Abstract
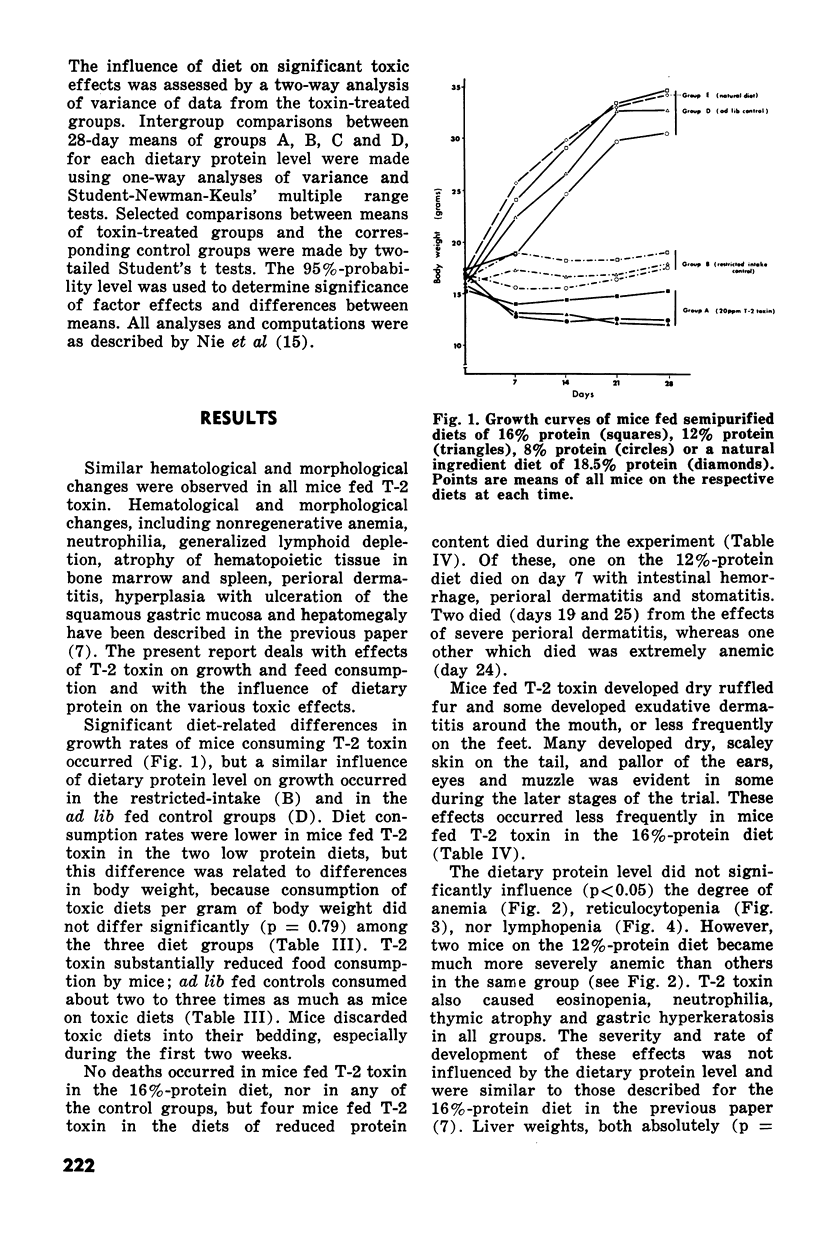
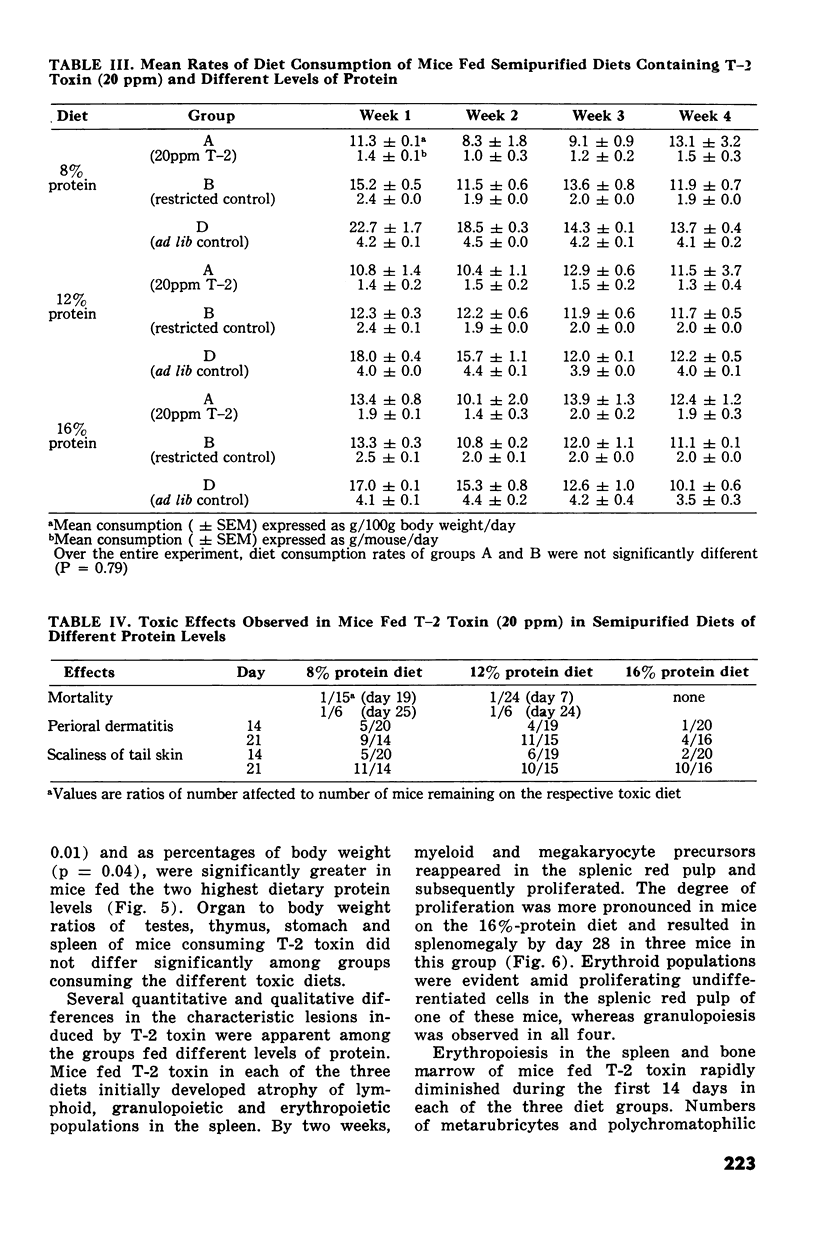
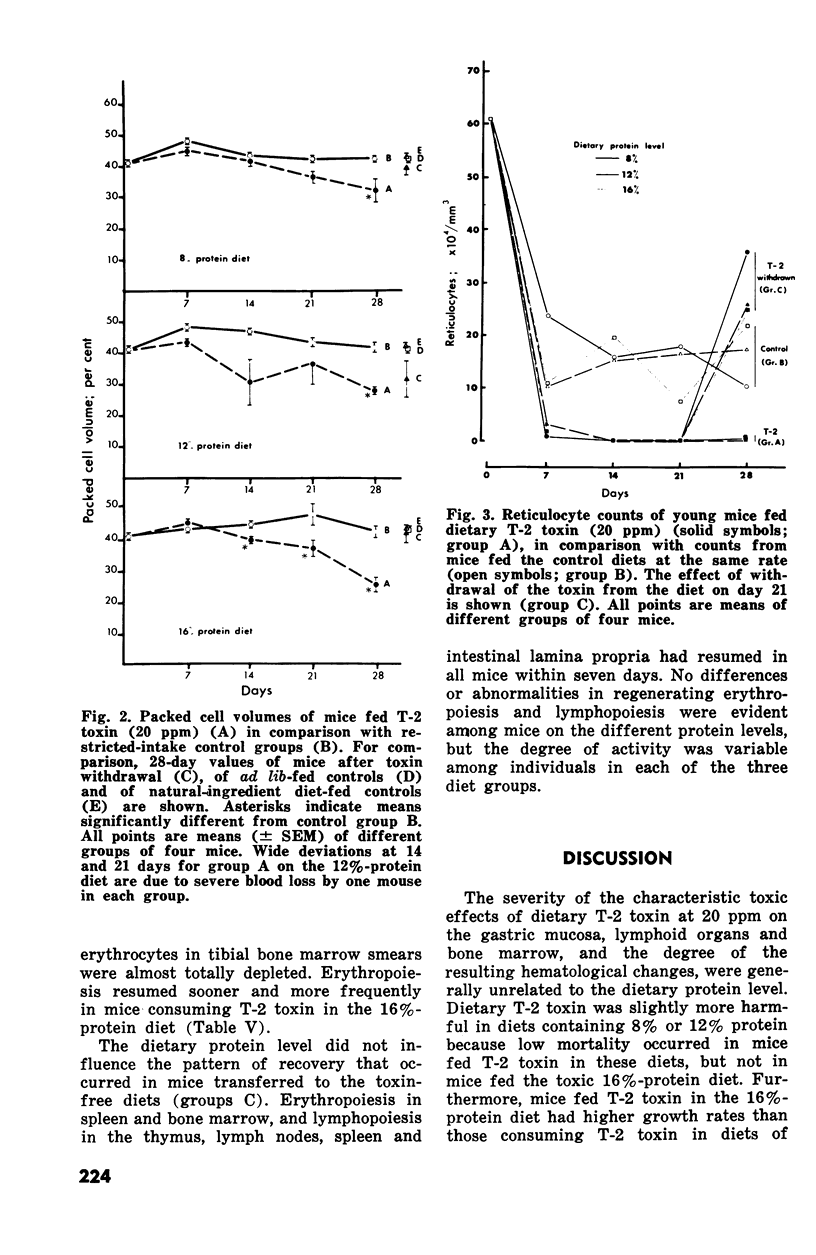
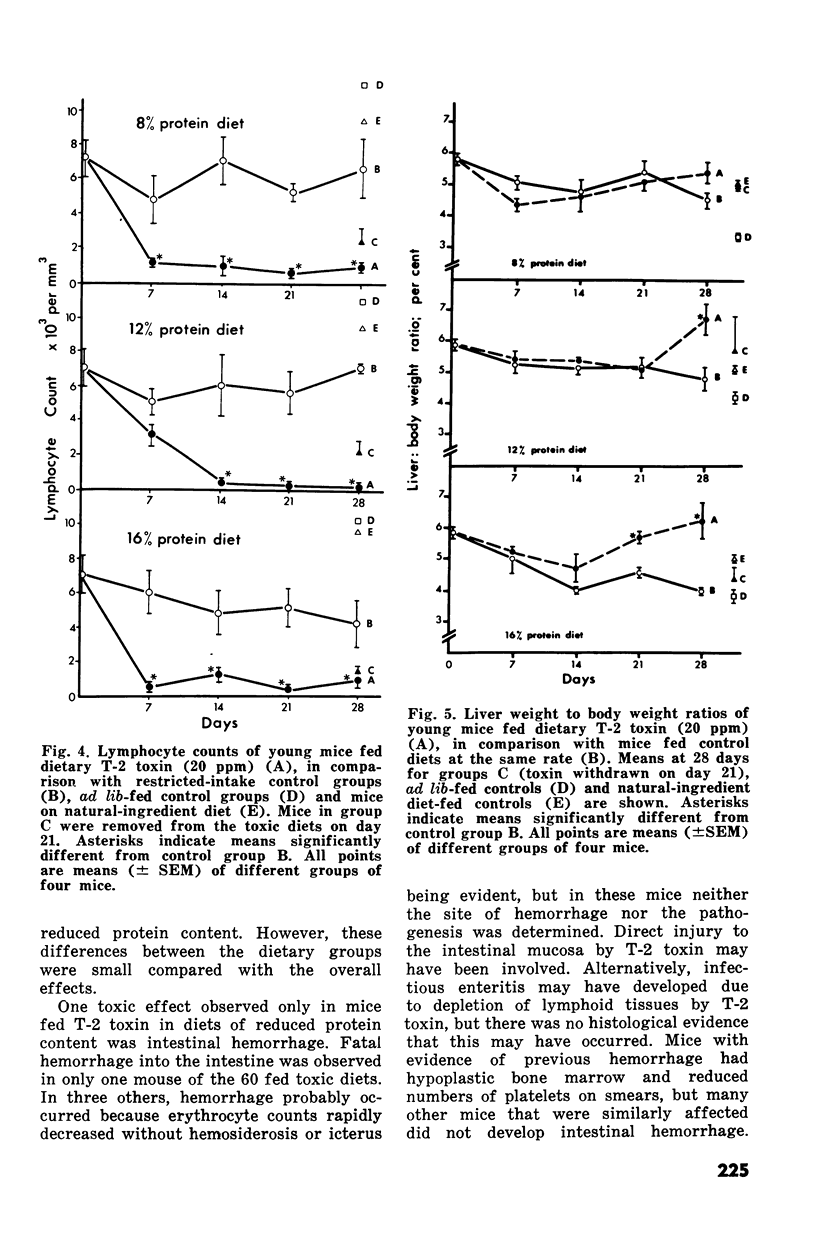
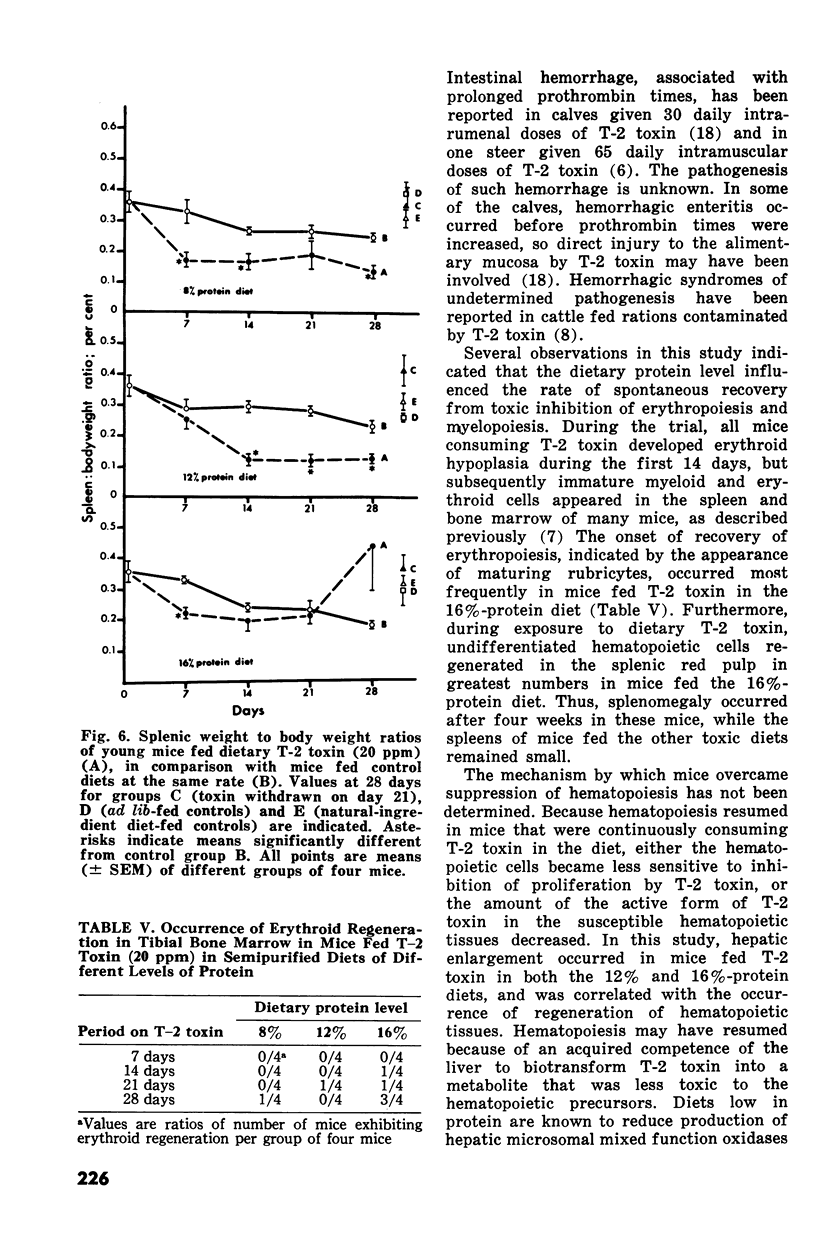
The subacute toxic effects of dietary T-2 toxin (20 ppm) incorporated in semipurified diets of 8%, 12% or 16% protein, were examined in young Swiss mice after one, two, three and four weeks. Dietary T-2 toxin caused substantial reductions in growth and food consumptaion, the degrees of which were greatest in mice fed the diets of reduced protein content. T-2 toxin consistently caused similar degrees of nonregenerative anemia, lymphopenia, thymic atrophy and gastric hyperkeratosis irrespective of the dietary protein level. However, erythroid hypoplasia was temporary in mice fed T-2 toxin in the 16%-protein diet such that erythroid precursors regenerated in splenic and bone marrow and were hyperplastic after four weeks. Liver to body weight ratios of mice fed T-2 toxin in the 16%-and 12%-protein diets increased during the four week trial in comparison to control mice fed at a similar rate. These observations indicated that suppression of erythropoiesis in mice by dietary T-2 toxin was temporarty and that the interval before regeneration was prolonged by diets of reduced protein content.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell T. C., Hayes J. R. The effect of quantity and quality of dietary protein on drug metabolism. Fed Proc. 1976 Nov;35(13):2470–2474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi M. S., Mirocha C. J., Kurtz H. J., Weaver G., Bates F., Shimoda W. Subacute toxicity of T-2 toxin in broiler chicks. Poult Sci. 1977 Jan;56(1):306–313. doi: 10.3382/ps.0560306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. A., Kotsonis F. N. In vitro metabolism of T-2 toxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):423–424. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.423-424.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway J. A., Puls R. Fusariotoxicosis from barley in British Columbia. I. Natural occurrence and diagnosis. Can J Comp Med. 1976 Jan;40(1):12–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove M. D., Yates S. G., Tallent W. H., Ellis J. J., Wolff I. A., Kosuri N. R., Nichols R. E. Mycotoxins produced by Fusarium tricinctum as possible causes of cattle disease. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Jul-Aug;18(4):734–736. doi: 10.1021/jf60170a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. A., Bellamy J. E., Schiefer H. B. Subacute toxicity of dietary T-2 toxin in mice: morphological and hematological effects. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Apr;44(2):203–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ribelin W. E. Identification of T-2 toxin in moldy corn associated with a lethal toxicosis in dairy cattle. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):684–690. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.684-690.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John A. M., Bell J. M. Amino acid requirements of the growing mouse. J Nutr. 1976 Sep;106(9):1361–1367. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.9.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsky I., Mor N., Yagen B., Joffe A. Z. The role of T-2 toxin in experimental alimentary toxic aleukia: a toxicity study in cats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;43(1):111–124. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(78)80036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasas W. F., Bamburg J. R., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ragland W. L., Degurse P. E. Toxic effects on trout, rats, and mice of T-2 toxin produced by the fungus Fusarium tricinctum (Cd.) Snyd. et Hans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;15(2):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(69)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. E., McLean E. Diet and toxicity. Br Med Bull. 1969 Sep;25(3):278–281. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberne P. M. Mycotoxins: toxicity, carcinogenicity, and the influence of various nutritional conditions. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 Dec;9:1–32. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9-1475399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D. V., Williams R. T. Metabolism of toxic substances. Br Med Bull. 1969 Sep;25(3):256–262. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R. Induction of liver growth by xenobiotic compounds and other stimuli. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1974 Sep;3(1):97–158. doi: 10.3109/10408447409079856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver G. A., Kurtz H. J., Bates F. Y., Chi M. S., Mirocha C. J., Behrens J. C., Robison T. S. Acute and chronic toxicity of T-2 mycotoxin in swine. Vet Rec. 1978 Dec 9;103(24):531–535. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.24.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. D., Harris J. R., Hamilton P. B., Burmeister H. R. Possible outbreaks of fusariotoxicosis in avians. Avian Dis. 1972 Oct-Dec;16(5):1123–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


