Abstract
A stable L-form of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (Shope) was isolated from primary pig kidney cell tissue cultures which had been inoculated 28 days previously with glycine induced spheroplasts of this organism.
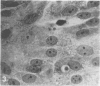
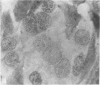
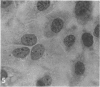
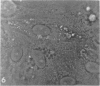
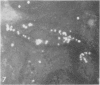
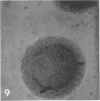
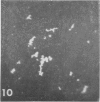
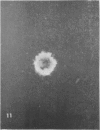
H. pleuropneumoniae was definitely cytopathic in primary pig kidney cell cultures, producing cell rounding, cytoplasmic vacuolation and nuclear enlargement with peripheral condensation of nuclear DNA. By contrast, the effect of spheroplasts was much less distinct, producing only loss of cytoplasmic granularity coincident with apparent loss of some cytoplasmic RNA, and slight nuclear enlargement.
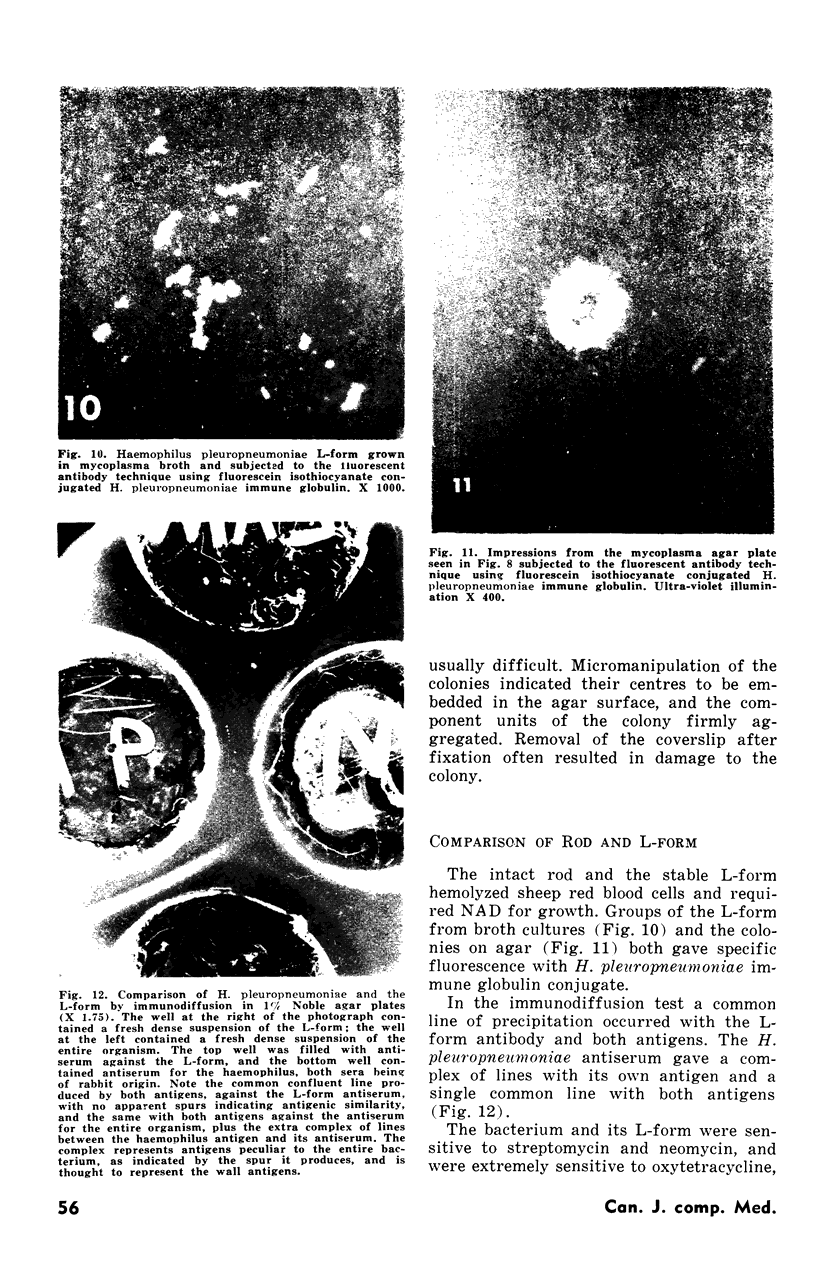
Both the organism and its L-form were shown to be related by cultural methods, antibiotic sensitivity tests, immunofluorescence and immunodiffusion.
The L-form remained stable after 90 serial passages on agar and 45 in broth, each medium being capable of supporting the growth of both forms of the organism.
Full text
PDF


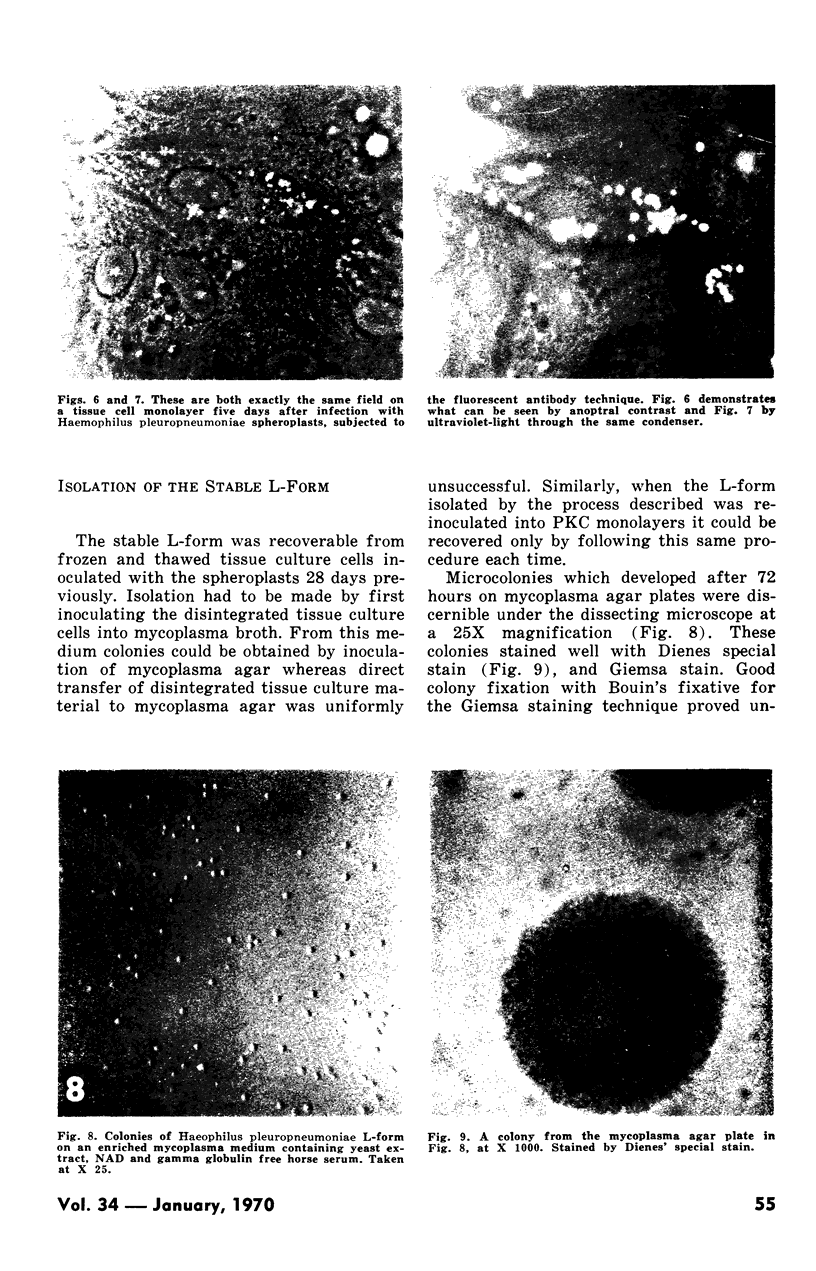


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BISSET K. A., HALE C. M. Complex cellular structure in bacteria. Exp Cell Res. 1953 Dec;5(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(53)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIENES L., ZAMECNIK P. C. Transformation of bacteria into L forms by amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):770–771. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.770-771.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guze L. B., Kalmanson G. M. Persistence of Bacteria in "Protoplast" Form after Apparent Cure of Pyelonephritis in Rats. Science. 1964 Mar 20;143(3612):1340–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3612.1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten B. A., Sulkin S. E. Intracellular production of Brucella L forms . II. Induction and survival of Brucella abortus L forms in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):14–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.14-20.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapinski E. M., Flakas E. D. Induction of L forms of Haemophilus influenzae in culture and their demonstration in human bronchial secretions. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1438–1445. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1438-1445.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay K. A., Abelseth M. K., Vandreumel A. A. Production of an enzootic-like pneumonia in pigs with "protoplasts" of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):359–360. doi: 10.1038/212359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay K. A., Corner A. H., Byrne J. L. Microbial persistence and latent infection. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1967 Oct;31(10):256–259. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E., WHITE D. C., LEIDY G. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. II. STUDIES OF THE PATHOGENICITY OF THE ETIOLOGICAL AGENT, HEMOPHILUS PLEUROPNEUMONIAE. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:369–375. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., LEIDY G., JAMIESON J. D., SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. 3. INTERRELATIONSHIP OF HEMOPHILUS PLEUROPNEUMONIAE TO OTHER SPECIES OF HEMOPHILUS: NUTRITIONAL, METABOLIC, TRANSFORMATION, AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDIES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:1–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]