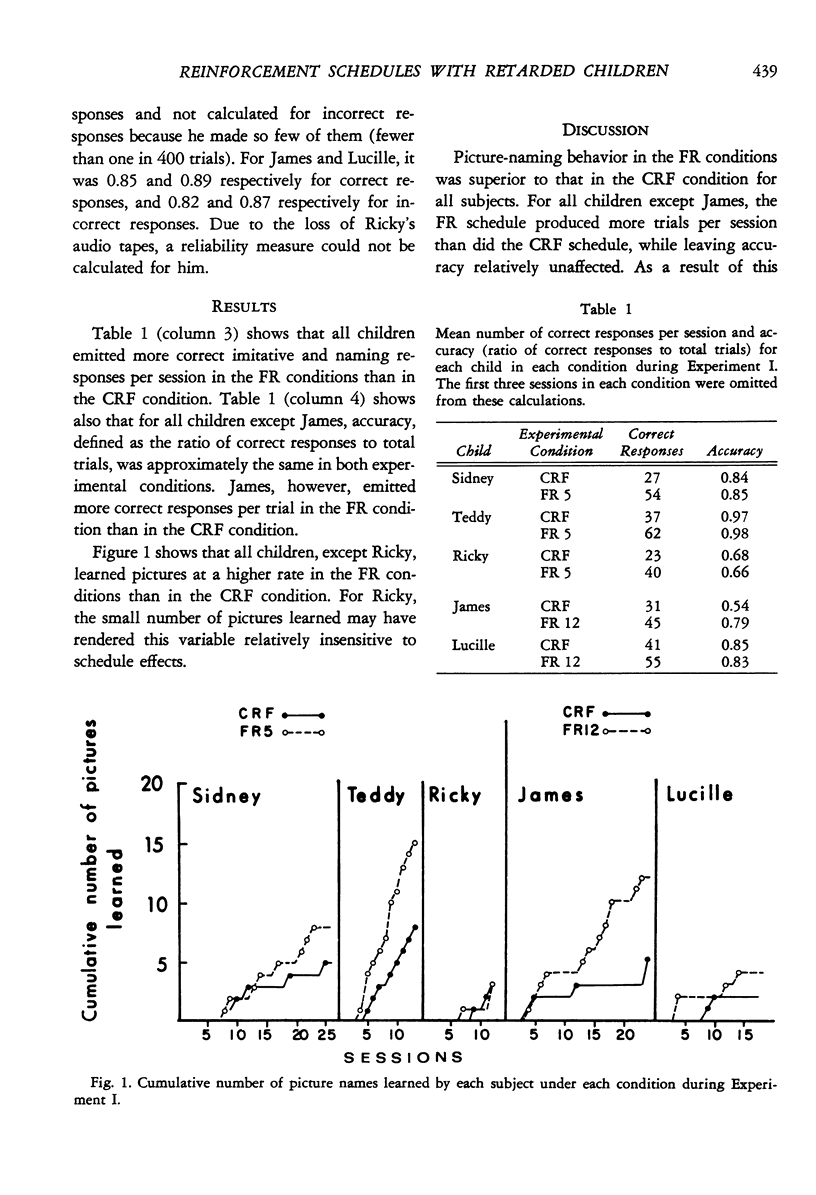
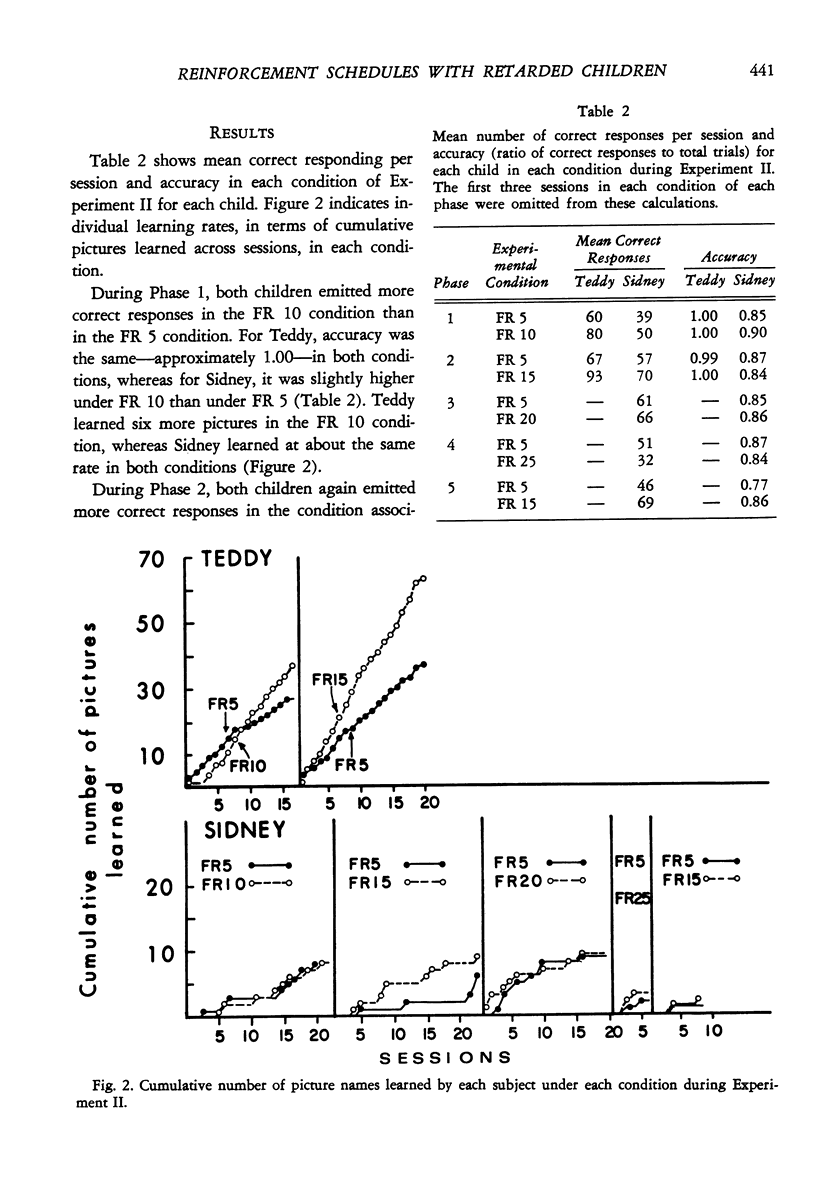
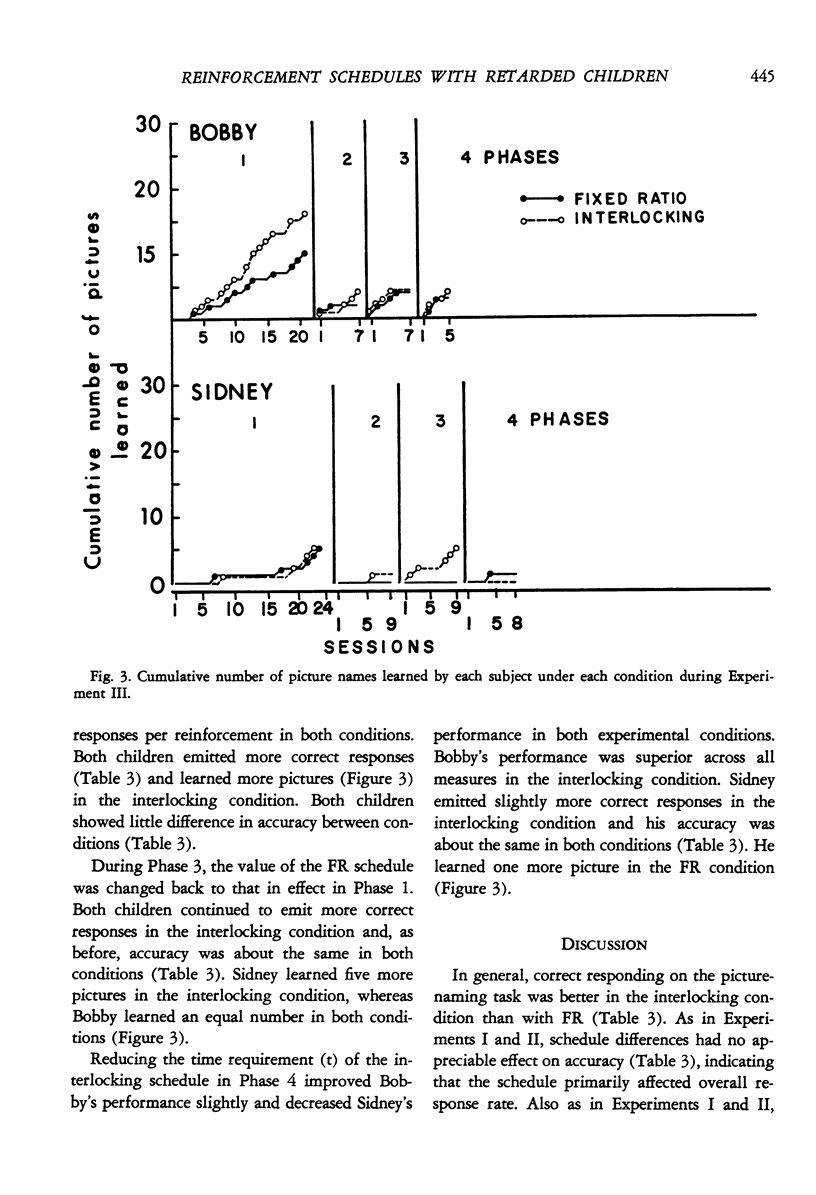
Abstract
The effects of several different schedules of primary reinforcement were compared in a picture-naming task with retarded children. In Experiment I, number of correct responses and learning rate were higher under fixed-ratio schedules than under continuous reinforcement. In Experiment II, number of correct responses and learning rate tended to be greater under in intermediate than under low or high fixed-ratio schedules. In Experiment III, number of correct responses was higher under interlocking schedules, in which the response requirement increased with time following the previous reinforcement, than under comparable fixed-ratio schedules. Learning rates were generally low and, perhaps because of this, not very different under the two types of schedules in this experiment. Accuracy (i.e., proportion of trials on which correct responses occurred) was typically high and insensitive to variations in schedule and schedule parameter throughout each experiment.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton E. S. Inappropriate speech in a severely retarded child: a case study in language conditioning and generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Winter;3(4):299–307. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. A., Osborne J. G. Fixed-ratio and fixed-interval schedule control of matching-to-sample errors by children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS N. R., BARNETT C. D., PRYER M. W. Operant behavior in mental defectives: exploratory studies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jan;3:63–69. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B. Intermittent reinforcement of matching to sample in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:259–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton M., Lyon D. O. The post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):131–134. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferster C. B. Intermittent Reinforcement of a Complex Response in a Chimpanzee. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):163–165. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E., Guess D., Byrnes J. Development of syntax in a retarded girl using procedures of imitation, reinforcement, and modelling. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Summer;6(2):299–310. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E. The training and generalization of a conversational speech form in nonverbal retardates. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Spring;7(1):137–149. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guess D., Baer D. M. An analysis of individual differences in generalization between receptive and productive language in retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Summer;6(2):311–329. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kircher A. S., Pear J. J., Martin G. L. Shock as punishment in a picture-naming task with retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Fall;4(3):227–233. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. R., Hammack J. T., May F., Campbell B. J. Intermittent reinforcement of operant behavior in children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Oct;1(4):315–339. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. L., England G., Kaprowy E., Kilgour K., Pilek V. Operant conditioning of kindergarten-class behavior in autistic children. Behav Res Ther. 1968 Aug;6(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(68)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L. V. Application of timeout from positive reinforcement for increasing the efficiency of speech training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):199–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVIN J. A., CUMMING W. W., BERRYMAN T. Ratio reinforcement of matching behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:149–154. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLANDO R., BIJOU S. W. Single and multiple schedules of reinforcement in developmentally retarded children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Oct;3:339–348. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sailor W., Taman T. Stimulus factors in the training of prepositional usage in three autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Summer;5(2):183–190. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardosz S., Baer D. M. Training two severely retarded adolescents to ask questions. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):655–661. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman T. L., Zakaras M., Chardos S. Effects of reinforcement and guidance procedures on instruction-following behavior of severely retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Winter;4(4):283–290. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


