Abstract
Objective:
To examine the nature and incidence of injuries suffered by racewalkers.
Design and Setting:
A total of 682 questionnaires were distributed to racewalkers in the San Diego/Long Beach, CA area, participants in a national qualifying race held in Washington, DC, and subscribers to The Ohio Racewalker.
Subjects:
Four hundred questionnaires were returned to the investigators, for a return rate of 58.7%.
Measurements:
Questions addressed demographics, exercise patterns, competitive history, walking surfaces, types of footwear normally used for training and competition, and injuries suffered during racewalking. Questionnaire results were tabulated and chi-square analyses were used to test for interrelationships. A stepwise discriminant analysis was used to develop a model for the prediction of injury in racewalking.
Results:
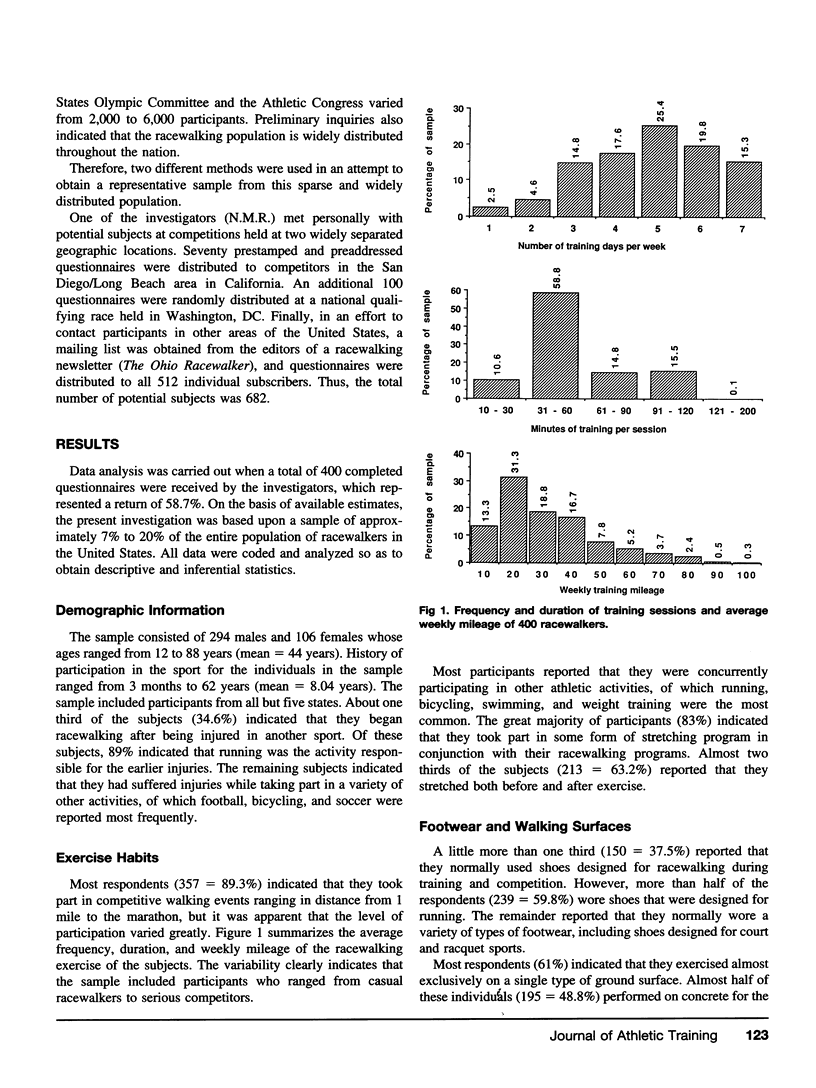
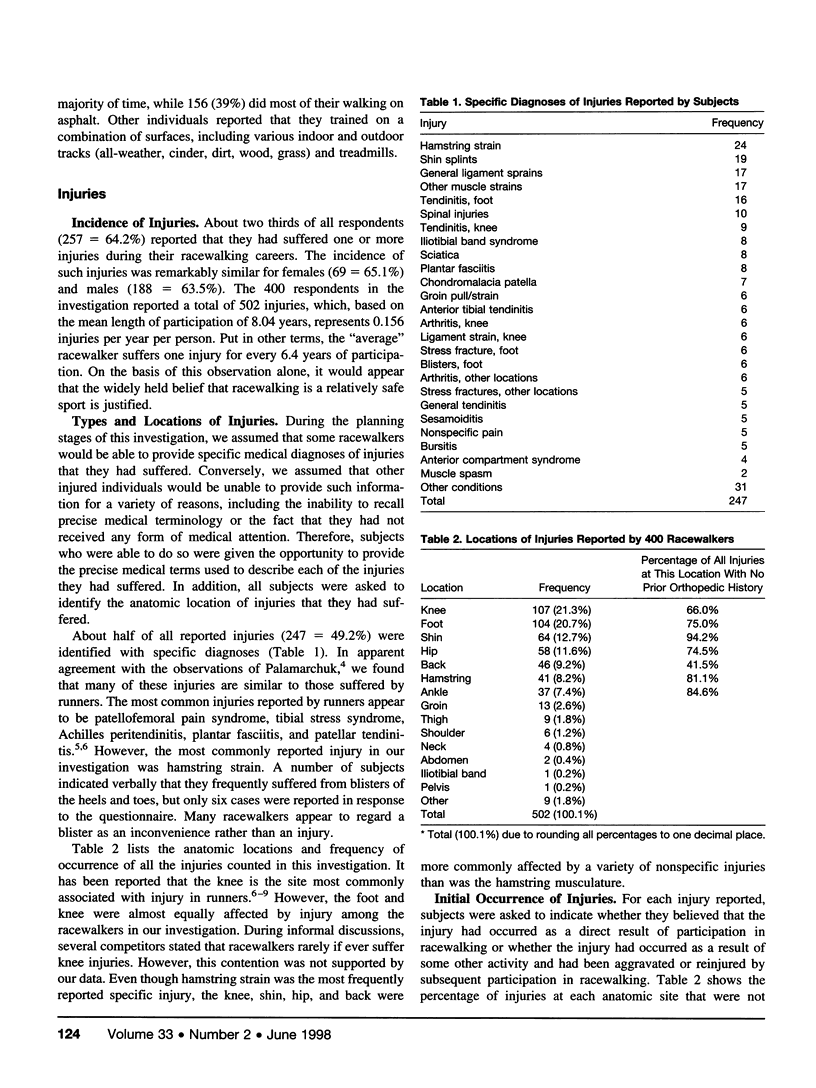
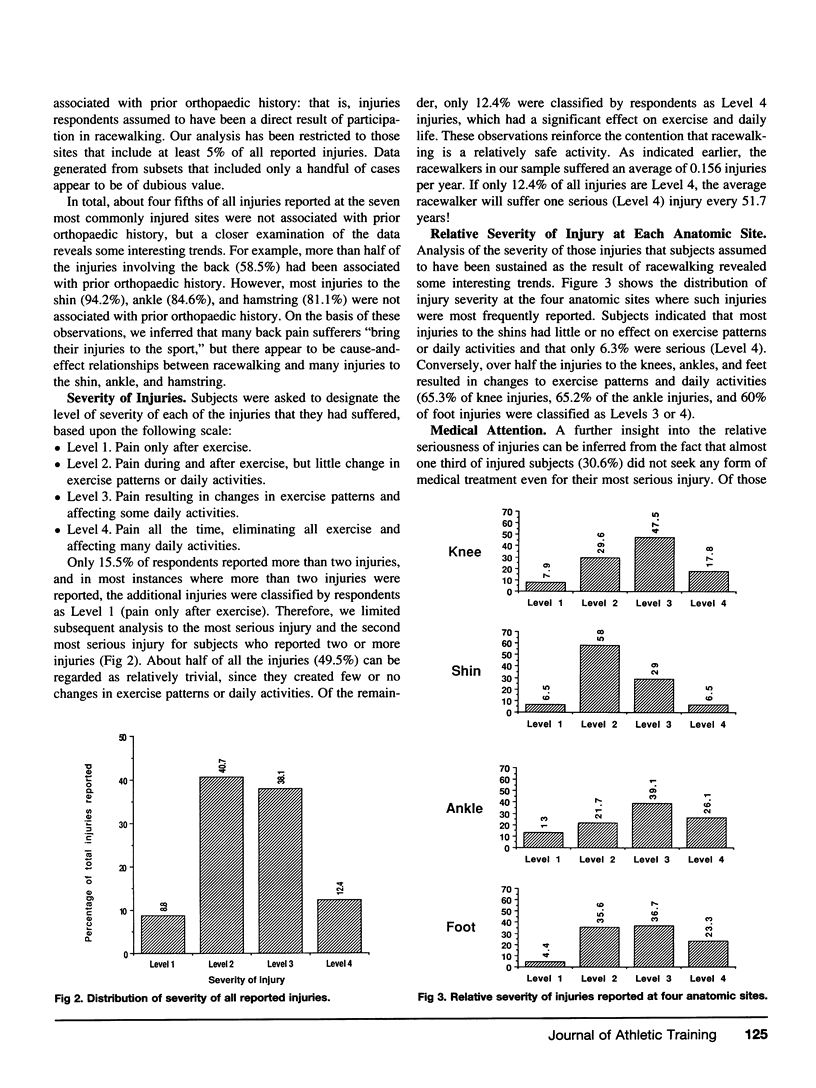
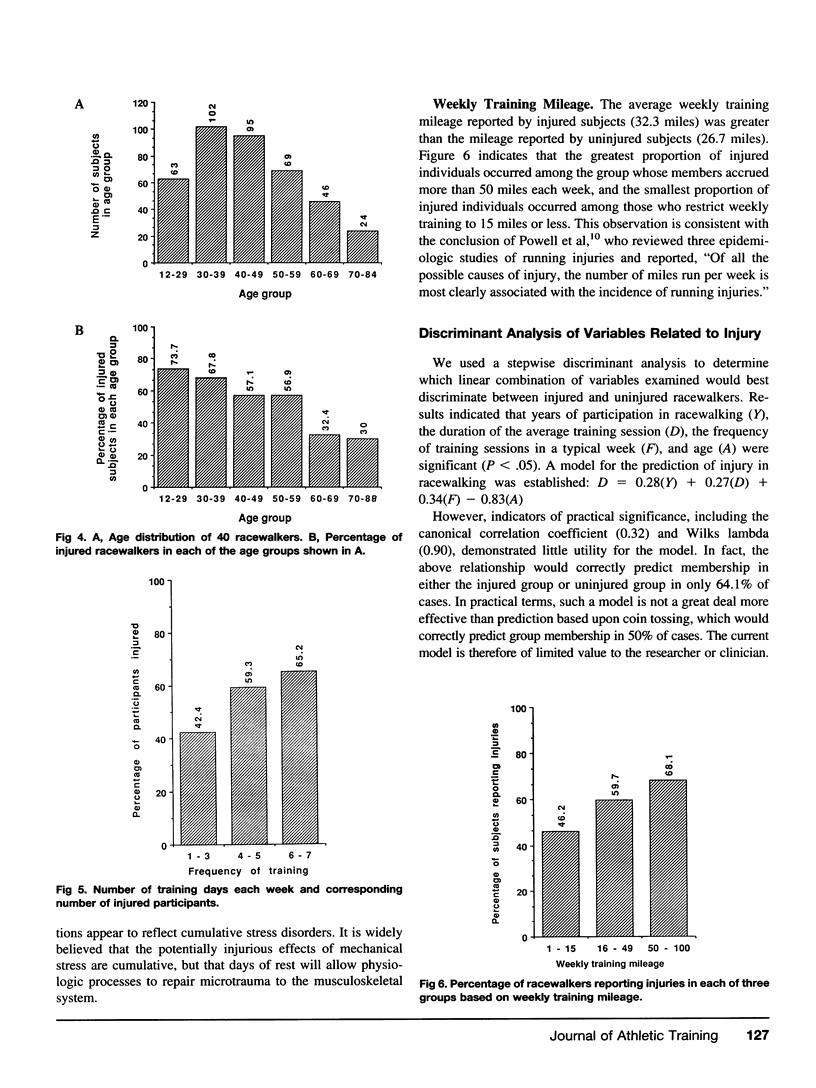
Racewalking participation peaks in the 30- to 39-year-old age group, while the proportion of injured participants is greatest in those under 30. Most injuries involved the lower extremity, but the “average” racewalker suffered only one serious injury every 51.7 years. Those participants who trained six or seven times per week were most likely to be injured; those who trained three or fewer times per week were least likely to be injured. The percentage of injured participants increased progressively with weekly training mileage. A model based on the data from this investigation correctly predicted membership in either the injured or uninjured group in only 64.1% of cases and is, therefore, of limited use to the researcher or clinician.
Conclusions:
Although the rate of injuries in racewalkers is low, more systematic research is necessary before sports medicine professionals can confidently recommend consistently effective injury prevention procedures.
Keywords: walking surfaces, footwear, training, injury prediction
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody D. M. Running injuries. Clin Symp. 1980;32(4):1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Bates B. T., Osternig L. R. Injuries to runners. Am J Sports Med. 1978 Mar-Apr;6(2):40–50. doi: 10.1177/036354657800600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplan J. P., Powell K. E., Sikes R. K., Shirley R. W., Campbell C. C. An epidemiologic study of the benefits and risks of running. JAMA. 1982 Dec 17;248(23):3118–3121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


