Abstract
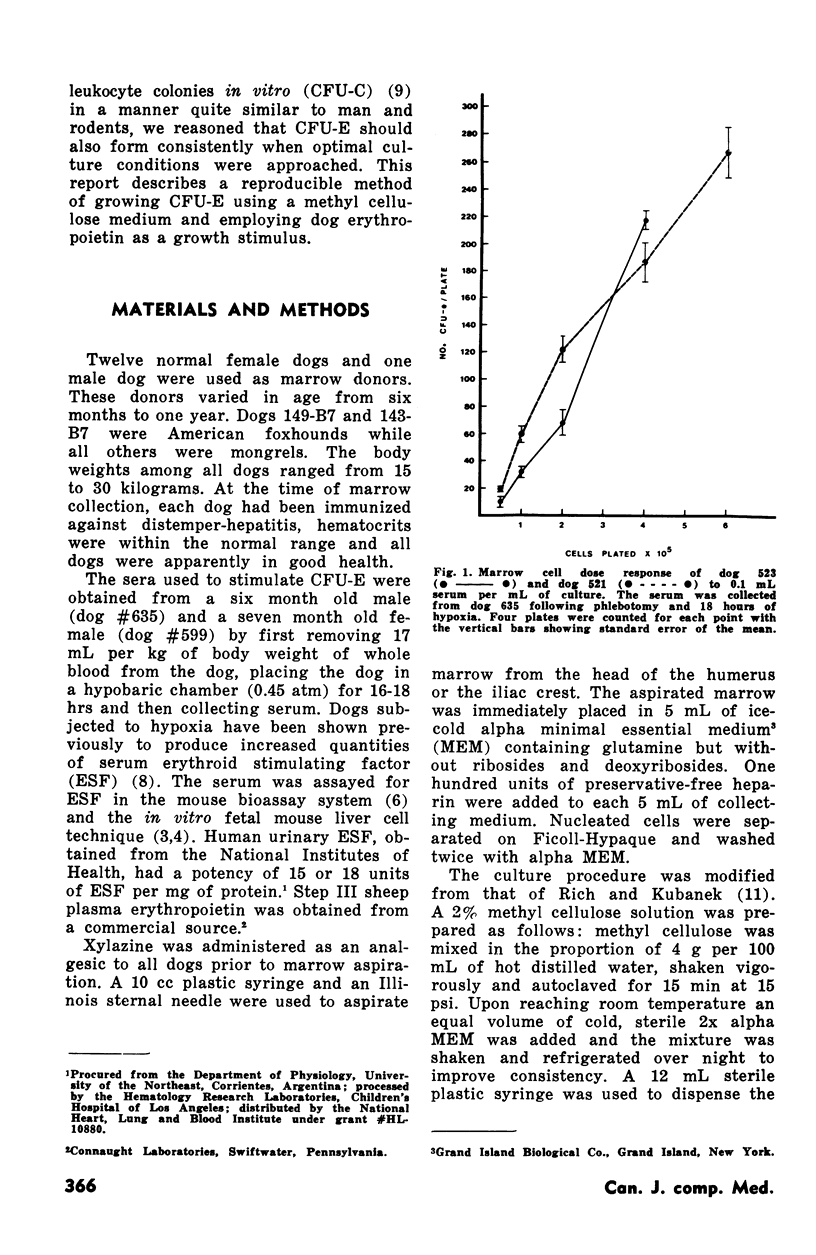
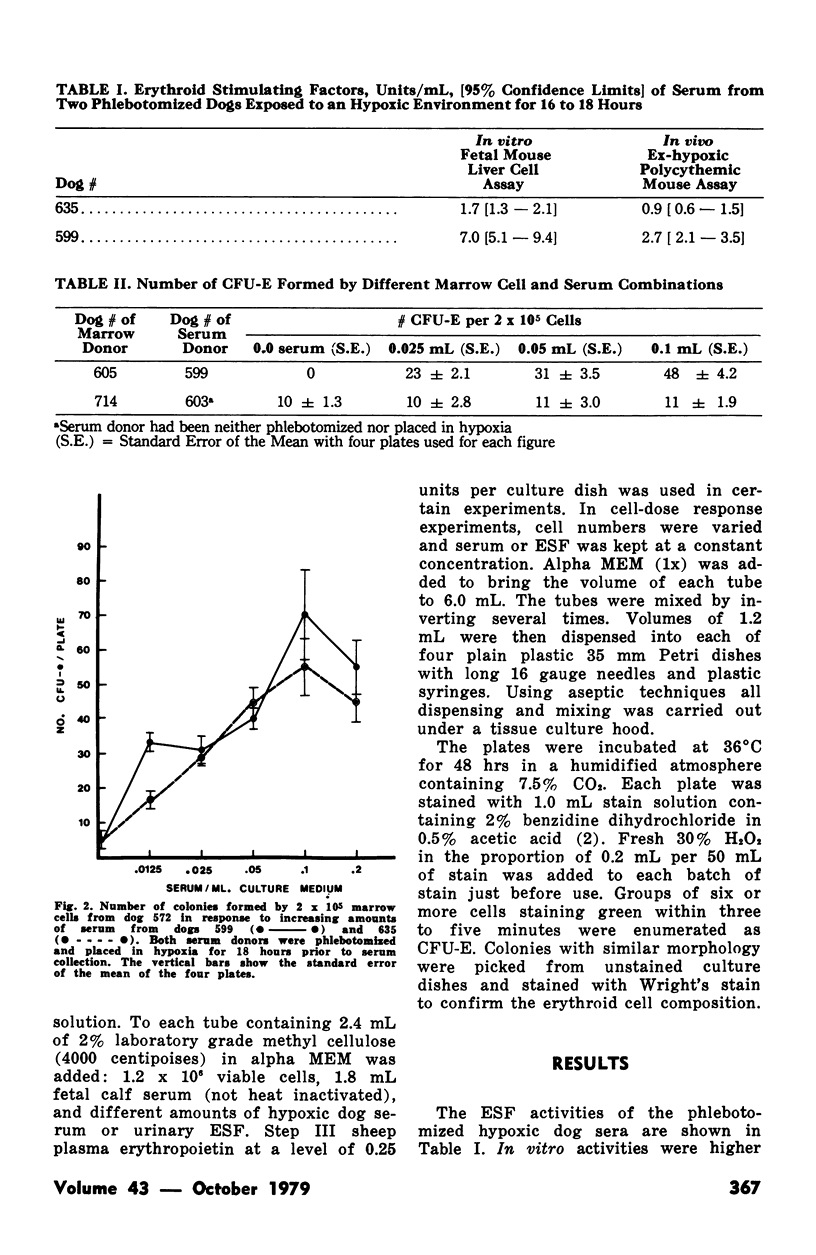
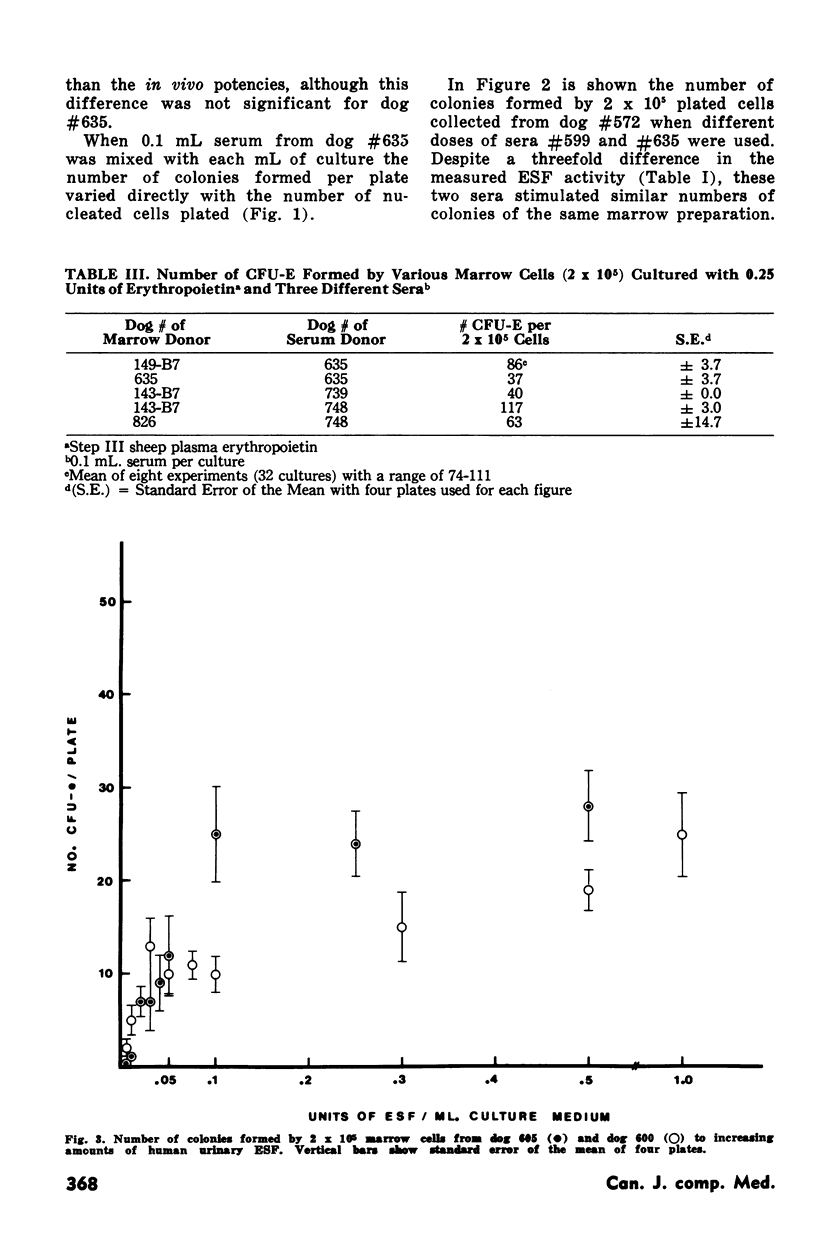
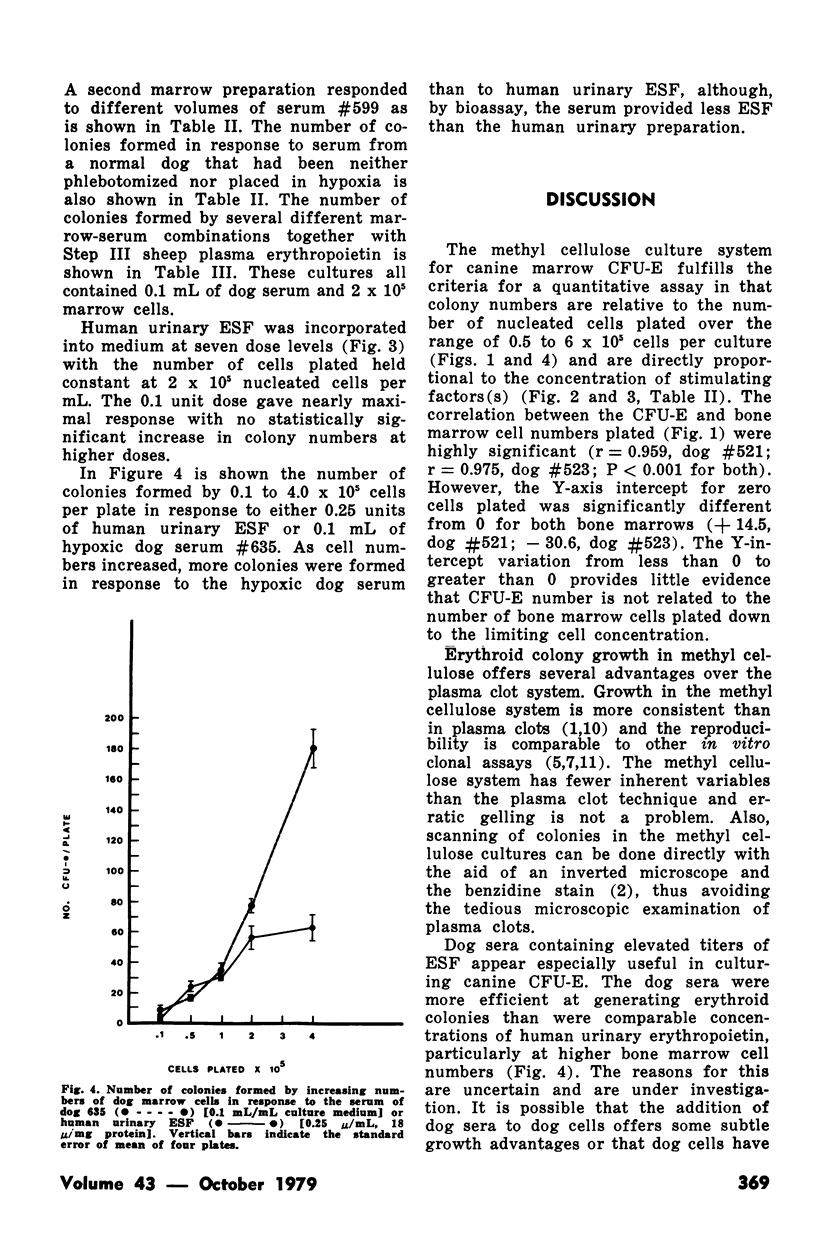
Enriched methyl cellulose media together with either human urinary erythropoietin or serum collected from phlebotomized dogs exposed to hypoxia was used in the study of the erythroid colony forming (CFU-E) capacity of dog marrow. The dog serum erythropoietin was found to be more efficient in stimulating CFU-E than comparable concentrations of human urinary erythropoietin. Numbers of CFU-E were directly related to the culture concentration of the stimulating serum and to the number of cells per plate. Sheep plasma erythropoietin was also found to be effective in stimulating CFU-E growth. The system described is chemically better defined and produced more consistent results than has been reported for the plasma clot method.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Adamson J. W. Modulation of in vitro erythropoiesis: enhancement of erythroid colony growth by cyclic nucleotides. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 May;10(3):289–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1977.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. C., Levy J., Cantor L. N., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. The effect of erythropoietin on colonial growth of erythroid precursor cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1677–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn C. D., Jarvis J. H., Greenman J. M. A quantitative bioassay for erythropoietin using mouse fetal liver cells. Exp Hematol. 1975 Jan;3(1):65–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn C. D., Napier J. A. An evaluation of factors affecting the in vitro bioassay for erythropoietin. Exp Hematol. 1975 Nov;3(6):362–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. Y., Douglas I. D. The effect of peripheral blood contamination on colony yield from human bone marrow aspirates. Exp Hematol. 1977;5(4):274–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki A. T., Lange R. D. A method for the concentration of erythropoietin from human urine. Biochem Med. 1974 May;10(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Sieber F. Erythroid progenitors in mouse bone marrow detected by macroscopic colony formation in culture. Exp Hematol. 1975 Jan;3(1):32–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Lange R. D., Yang T. J., Vodopick H., Jones E. S. Canine cyclic neutropenia: Erythropoietin and platelet cycles after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1975 Feb;45(2):213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Katzenstein A., Marsh J. C. Kinetics of canine hematopoietic colonies grown in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):408–411. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic W. J., Brown J. E., Adamson J. W. The influence of thyroid hormones on in vitro erythropoiesis. Mediation by a receptor with beta adrenergic properties. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):907–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI108845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich I. N., Kubanek B. Erythroid colony formation (CFUe) in fetal liver and adult bone marrow and spleen from the mouse. Blut. 1976 Sep;33(3):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00995998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


