Abstract
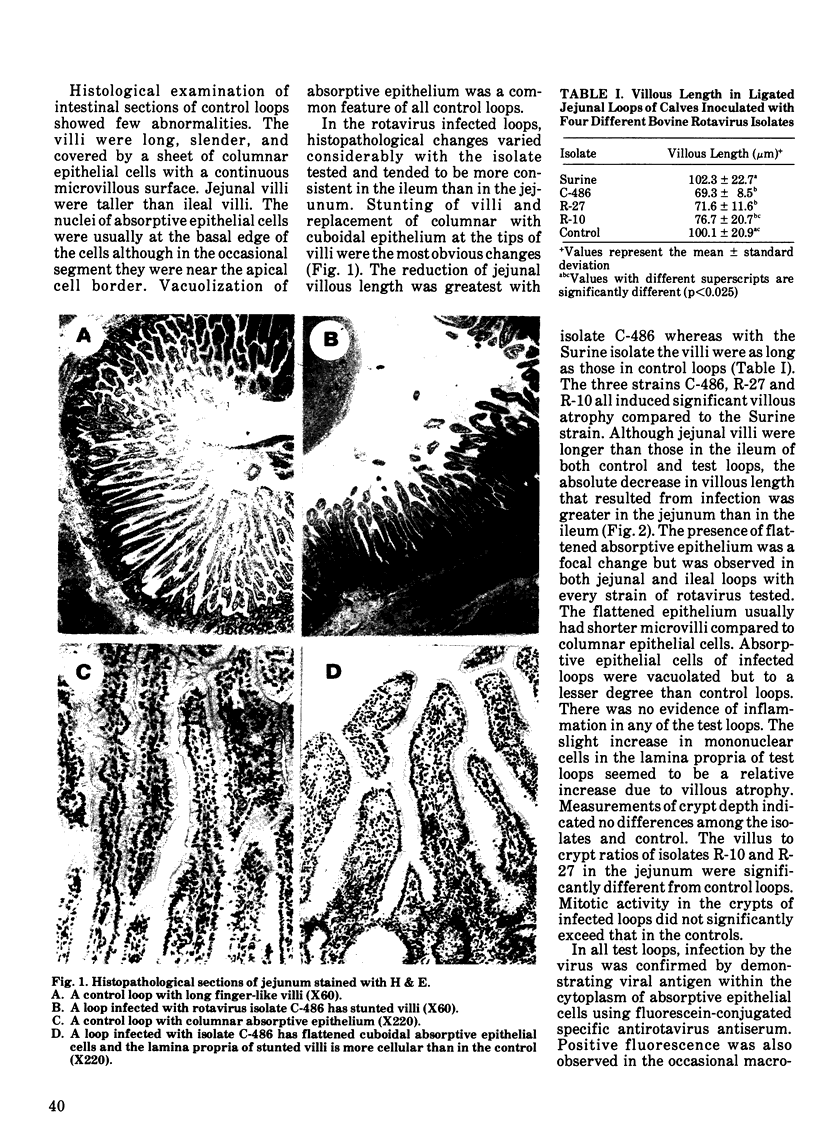
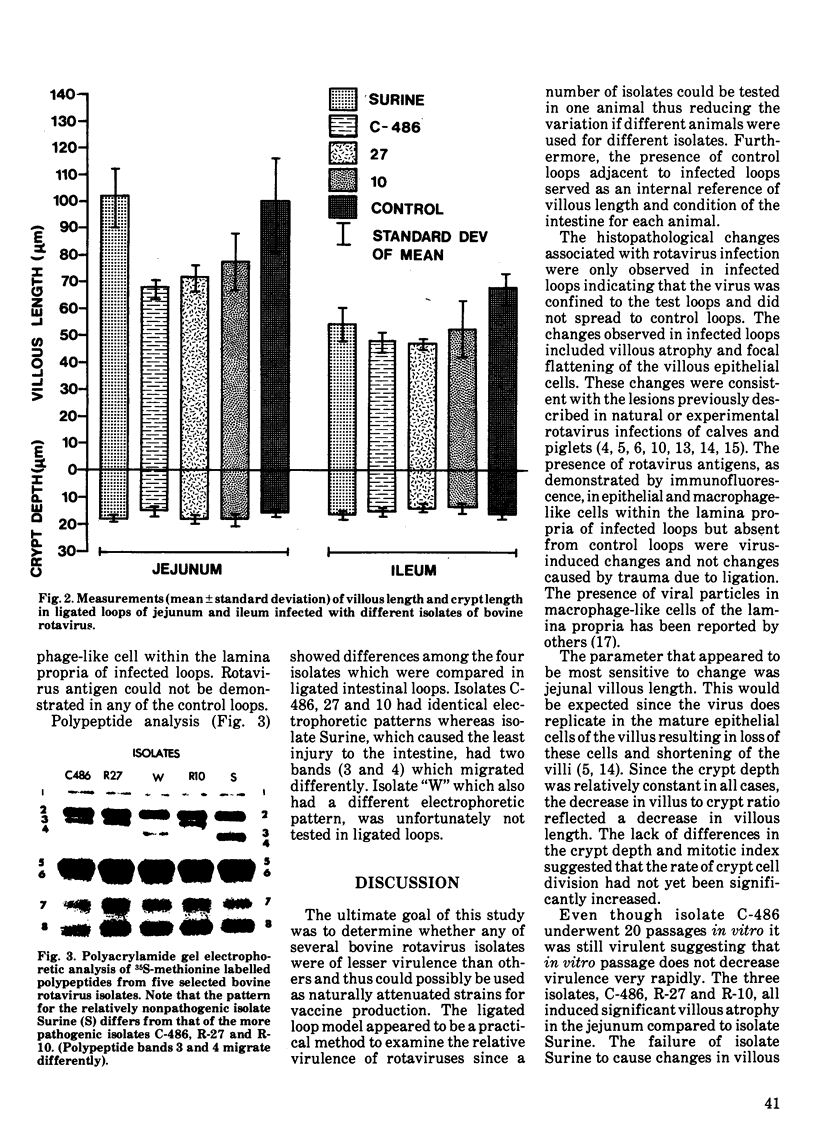
Intestinal loops, ligated in colostrum-deprived calves were used to compare the virulence of four isolates of bovine rotavirus. Histopathological studies were carried out on infected and control loops and measurements of villous length, crypt depth, villus:crypt ratio and crypt mitotic index were recorded. Pathological changes associated with the rotaviruses included villous atrophy, flattening of absorptive epithelium and reduced villus:crypt ratios. The changes were confined to infected intestinal loops in which the presence of virus was demonstrated by specific immunofluorescence. Consistent differences in the measured histopathological changes suggested differences in virulence among the rotavirus isolates tested. The least virulent rotavirus isolate had a polypeptide electrophoretic pattern that differed from the other three more virulent isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiuk L. A., Mohammed K., Spence L., Fauvel M., Petro R. Rotavirus isolation and cultivation in the presence of trypsin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):610–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.610-617.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernelius A. L., Ritchie A. E., Classick L. G., Norman J. O., Mebus C. A. Cell culture adaptation and propagation of a reovirus-like agent of calf diarrhea from a field outbreak in Nebraska. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(1):114–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01241157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. A., Bridger J. C., Chandler R. L., Woode G. N. Gnotobiotic piglets experimentally infected with neonatal calf diarrhoea reovirus-like agent (Rotavirus). Vet Pathol. 1976;13(3):197–210. doi: 10.1177/030098587601300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpin C. G., Caple I. W. Changes in intestinal structure and function of neonatal calves infected with reovirus-like agent and Eschericia coli. Aust Vet J. 1976 Oct;52(10):438–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1976.tb05384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W., Mock R. Reovirus-like agent associated with fatal diarrhea in neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):816–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.816-825.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., McFerran J. B. Isolation of a cytopathic calf rotavirus. Res Vet Sci. 1976 Jul;21(1):114–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Curran W. L., McFerran J. B. The morphogenesis of a cytopathic bovine rotavirus in Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):503–508. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Kono M., Underdahl N. R., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can Vet J. 1971 Mar;12(3):69–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin M., Lamothe P., Gagnon A., Malo R. A case of viral neonatal calf diarrhea in a Quebec dairy herd. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jul;38(3):236–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S., Logan E. F. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal calves naturally infected with reo-like virus (rotavirus). Vet Rec. 1978 May 27;102(21):454–458. doi: 10.1136/vr.102.21.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal pigs infected with a pig reovirus-like agent (rotavirus). J Comp Pathol. 1977 Jul;87(3):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence L., Fauvel M., Petro R., Babiuk L. A. Comparison of rotavirus strains by hemagglutination inhibition. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Apr;24(4):353–362. doi: 10.1139/m78-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stair E. L., Mebus C. A., Twiehaus M. J., Underdahl N. R. Neonatal calf diarrhea. Electron microscopy of intestines infected with a reovirus-like agent. Vet Pathol. 1973;10(2):155–170. doi: 10.1177/030098587301000208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C. Viral enteritis of calves. Vet Rec. 1975 Jan 25;96(4):85–88. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.4.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




