Abstract
Seven isolates of bluetongue virus with different isolation histories and one isolate of the virus of epizootic hemorrhagic disease of deer were cloned by three consecutive plaquings in L-929 cells. The isolates were categorized on plaque size and margin. Antisera to the bluetongue virus isolates were produced in calves and antiserum to epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus in deer. Plaque reduction neutralization tests were done using the eight isolates and antisera to six of these.
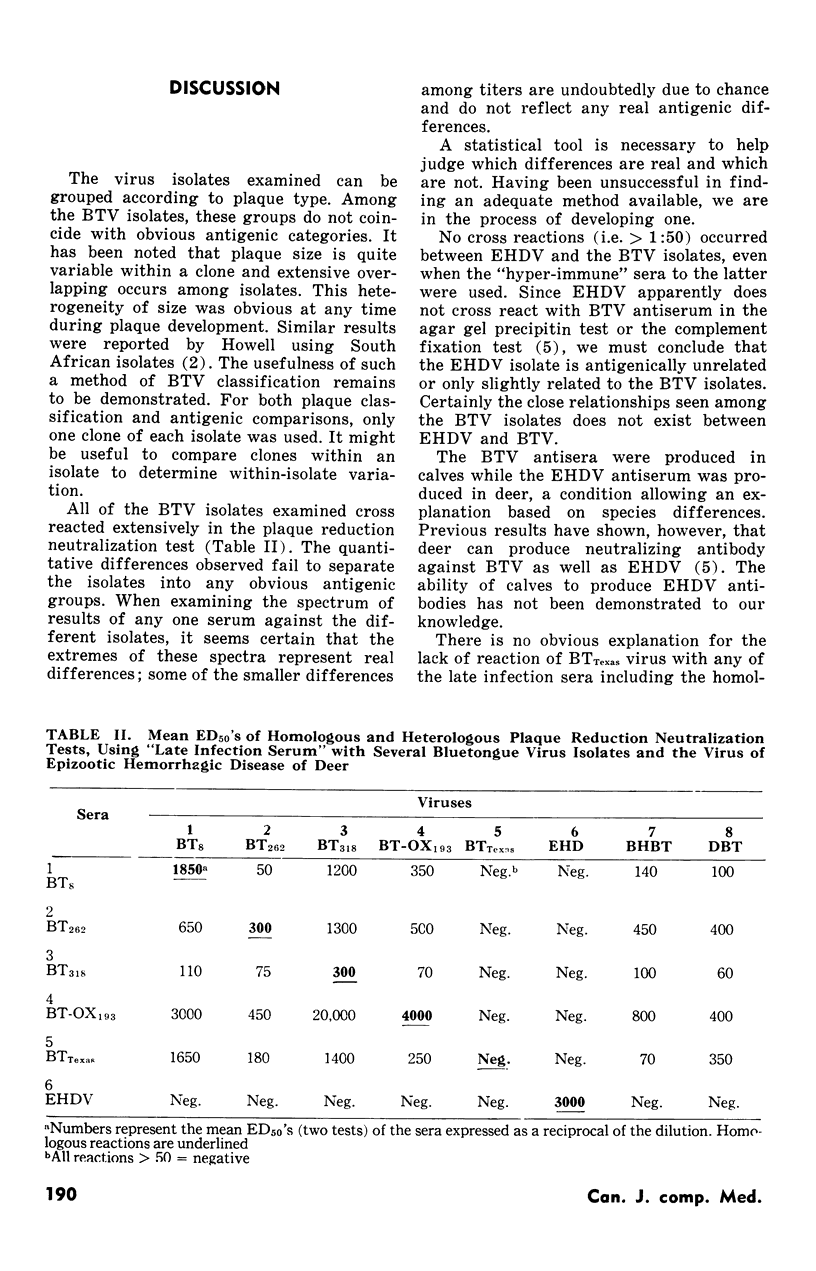
The isolates could be partially categorized on plaque type. In the plaque reduction neutralization test, all of the bluetongue viruses cross reacted and although differences were frequently observed, no obvious antigenic classification was possible. Reactions between the bluetongue viruses and epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus were all within the limits of what is presently considered to be non-specific inhibition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Howell P. G., Verwoerd D. W., Oellermann R. A. Plaque formation by bluetongue virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1967 Dec;34(2):317–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedke A. J., Jochim M. M. Clinical and serologic responses in vaccinated sheep given challenge inoculation with isolates of bluetongue virus. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Apr;29(4):841–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Miller J. A comparison of bluetongue virus and EHD virus: electronmicroscopy and serology. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jan;35(1):22–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Trainer D. O. Bluetongue virus: (1) in pregnant white-tailed deer (2) a plaque reduction neutralization test. J Wildl Dis. 1970 Oct;6(4):384–388. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-6.4.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



