Abstract
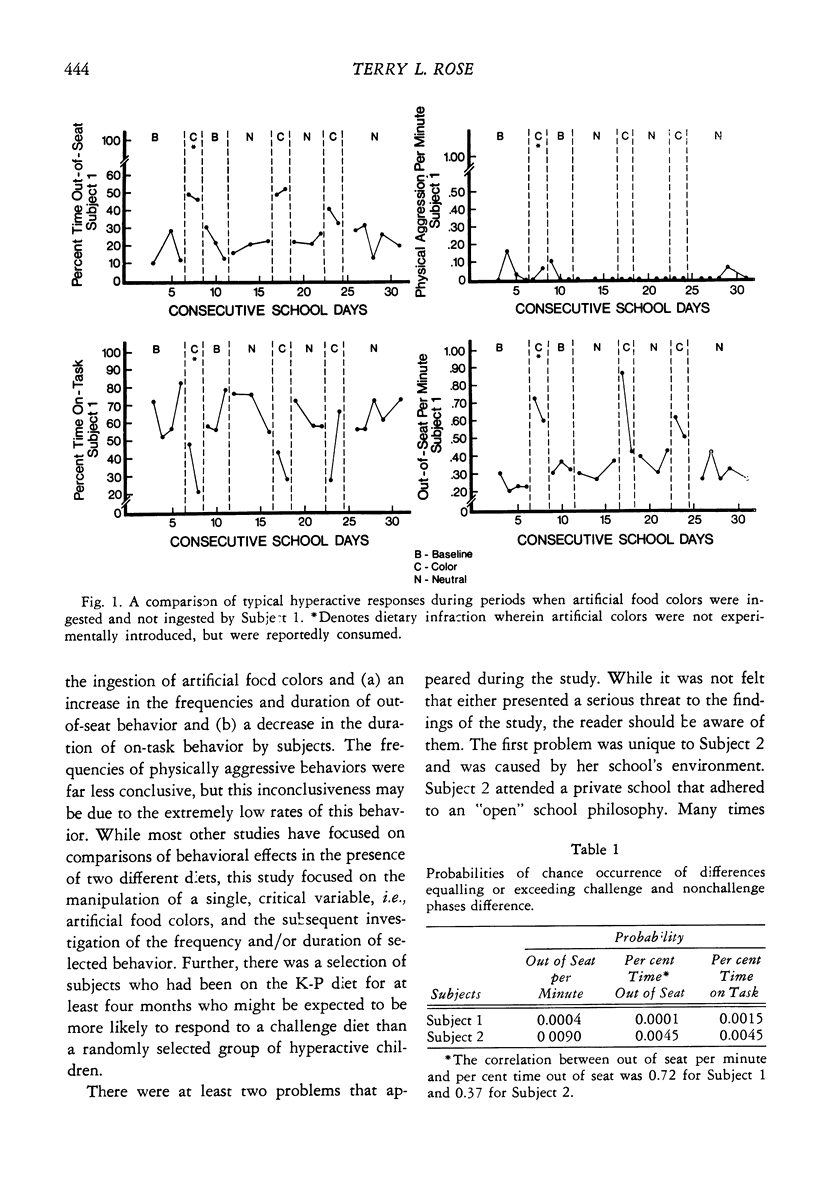
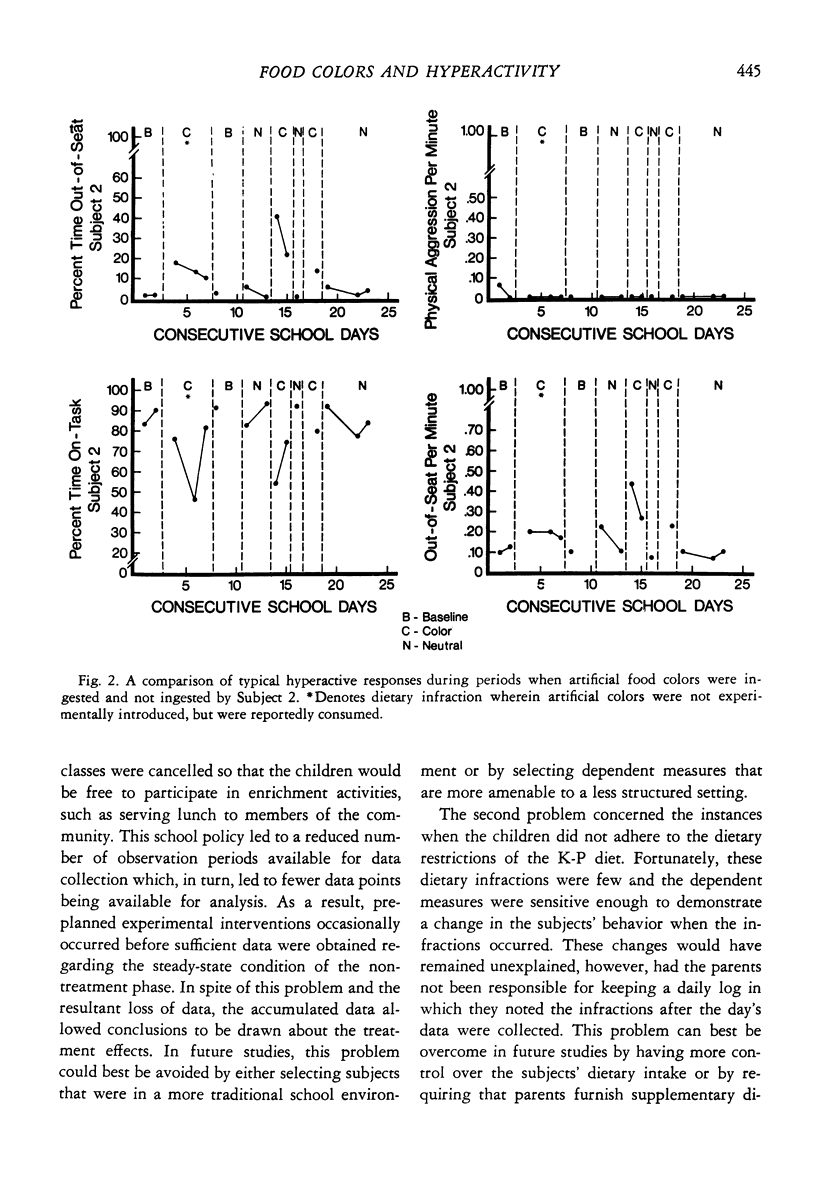
The presence of a functional relationship between the ingestion of artificial food colors and an increase in the frequency and/or duration of selected behaviors that are representative of the hyperactive behavior syndrome was experimentally investigated. Two eight-year-old females, who had been on the Feingold K-P diet for a minimum of 11 months, were the subjects studied. The experimental design was a variation of the BAB design, with double-blind conditions. This design allowed an experimental analysis of the placebo phases as well as challenge phases. Data were obtained by trained observers on Out of Seat, On Task, and Physically Aggressive behaviors, as they occurred in the subjects' regular class setting. Results indicated (a) the existence of a functional relationship between the ingestion of artificial food colors and an increase in both the duration and frequency of hyperactive behaviors, (b) the absence of a placebo effect, and (c) differential sensitivity of the dependent variables to the challenge effects.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conners C. K., Goyette C. H., Southwick D. A., Lees J. M., Andrulonis P. A. Food additives and hyperkinesis: a controlled double-blind experiment. Pediatrics. 1976 Aug;58(2):154–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. S., Woodhill J. M. The Feingold dietary treatment of the hyperkinetic syndrome. Med J Aust. 1976 Jul 17;2(3):85-8, 90. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb134412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diet and hyperactivity: any connection? Nutr Rev. 1976 May;34(5):151–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1976.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubey D. R. Organic factors in hyperkinesis: a critical evaluation. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1976 Apr;46(2):353–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1976.tb00934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold B. F. Hyperkinesis and learning disabilities linked to artificial food flavors and colors. Am J Nurs. 1975 May;75(5):797–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOBEL M. Psychopharmacology for the hyperkinetic child. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1962 Mar;6:198–202. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1962.01710210014002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. K. Hyperactivity and learning disorders: review and speculation. Except Child. 1971 Oct;38(2):101–109. doi: 10.1177/001440297103800201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUFER M. W., DENHOFF E. Hyperkinetic behavior syndrome in children. J Pediatr. 1957 Apr;50(4):463–474. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. D., Liden C. B. Food for inefficient thought. Pediatrics. 1976 Aug;58(2):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwit S. J., Stenner A. J. Hyperkinesis: delineation of two patterns. Except Child. 1972 Jan;38(5):401–406. doi: 10.1177/001440297203800506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Rapoport J. L., Quinn P. O. Food additives and hyperactivity. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1975 Oct;14(10):956–959. doi: 10.1177/000992287501401014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repp A. C., Deitz D. E., Boles S. M., Deitz S. M., Repp C. F. Differences among common methods for calculating interobserver agreement. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):109–113. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman L. K. Allergy testing, psychological assessment and dietary treatment of the hyperactive child syndrome. Med J Aust. 1976 Aug 14;2(7):248–251. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1976.tb130144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine J. J. Symptom alleviation in the hyperactive child by dietary modification: a report of two cases. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1976 Oct;46(4):637–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1976.tb00962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


