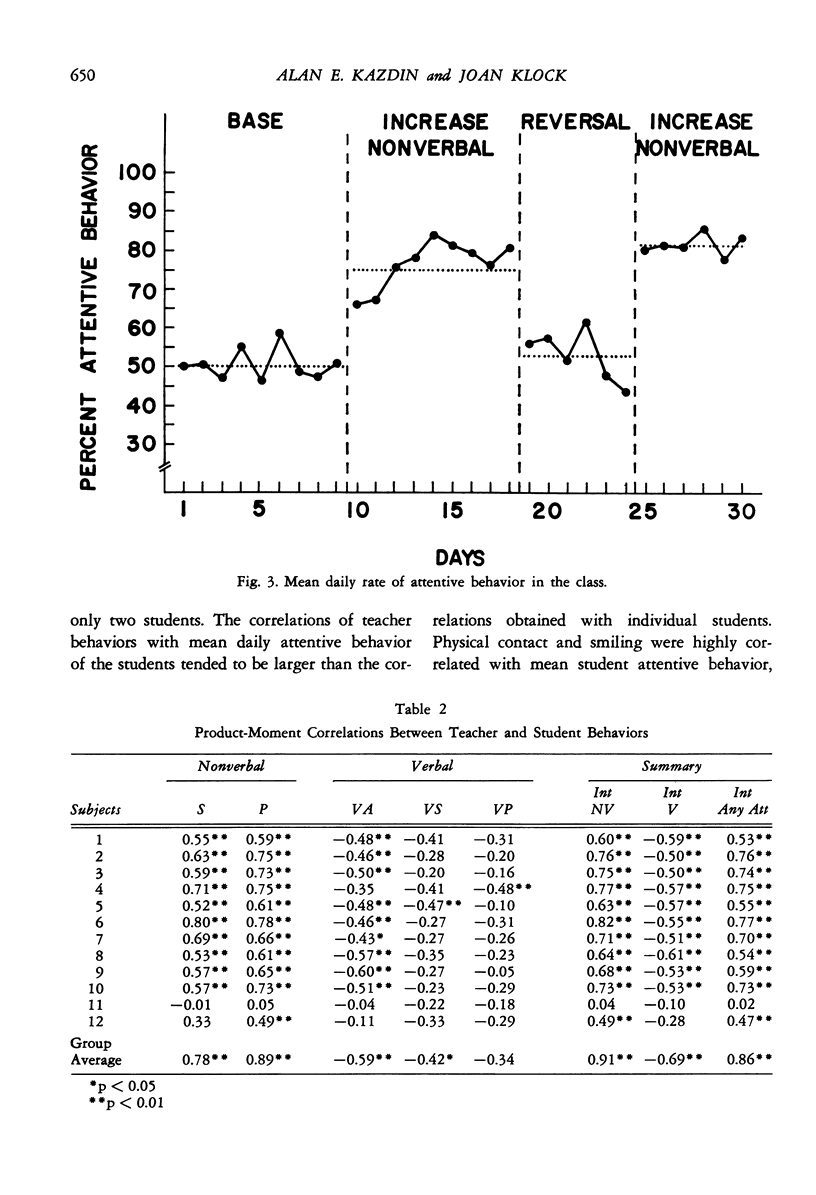
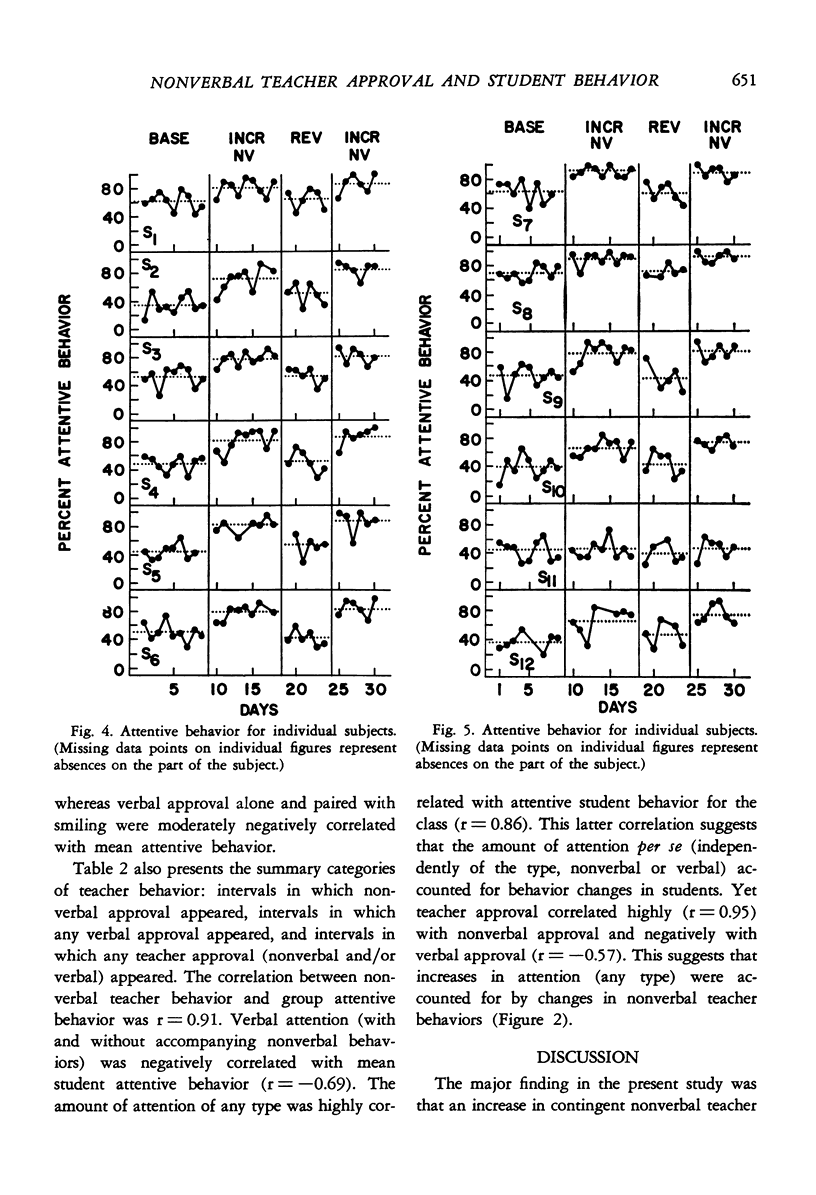



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayes M. A. Behavioral cues of interpersonal warmth. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1972 Oct;39(2):333–339. doi: 10.1037/h0033367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell J. Collateral social development accompanying reinforcement of outdoor play in a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):167–173. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushell D., Wrobel P. A., Michaelis M. L. Applying "group" contingencies to the classroom study behavior of preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):55–61. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. L., Thomson C. L., Baer D. M. The experimental modification of teacher attending behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Summer;3(2):153–157. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. V., Lund D., Jackson D. Effects of teacher attention on study behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. V., Panyan M., Rabon D., Broden M. Instructing beginning teachers in reinforcement procedures which improve classroom control. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):315–322. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasazi J. E., Hasazi S. E. Effects of teacher attention on digit-reversal behavior in an elementary school child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Summer;5(2):157–162. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman K. F., O'leary K. D. Reward, cost, and self-evaluation procedures for disruptive adolescents in a psychiatric hospital school. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Fall;5(3):293–309. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E. Role of instructions and reinforcement in behavior changes in token reinforcement programs. J Educ Psychol. 1973 Feb;64(1):63–71. doi: 10.1037/h0034073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen C. H., Becker W. C., Thomas D. R. Rules, praise, and ignoring: elements of elementary classroom control. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):139–150. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister L. W., Stachowiak J. G., Baer D. M., Conderman L. The application of operant conditioning techniques in a secondary school classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Winter;2(4):277–285. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer H. H., Martin P. L. Behavioral therapy for "apathy" of hospitalized schizophrenics. Psychol Rep. 1966 Dec;19(3):1147–1158. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1966.19.3f.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte R. C., Hopkins B. L. The effects of teacher attention on following instructions in a kindergarten class. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Summer;3(2):117–122. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. R., Becker W. C., Armstrong M. Production and elimination of disruptive classroom behavior by systematically varying teacher's behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):35–45. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G. Setting generality: some specific and general effects of child behavior therapy. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Winter;2(4):239–246. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. H., Baker B. L. Reinforcement therapy in the classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):323–328. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasik B. H., Senn K., Welch R. H., Cooper B. R. Behavior modification with culturally deprived school children: two case studies. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):181–194. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


