Abstract
Mental hospital patients in a motivating ward environment were using the available reinforcers less than was desired. A procedure for increasing the frequency of using reinforcers was developed: all patients were required to engage in the reinforcing event each time it was available but the duration of this required participation was limited so that the event was merely sampled. The effect of this required sampling was experimentally evaluated for three different reinforcers: going for a walk, watching a movie, and attending a music session. More patients used each of the three reinforcers and to a greater extent when the sampling procedure was used. Participation was increased even for those patients who had already been using the reinforcers, demonstrating that the technique did more than provide simple familiarization. Some familiarization was involved since the participation was slightly increased even after the sampling procedure was discontinued. The technique appears to be especially applicable when reinforcers are being delivered infrequently.
Full text
PDF

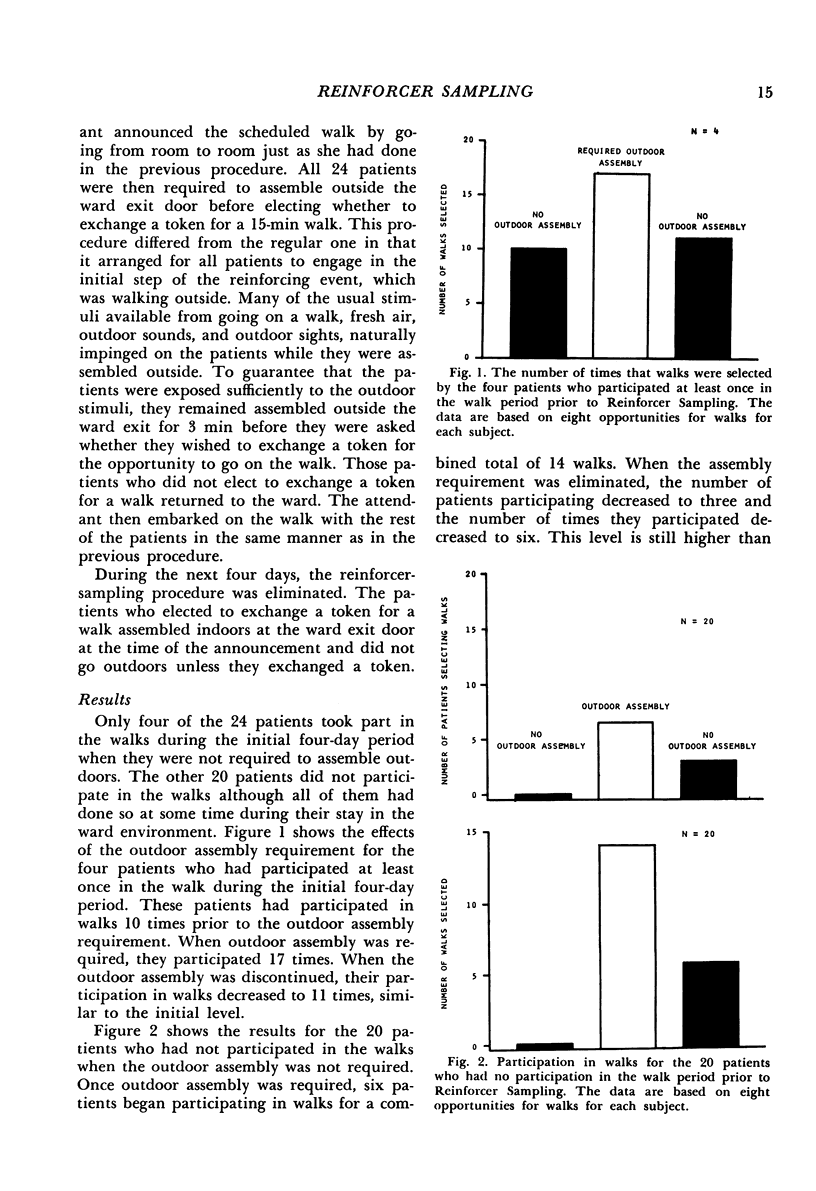


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayllon T., Azrin N. H. The measurement and reinforcement of behavior of psychotics. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Nov;8(6):357–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT B. H. Reduction in rate of multiple tics by free operant conditioning methods. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1962 Sep;135:187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijou S. W., Orlando R. Rapid development of multiple-schedule performances with retarded children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4(1):7–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHINSON R. R., AZRIN N. H. Conditioning of mental-hospital patients to fixed-ratio schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:87–95. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS W., THOMAS J., GOLDIAMOND I. Application of operant conditioning to reinstate verbal behavior in psychotics. J Speech Hear Disord. 1960 Feb;25:8–12. doi: 10.1044/jshd.2501.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Berberich J. P., Perloff B. F., Schaeffer B. Acquisition of imitative speech by schizophrenic children. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T., Wolf M. Establishing functional speech in echolalic children. Behav Res Ther. 1967 May;5(2):73–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(67)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAATS A. W., FINLEY J. R., MINKE K. A., WOLF M. REINFORCEMENT VARIABLES IN THE CONTROL OF UNIT READING RESPONSES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:139–149. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


