Abstract
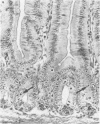
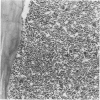
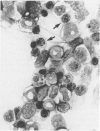
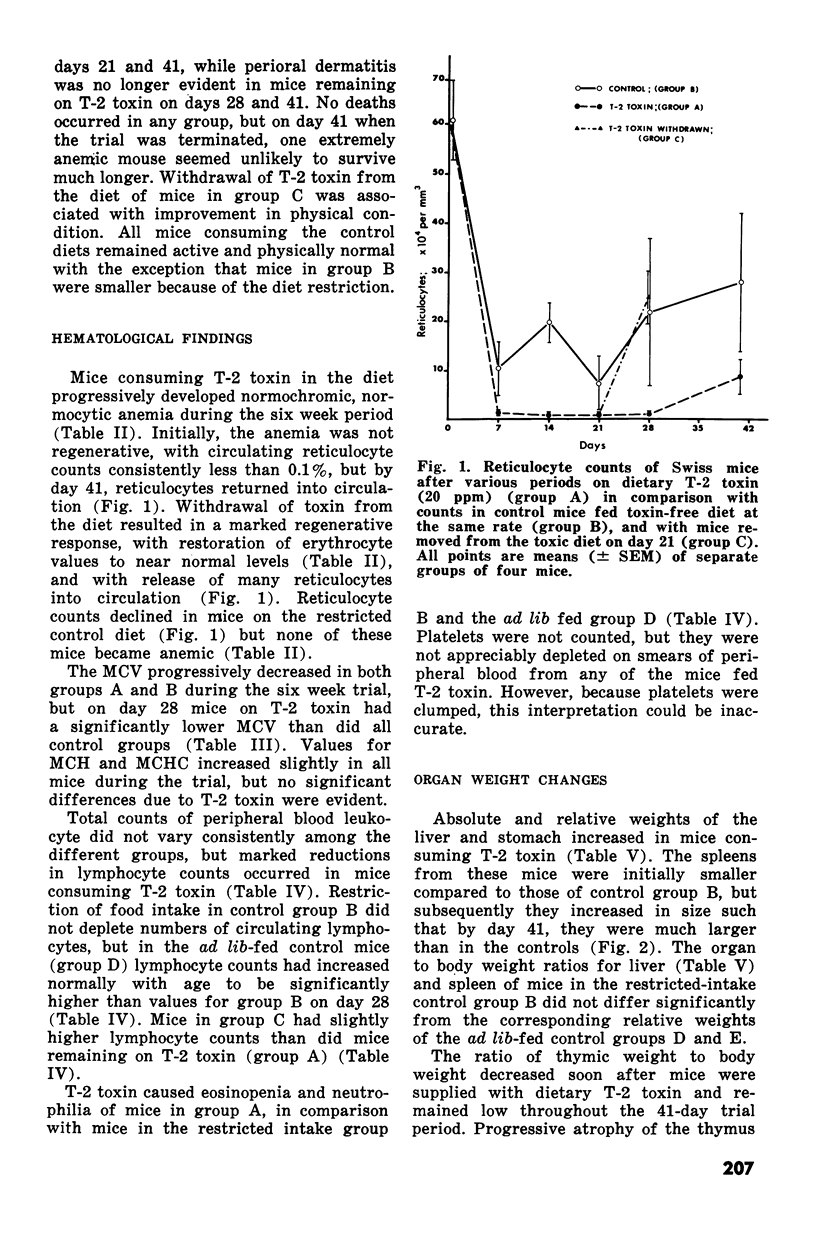
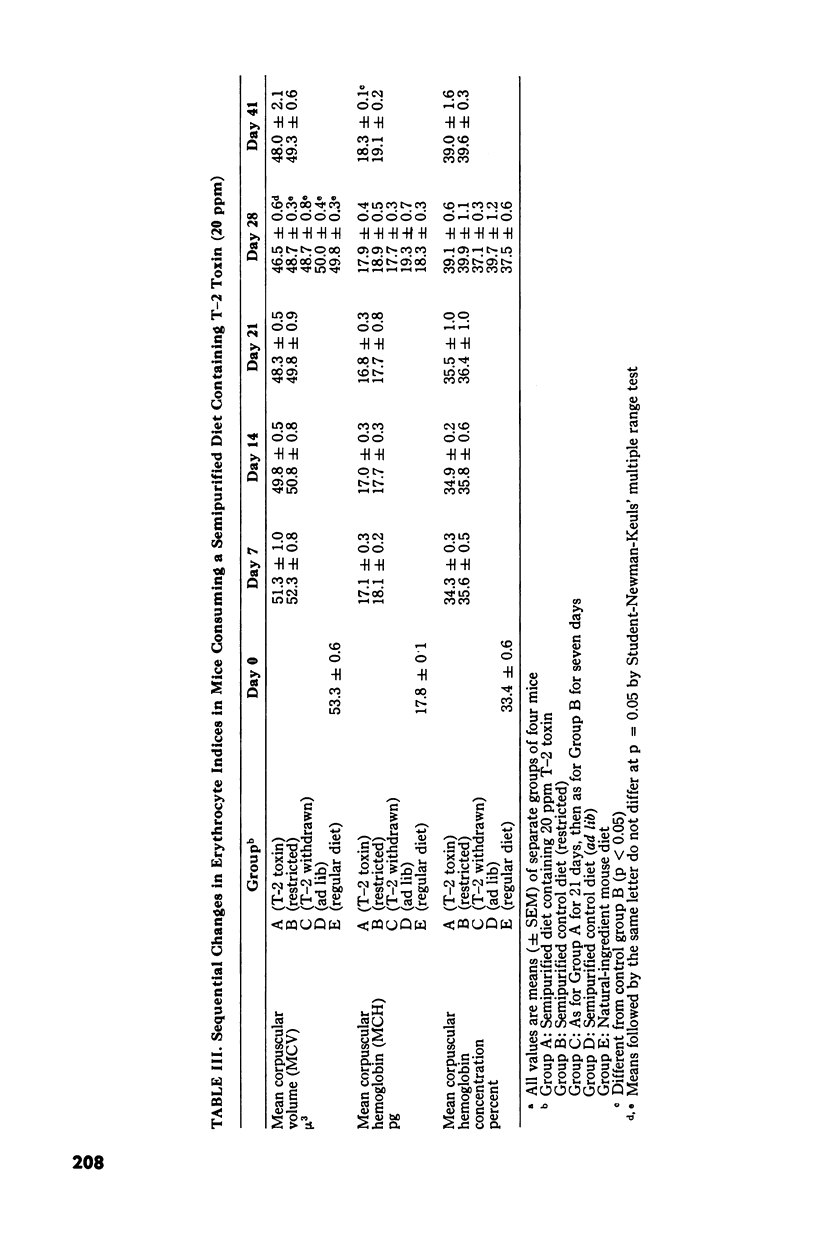
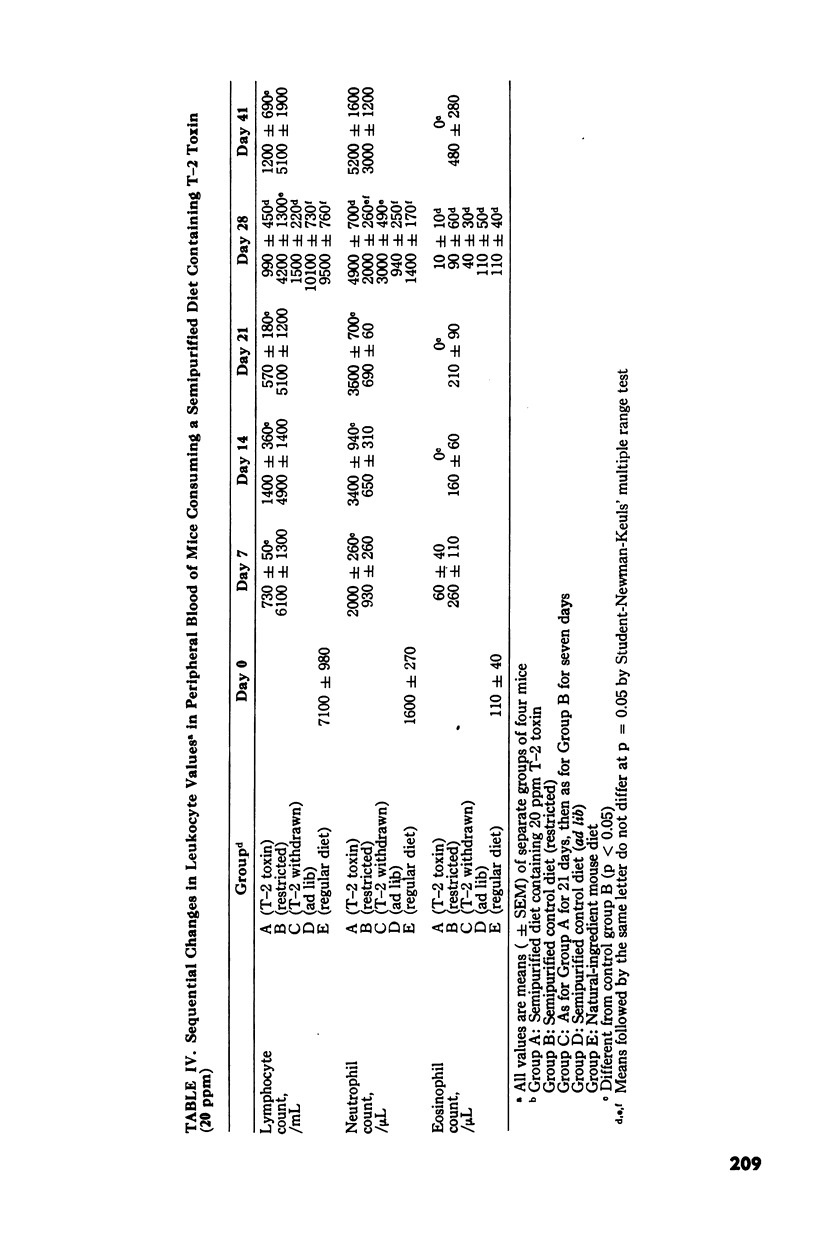
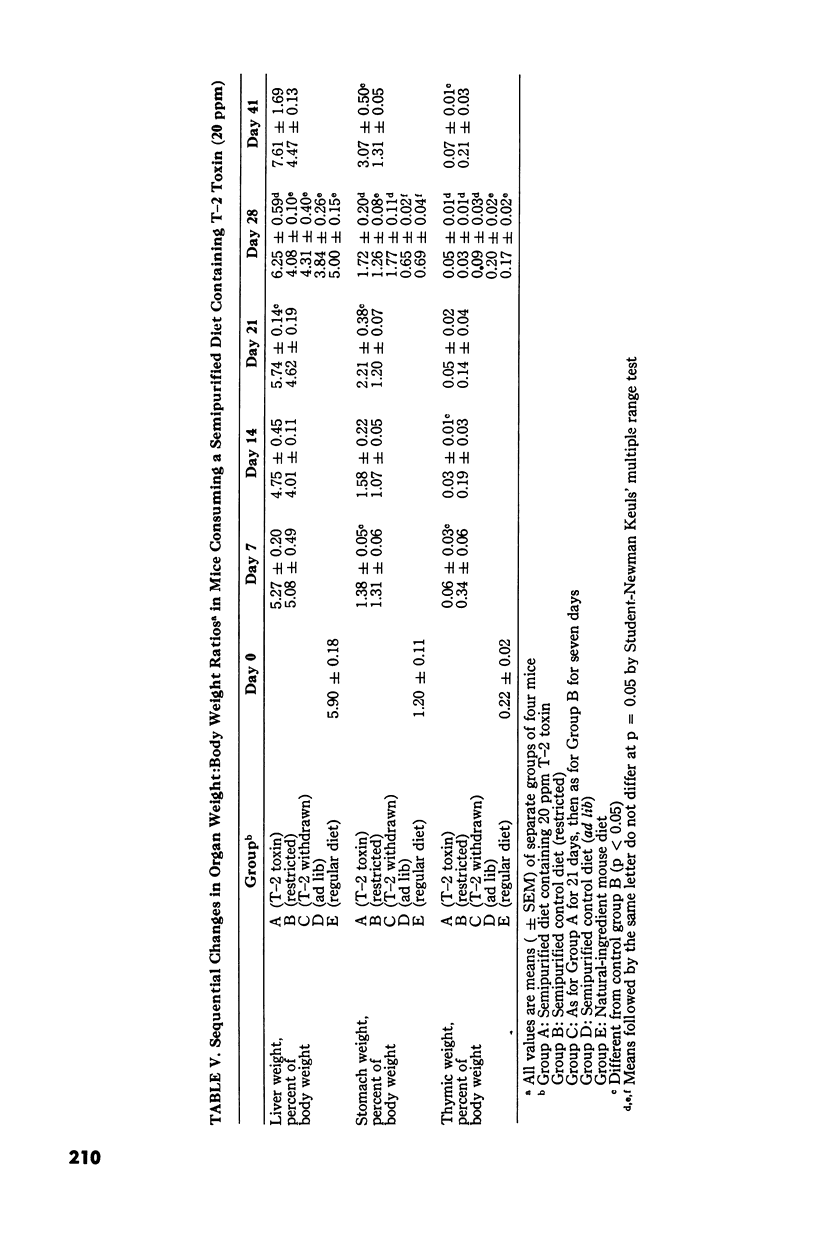
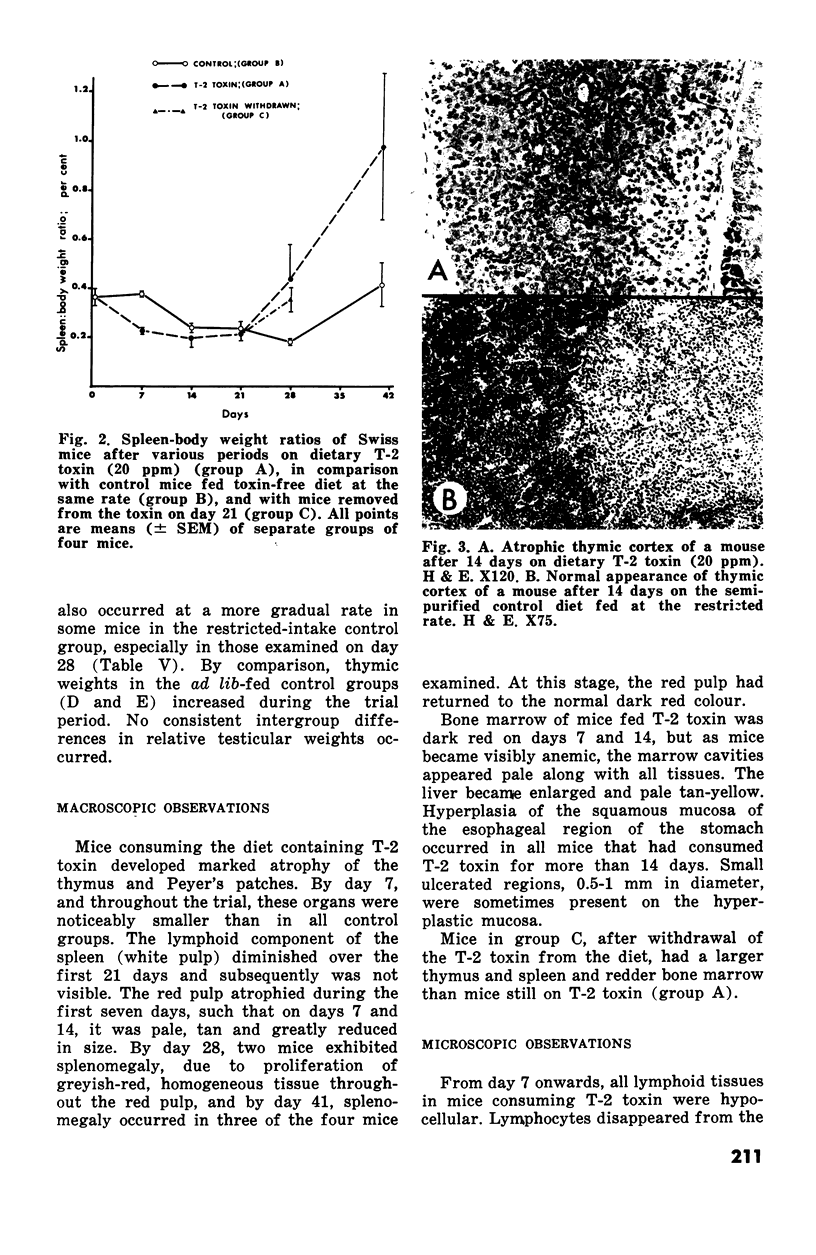
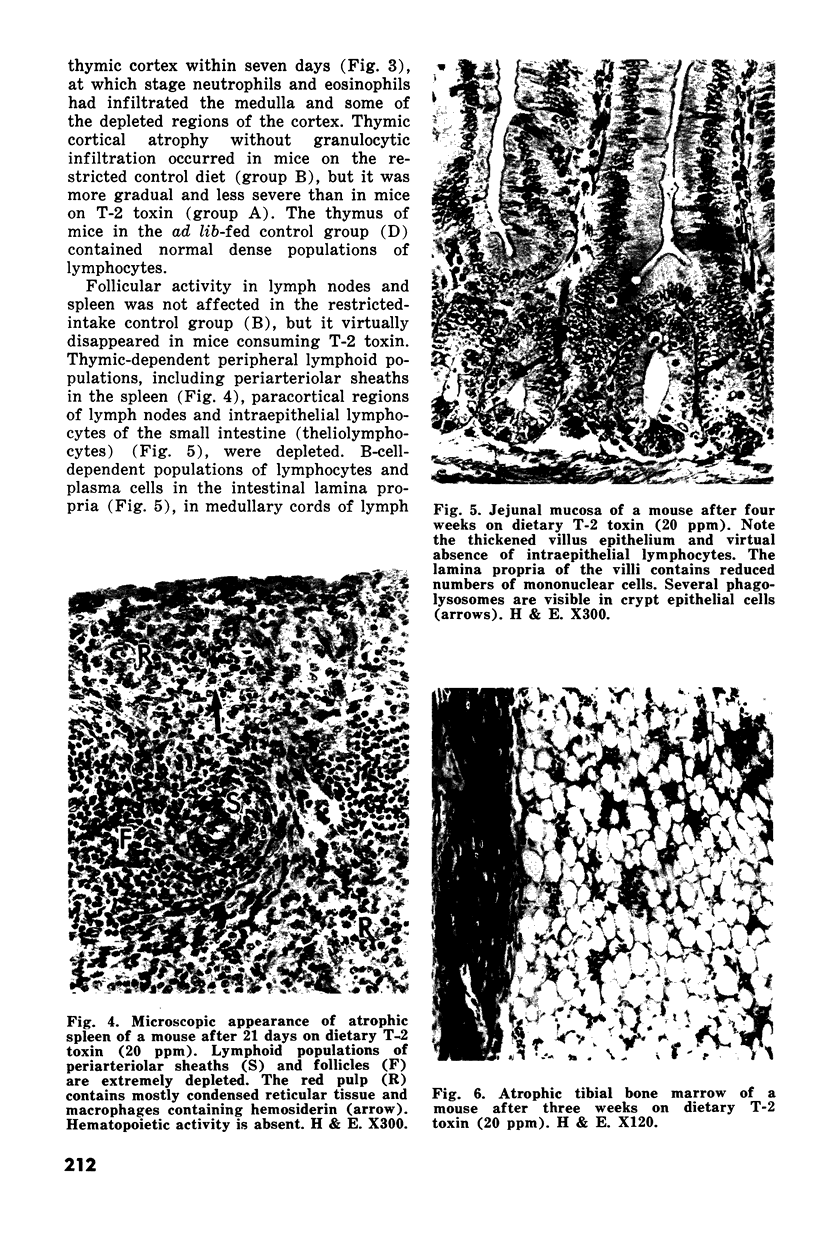
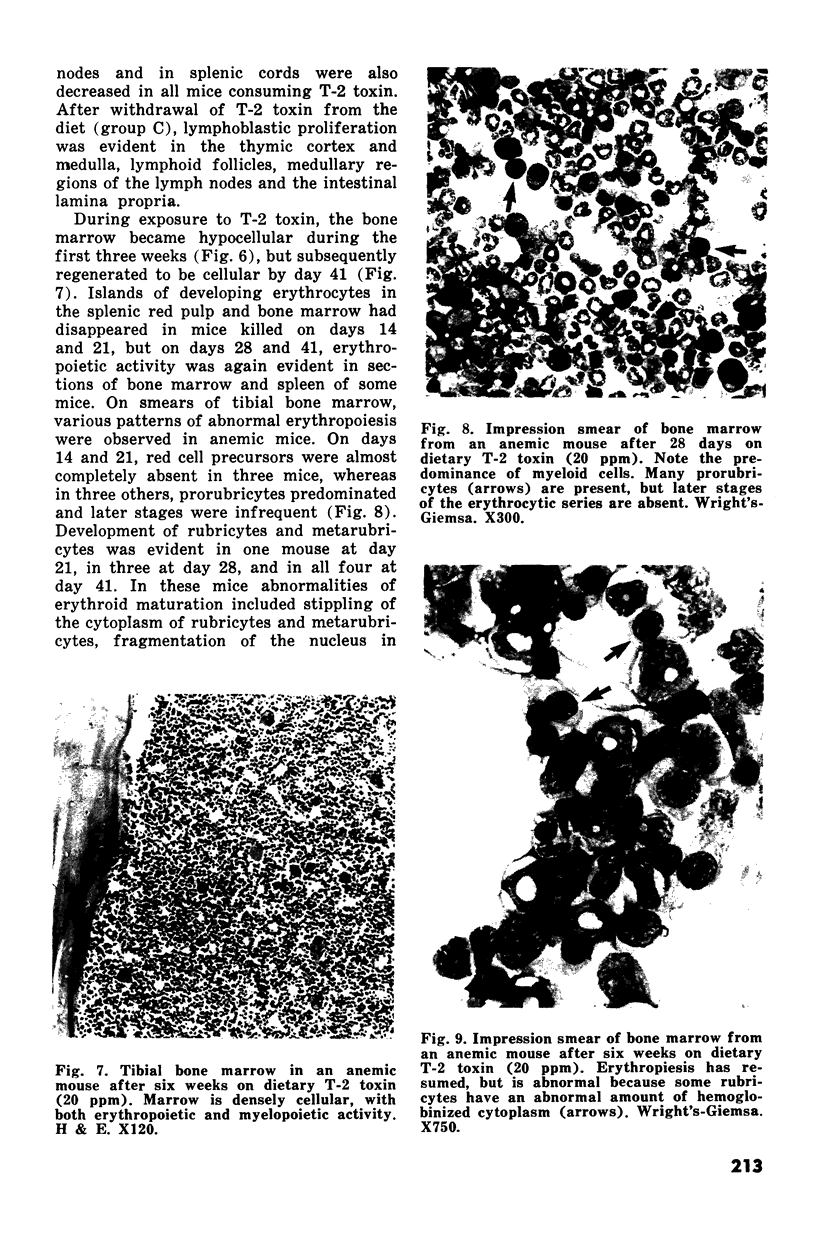
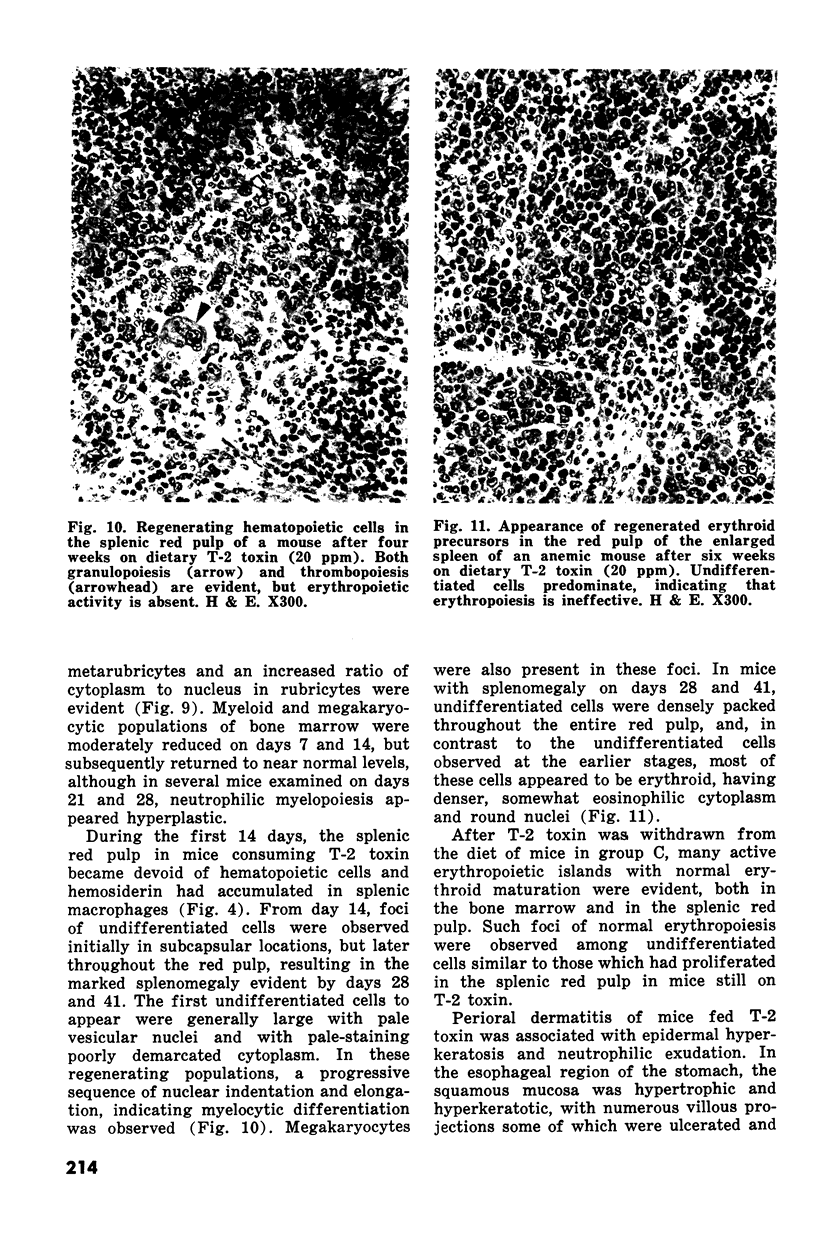
Changes in hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues of young Swiss mice fed a balanced semipurified diet containing T-2 toxin (20 ppm) were examined after one, two, three, four or six weeks. During the first three weeks of exposure of T-2 toxin, lymphoid tissues, bone marrow and splenic red pulp became hypoplastic, resulting in anemia, lymphopenia and eosinopenia. Subsequently, during continued exposure to T-2 toxin, hematopoietic cells regenerated in bone marrow and splenic red pulp and became hyperplastic by six weeks. Granulopoiesis and thrombopoiesis resumed in advance of erythropoiesis. All lymphoid tissues remained atrophic throughout the six week trial. Mice exposed to T-2 toxin also developed perioral dermatitis and hyperkeratosis with ulceration of the mucosa of the esophageal region of the stomach. These results indicated that young mice were susceptible to both the irritant and the hematopoietic-suppressive toxic effects of dietary T-2 toxin. However, supression of hematopoiesis was transient and did not lead to hematopoietic failure.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chi M. S., Mirocha C. J., Kurtz H. J., Weaver G., Bates F., Shimoda W. Subacute toxicity of T-2 toxin in broiler chicks. Poult Sci. 1977 Jan;56(1):306–313. doi: 10.3382/ps.0560306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppley R. M., Bailey W. J. 12,13-Epoxy-delta 9-trichothecenes as the probable mycotoxins responsible for stachybotryotoxicosis. Science. 1973 Aug 24;181(4101):758–760. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4101.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried W., Barone S. J., Anagnostou A. Effect of protein deprivation on hematopoietic stem cells and on peripheral blood counts. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Aug;92(2):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway J. A., Puls R. Fusariotoxicosis from barley in British Columbia. I. Natural occurrence and diagnosis. Can J Comp Med. 1976 Jan;40(1):12–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. A., Schiefer H. B. Subacute toxicity of Dietary T-2 toxin in mice: influence of protein nutrition. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Apr;44(2):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ribelin W. E. Identification of T-2 toxin in moldy corn associated with a lethal toxicosis in dairy cattle. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):684–690. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.684-690.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsonis F. N., Smalley E. B., Ellison R. A., Gale C. M. Feed refusal factors in pure cultures of Fusarium roseum 'graminearum'. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):362–368. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.362-368.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger G. R. Morphology of chemical immunosuppression. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1972;10:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsky I., Mor N., Yagen B., Joffe A. Z. The role of T-2 toxin in experimental alimentary toxic aleukia: a toxicity study in cats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;43(1):111–124. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(78)80036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER C. F. Endemic panmyelotoxicosis in the Russian grain belt. I. The clinical aspects of alimentary toxic aleukia (ATA); a comprehensive review. Mil Surg. 1953 Sep;113(3):173–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasas W. F., Bamburg J. R., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ragland W. L., Degurse P. E. Toxic effects on trout, rats, and mice of T-2 toxin produced by the fungus Fusarium tricinctum (Cd.) Snyd. et Hans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;15(2):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(69)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palyusik M., Koplik-Kovács E. Effect on laying geese of feeds containing the fusariotoxins T2 and F2. Acta Vet Acad Sci Hung. 1975;25(4):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard J. L., Cysewski S. J., Pier A. C., Booth G. D. Comparison of effects of dietary T-2 toxin on growth, immunogenic organs, antibody formation, and pathologic changes in turkeys and chickens. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Oct;39(10):1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein Y., Lafarge-Frayssinet C., Lespinats G., Loisillier F., Lafont P., Frayssinet C. Immunosuppressive activity of Fusarium toxins. Effects on antibody synthesis and skin grafts of crude extracts, T2-toxin and diacetoxyscirpenol. Immunology. 1979 Jan;36(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüsch M. E., Stähelin H. Uber einige biologische Wirkungen des Cytostaticum Verrucarin A. Arzneimittelforschung. 1965 Aug;15(8):893–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Enomoto M., Tatsuno T. Radiomimetic biological properties of the new scirpene metabolites of Fusarium nivale. Gan. 1969 Oct;60(5):599–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Ueno Y., Enomoto M. Toxicological approaches to the toxic metabolites of Fusaria. VIII. Acute and subacute toxicities of T-2 toxin in cats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;25(3):263–270. doi: 10.1254/jjp.25.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoental R., Joffe A. Z. Lesions induced in rodents by extracts from cultures of Fusarium poae and F. sporotrichioides. J Pathol. 1974 Jan;112(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/path.1711120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley E. B. T-2 toxin. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1973 Dec 1;163(11):1278–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe P. M., Brereton-Stiles G. G., Grace H. J., Mafoyane A., Schonland M., Coovadia H. M., Loening W. E., Parent M. A., Vos G. H. Thymolymphatic deficiency and depression of cell-mediated immunity in protein-calorie malnutrition. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):939–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Sato N., Ishii K., Sakai K., Enomoto M. Toxicological approaches to the metabolites of Fusaria. V. Neosolaniol, T-2 toxin and butenolide, toxic metabolites of Fusarium sporotrichioides NRRL 3510 and Fusarium poae 3287. Jpn J Exp Med. 1972 Oct;42(5):461–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver G. A., Kurtz H. J., Bates F. Y., Chi M. S., Mirocha C. J., Behrens J. C., Robison T. S. Acute and chronic toxicity of T-2 mycotoxin in swine. Vet Rec. 1978 Dec 9;103(24):531–535. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.24.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. D., Doerr J. A., Hamilton P. B., Burmeister H. R. Egg production, shell thickness, and other physiological parameters of laying hens affected by T-2 toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1975 May;29(5):641–645. doi: 10.1128/am.29.5.641-645.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. D., Harris J. R., Hamilton P. B., Burmeister H. R. Possible outbreaks of fusariotoxicosis in avians. Avian Dis. 1972 Oct-Dec;16(5):1123–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. D., Weeks B. A., Hamilton P. B., Burmeister H. R. Severe oral lesions in chickens caused by ingestion of dietary fusariotoxin T-2. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.251-257.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]