Abstract
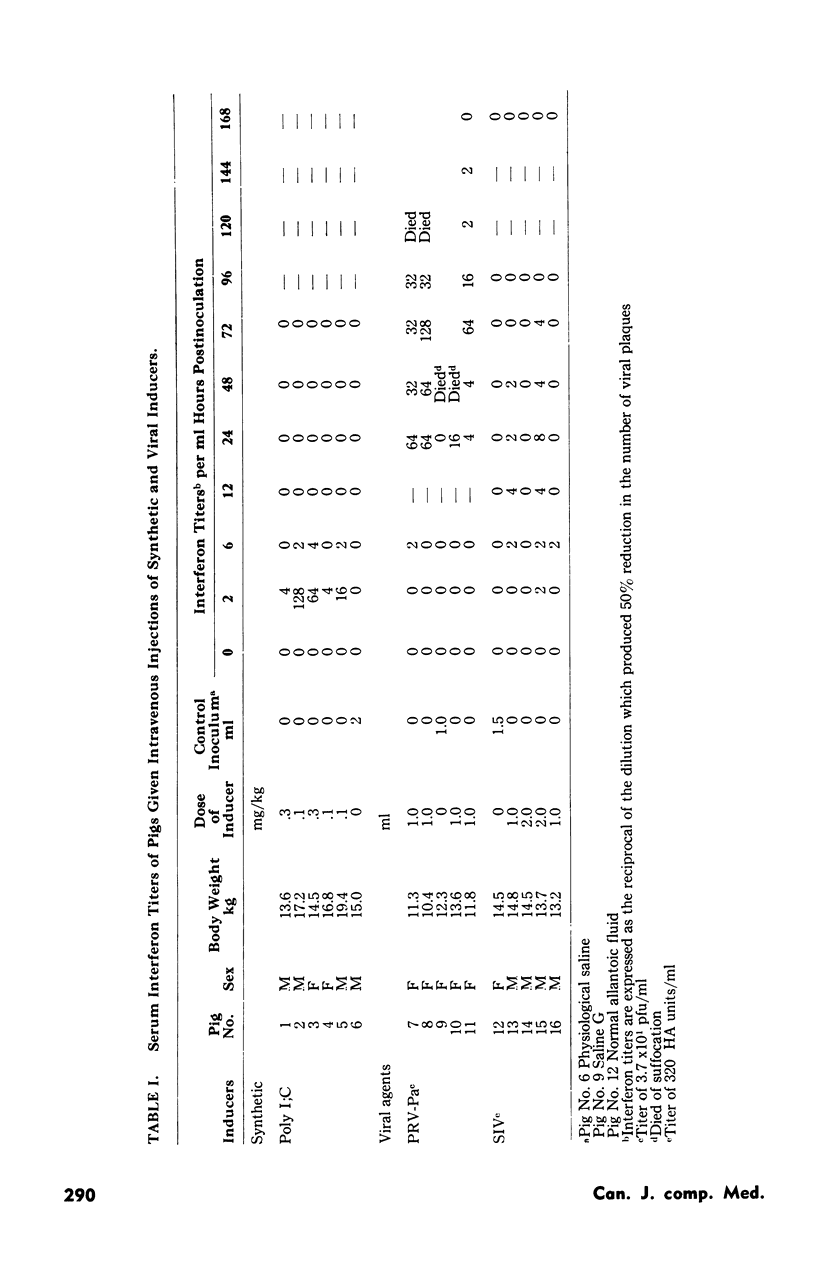
The production of interferon by pigs in response to viral and synthetic inducers was studied. The inducers used included polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid (Poly I:C), swine influenza virus and pseudorabies virus. Following intravenous inoculation of pigs with the inducers, sera were examined for interferon by the plaque-reduction method in porcine kidney (PK15) cell cultures using vesicular stomatitis virus as the challenge inoculum. It was shown that pigs can produce interferon in response to each of these inducers. The pseudorabies virus used in this investigation was found to be a better interferon inducer than the swine influenza virus.
The interferon produced in pigs was identified as an interferon because it was pH stable, non-dialyzable, sensitive to trypsin, non-sedimentable and possessed broad-spectrum antiviral activity as well as host-species specificity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron S. The biological significance of the interferon system. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):84–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., DuBuy H. G., Johnson M. L., Baron S. Kinetics of serum interferon response in mice after single and multiple injections of polyI-poly C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):394–398. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenje P., Postic B. Protection of rabbits against experimental rabies of poly I-poly C. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):171–172. doi: 10.1038/226171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Young C. W., Krakoff I. H., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Induction of interferon in human subjects by poly I:C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1180–1186. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Role of infection in viralinterference. I. Inhibition of lethal infections in chick embryos preinfected with influenza viruses. Arch Intern Med. 1962 Nov;110:653–659. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1962.03620230099014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Interferon: clinical application of molecular biology. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1068–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Prospects for the use of double-stranded ribonucleic acid (poly I:C) inducers in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):196–211. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn R. G., Osweiler G. D., Switzer W. P. Application of the orbital sinus bleeding technique to swine. Lab Anim Care. 1969 Jun;19(3):403–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay H. L., Trown P. W., Brandt J., Forbes M. Pyrogenicity of poly I. poly C in rabbits. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):717–718. doi: 10.1038/223717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Finkelstein M. S. Interferon-stimulating and in vivo antiviral effects of various synthetic anionic polymers. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy J., Merigan T. C. The effect of interferon and interferon inducers on avian influenza. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):545–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenquist B. D. Polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid-induced interferons in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Jan;32(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Scott W. D., Sulkin S. E. Relative sensitivities of viruses to different species of interferon. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):147–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.147-153.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torlone V., Titoli F., Gialletti L. Circulating interferon production in pigs infected with hog cholera virus. Life Sci. 1965 Sep;4(17):1707–1713. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vengris V. E., Maré C. J. Swine interferon. I. Induction in porcine cell cultures with viral and synthetic inducers. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jul;36(3):282–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


