Abstract
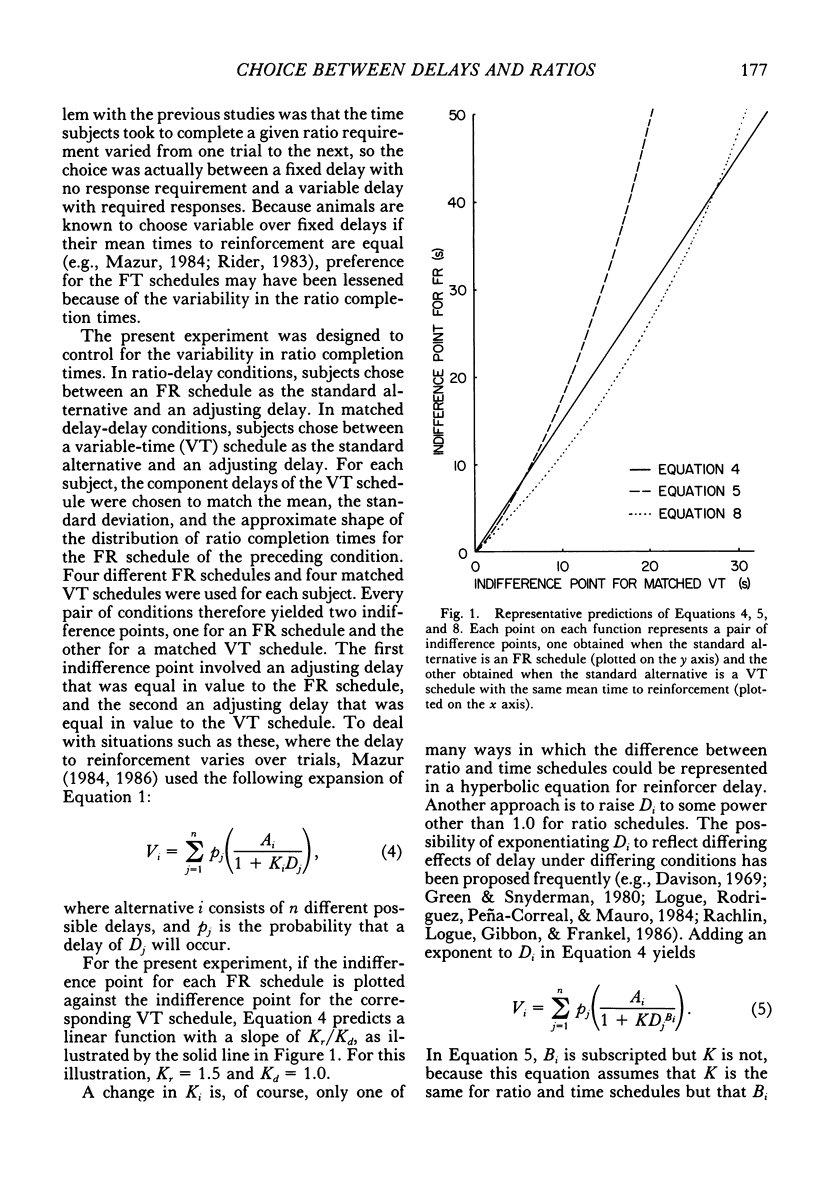
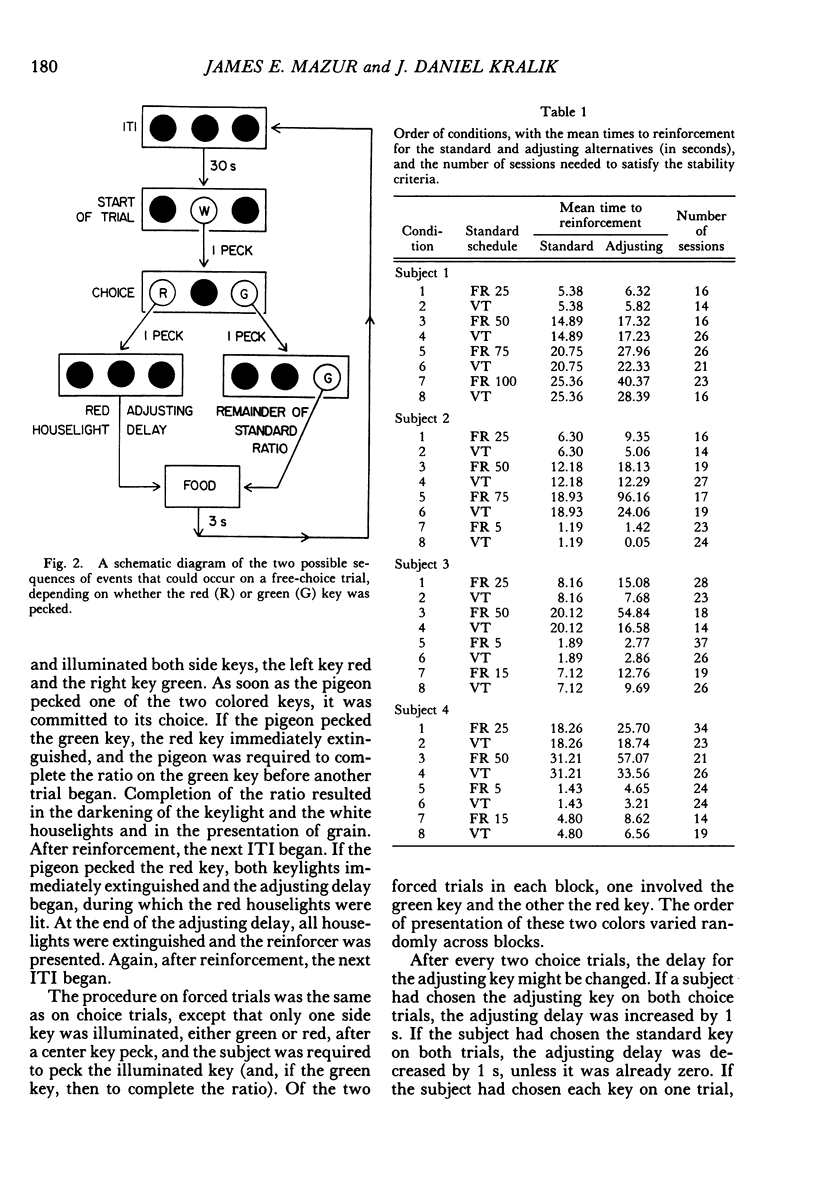
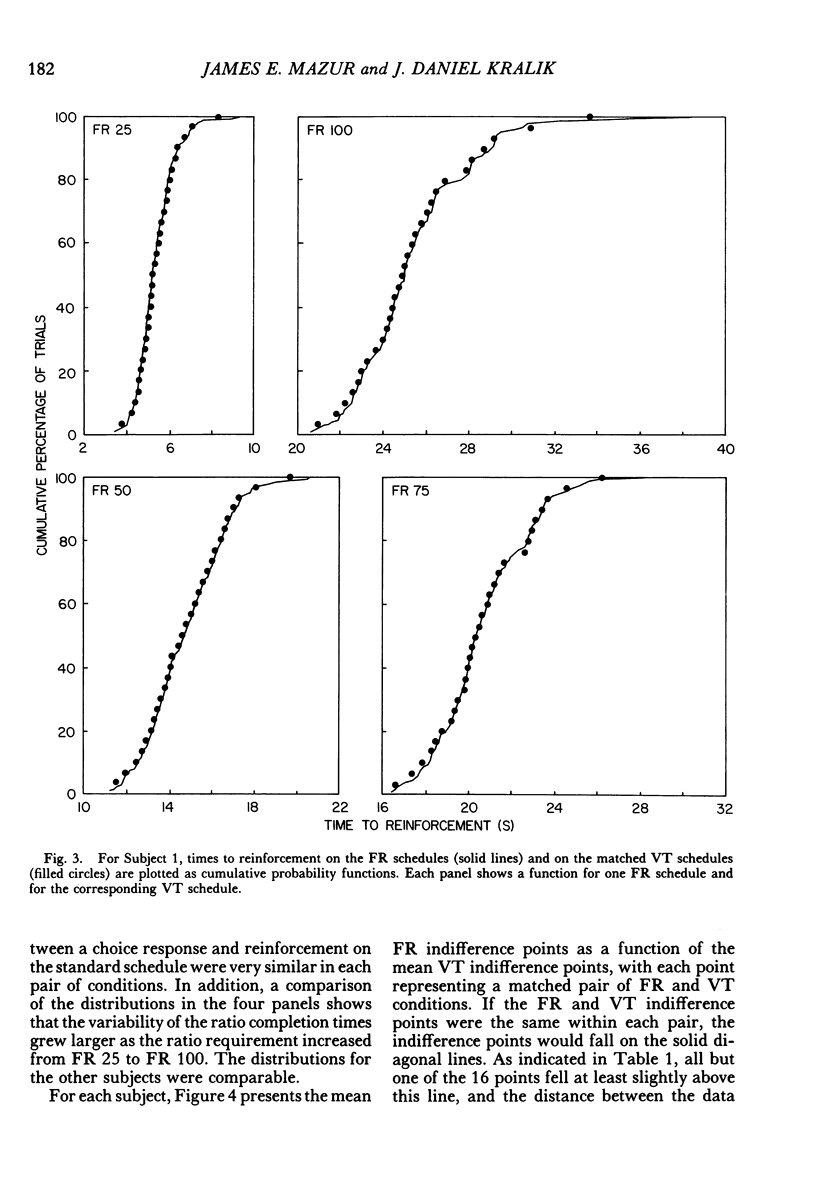
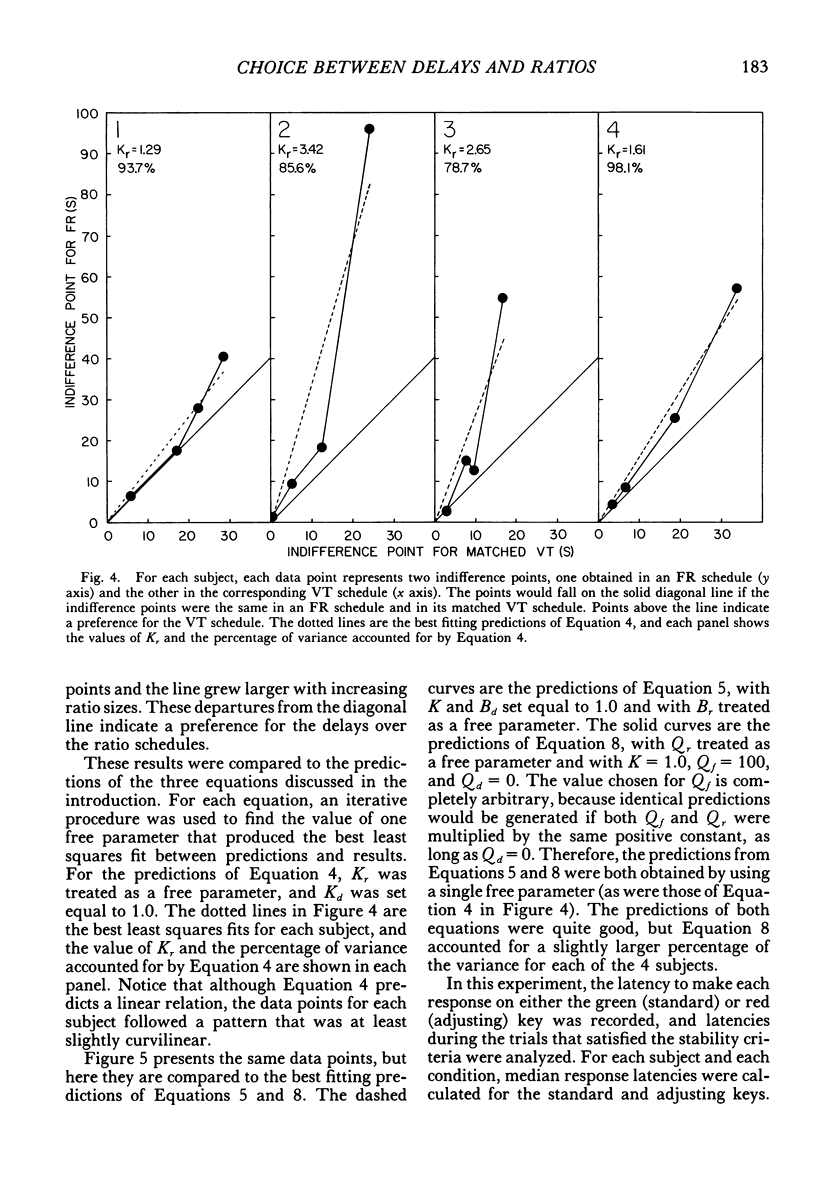
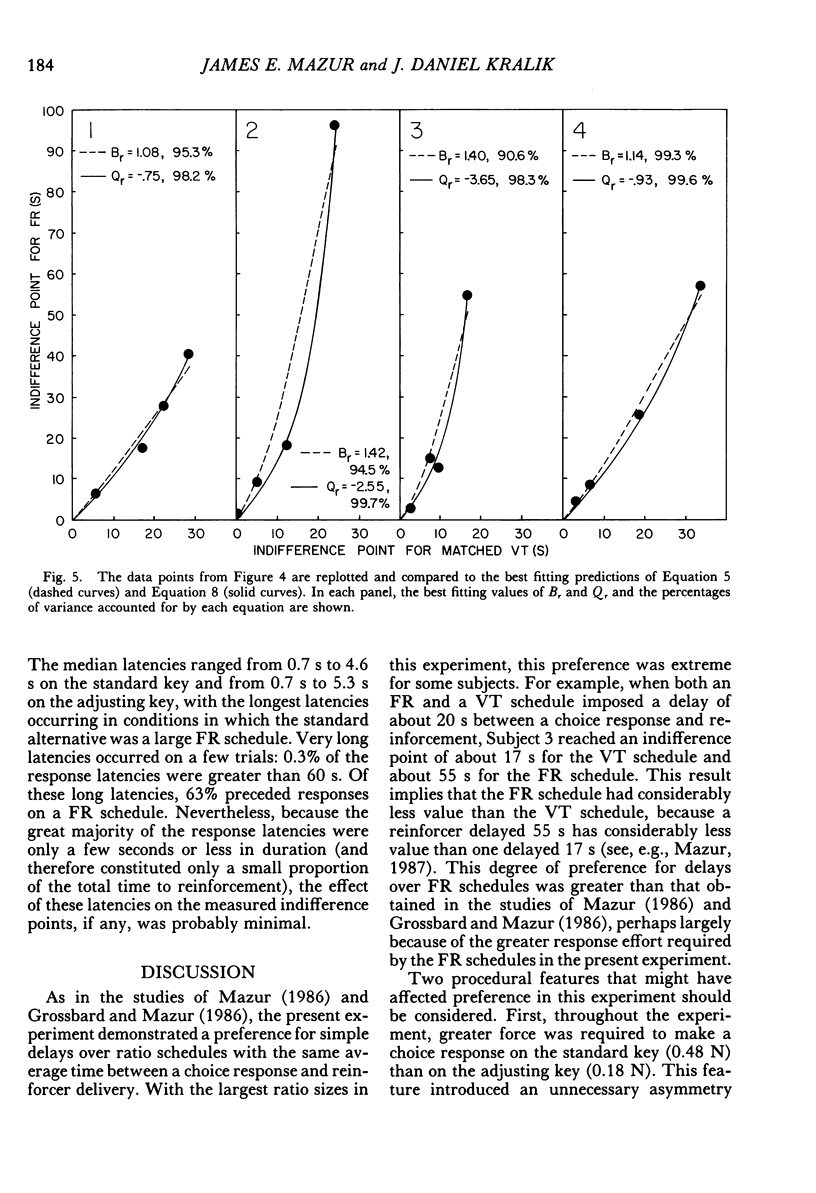
This experiment measured pigeons' choices between delayed reinforcers and fixed-ratio schedules in which a force of approximately 0.48 N was needed to operate the response key. In ratio-delay conditions, subjects chose between a fixed-ratio schedule and an adjusting delay. The delay was increased or decreased several times a session in order to estimate an indifference point--a delay duration at which the two alternatives were chosen about equally often. Each ratio-delay condition was followed by a delay-delay condition in which subjects chose between the adjusting delay and a variable-time schedule, with the components of this schedule selected to match the ratio completion times of the preceding ratio-delay condition. The adjusting delays at the indifference point were longer when the alternative was a fixed-ratio schedule than when it was a matched variable-time schedule, which indicated a preference for the matched variable-time schedules over the fixed-ratio schedules. This preference increased in a nonlinear manner with increasing ratio size. This nonlinearity was inconsistent with a theory that states that indifference points for both time and ratio schedules can be predicted by multiplying the choice response-reinforcer intervals of the two types of schedules by different multiplicative constants. Two other theories, which predict nonlinear increases in preference for the matched variable-time schedules, are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPEL J. B. Aversive aspects of a schedule of positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:423–428. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman E. K., Heaps R. S., Nunes D. L., Alferink L. A. The effects of number of responses on pause length with temporal variables controlled. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):115–120. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C. Preference for mixed-interval versus fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):247–252. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Snyderman M. Choice between rewards differing in amount and delay: Toward a choice model of self control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):135–147. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard C. L., Mazur J. E. A comparison of delays and ratio requirements in self-control choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 May;45(3):305–315. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logue A. W., Rodriguez M. L., Peña-Correal T. E., Mauro B. C. Choice in a self-control paradigm: Quantification of experience-based differences. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Jan;41(1):53–67. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur J. E. Fixed and variable ratios and delays: further tests of an equivalence rule. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1986 Apr;12(2):116–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur J. E. Probability and delay of reinforcement as factors in discrete-trial choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):341–351. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. L. Matching-based hedonic scaling in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):335–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Schneider B. A. Separating the effects of interreinforcement time and number of interreinforcement responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):661–667. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider D. P. Preference for mixed versus constant delays of reinforcement: Effect of probability of the short, mixed delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):257–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan W. Choice: A local analysis. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):383–405. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


