Abstract
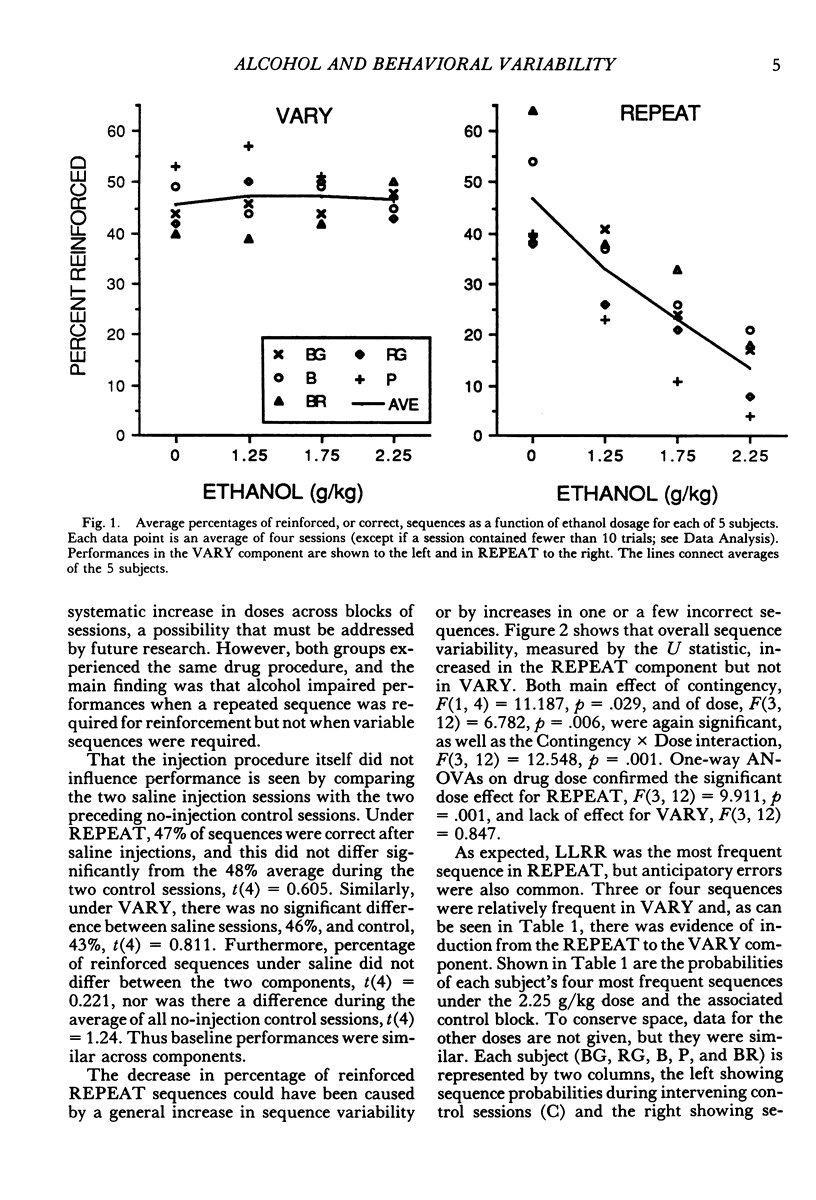
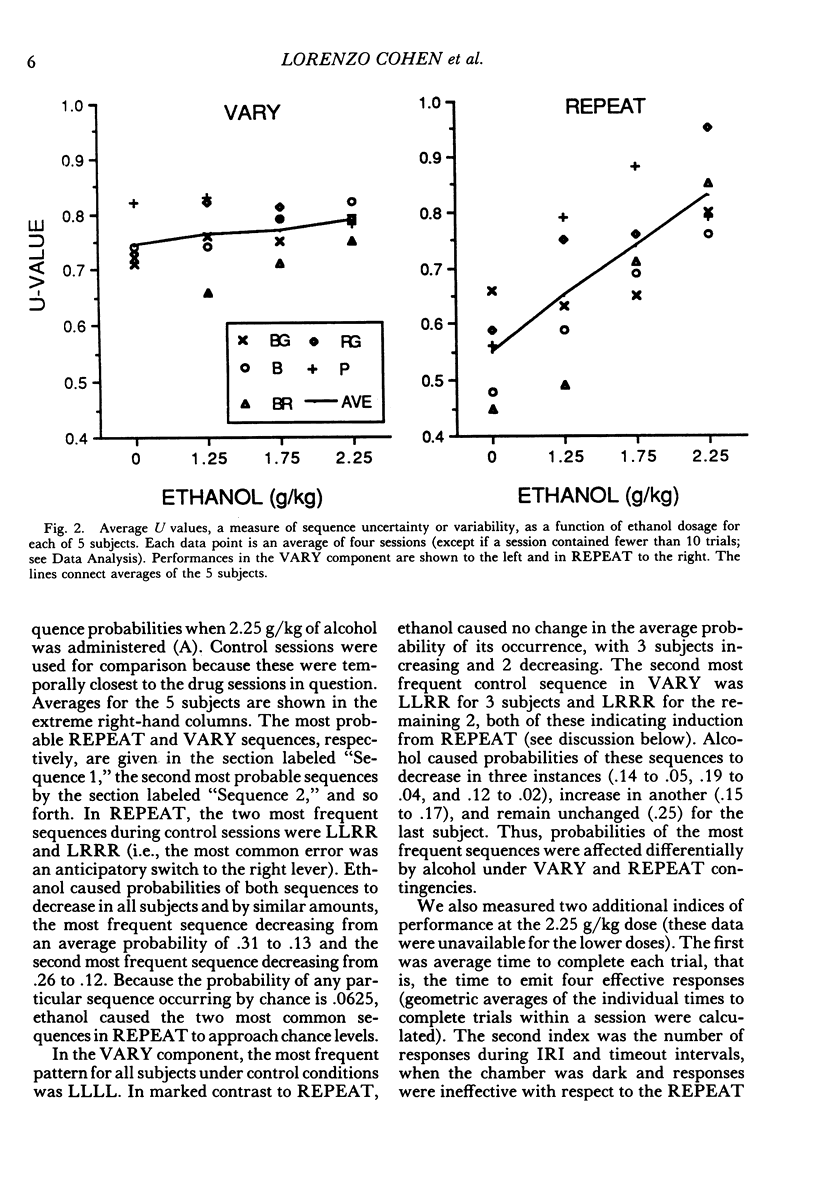
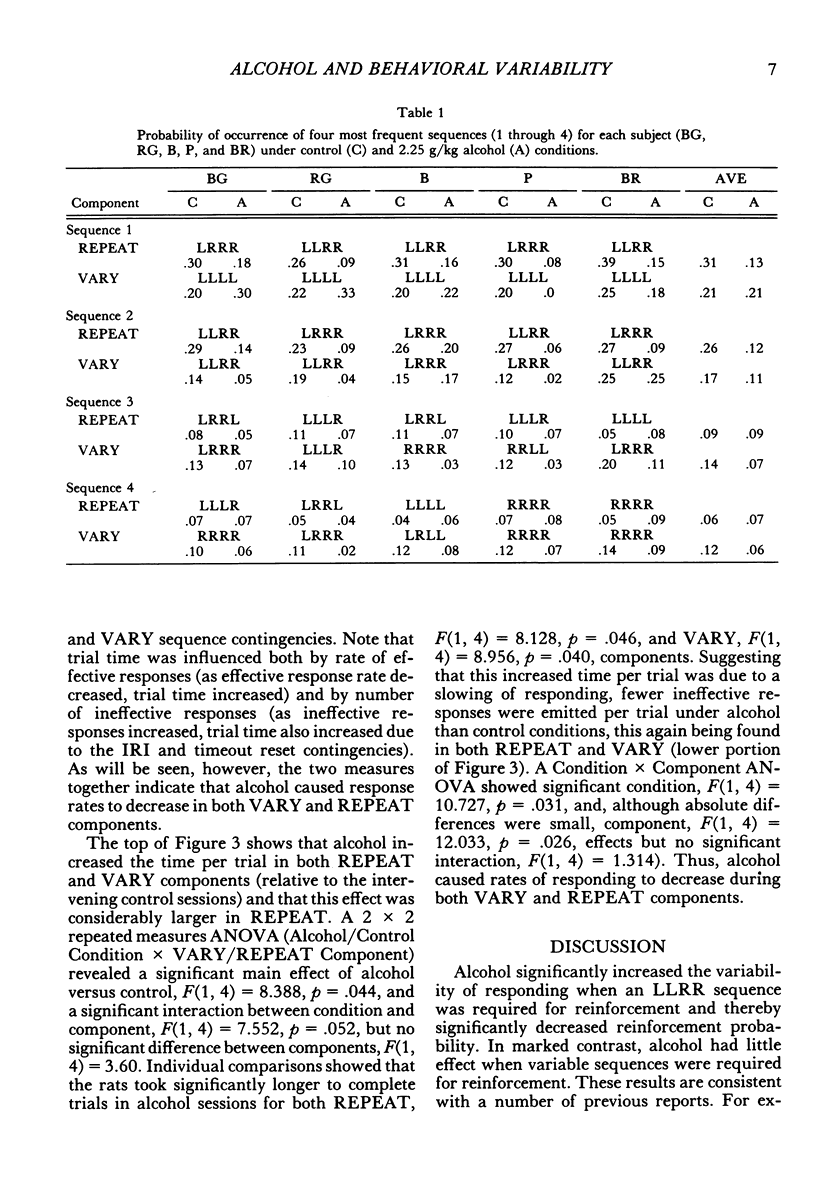
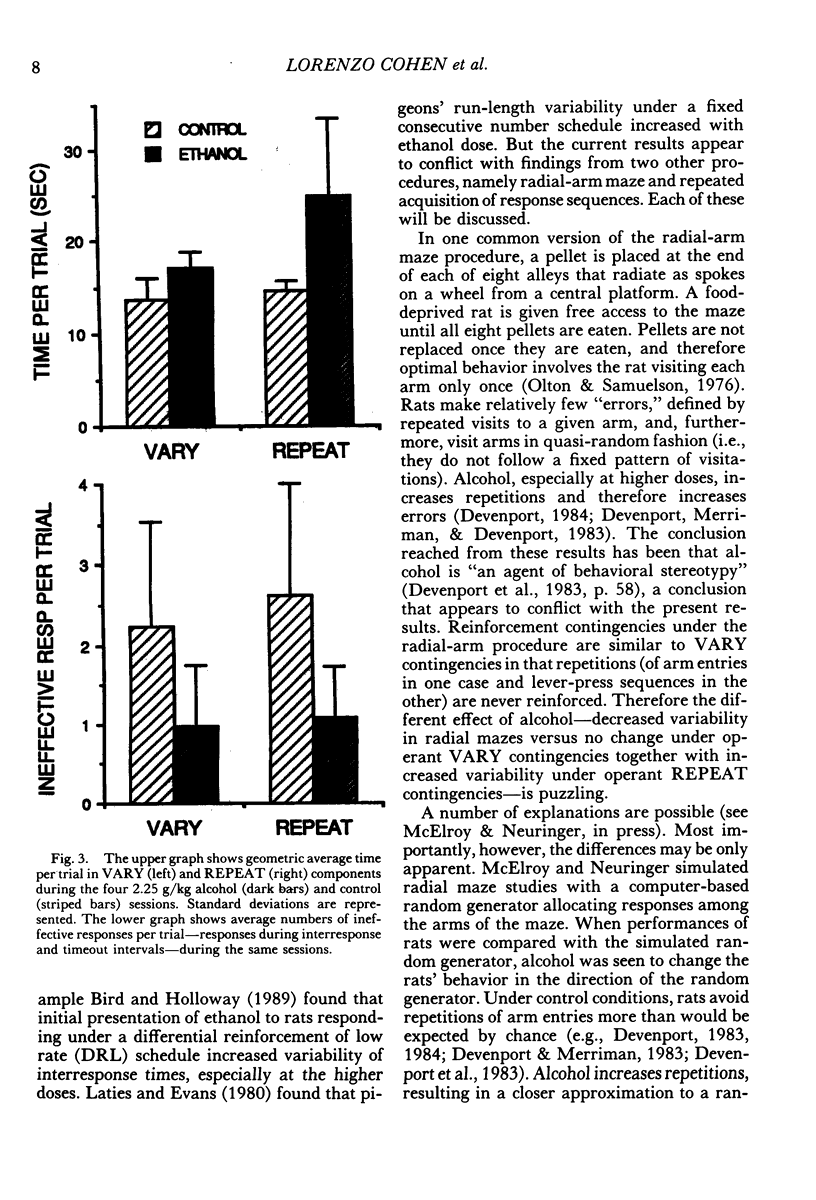
Response sequences emitted by five Long-Evans rats were reinforced under a two-component multiple schedule. In the REPEAT component, food pellets were contingent upon completion of a left-left-right-right (LLRR) sequence on two levers. In the VARY component, pellets were contingent upon variable sequences (i.e., a sequence was reinforced only if it differed from each of the previous five sequences). The rats learned to emit LLRR sequences in the REPEAT component and variable sequences in VARY. Intraperitoneal injections of ethanol (1.25, 1.75, and 2.25 g/kg) significantly increased sequence variability in REPEAT, thereby lowering reinforcement probability, but had little effect on sequence variability in the VARY component. These results extend previous findings that alcohol impairs the performance of reinforced repetitions but not of reinforced variations in response sequences.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett J. E., Stanley J. A. Effects of ethanol on multiple fixed-interval fixed-ratio schedule performances: dynamic interactions at different fixed-ratio values. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):185–198. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthalmus G. T., Leander J. D., McMillan D. E. Combined effects of ethanol and diazepam on performance and acquisition of serial position sequences by pigeons. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Sep 15;59(1):101–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00428039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird D. C., Holloway F. A. Development and loss of tolerance to the effects of ethanol on DRL performance of rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989;97(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00443411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. The reinforcement of least-frequent interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):581–591. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. V. A biobehavioral research perspective on alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Public Health Rep. 1988 Nov-Dec;103(6):699–707. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenport L. D. Extinction-induced spatial dispersion in the radial arm maze: arrest by ethanol. Behav Neurosci. 1984 Dec;98(6):979–985. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.98.6.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenport L. D., Merriman V. J., Devenport J. A. Effects of ethanol on enforced spatial variability in the 8-arm radial maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983 Jan;18(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenport L. D., Merriman V. J. Ethanol and behavioral variability in the radial-arm maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;79(1):21–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00433010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. W., Powell B., Bremer D., Hoine H., Stern J. Alcohol and recall: state-dependent effects in man. Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1358–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIMAN A. E. The effect of a preoperative preference for sugar over salt upon compensatory salt selection by adrenalectomized rats. J Nutr. 1955 Oct 10;57(2):271–276. doi: 10.1093/jn/57.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harting J., Mcmillian D. E. Effects of pentobarbital and d-amphetamine on the repeated acquisition of response sequences by pigeons. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Sep 29;49(3):245–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00426823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. T., Bickel W. K., O'Leary D. K., Yingling J. Acute effects of ethanol and diazepam on the acquisition and performance of response sequences in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G., Evans H. L. Methylmercury-induced changes in operant discrimination by the pigeon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):620–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G., Weiss B. Influence of drugs on behavior controlled by internal and external stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER G. A., FRICK F. C. Statistical behavioristics and sequences of responses. Psychol Rev. 1949 Nov;56(6):311–324. doi: 10.1037/h0060413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machado A. Operant conditioning of behavioral variability using a percentile reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1989 Sep;52(2):155–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1989.52-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur J., dos Santos H. M. Response variability of ethanol-induced locomotor activation in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;96(4):547–550. doi: 10.1007/BF02180038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. J. The operant conditioning of response variability: Free-operant versus discrete-response procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 May;47(3):273–277. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.47-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor K. W., Haag R., O'reilly J. The creative porpoise: training for novel behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):653–661. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiger P. K., White J. M. Conditioned alcohol-like and alcohol-opposite responses in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1988;95(1):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00212773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuchinich R. E., Tucker J. A. Contributions from behavioral theories of choice to an analysis of alcohol abuse. J Abnorm Psychol. 1988 May;97(2):181–195. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.97.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hest A., van Haaren F., van de Poll N. E. Operant conditioning of response variability in male and female Wistar rats. Physiol Behav. 1989 Mar;45(3):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(89)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


