Abstract
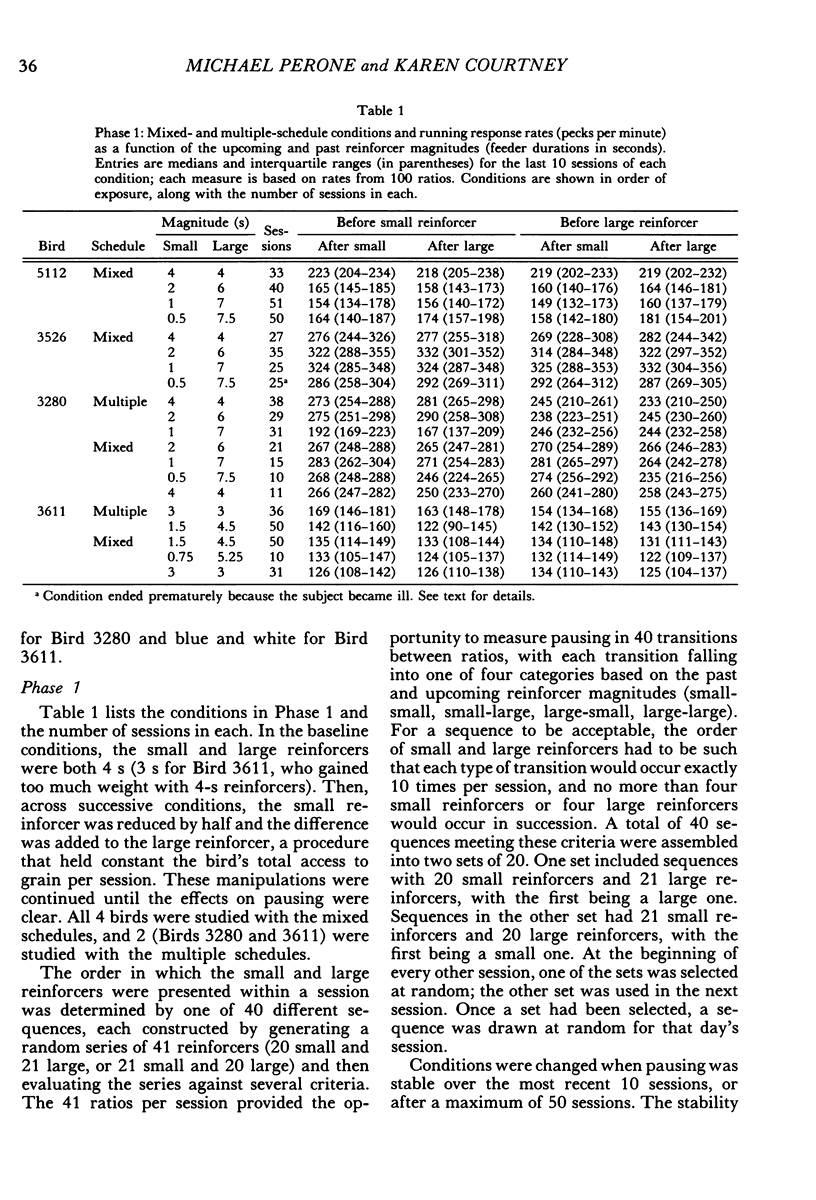
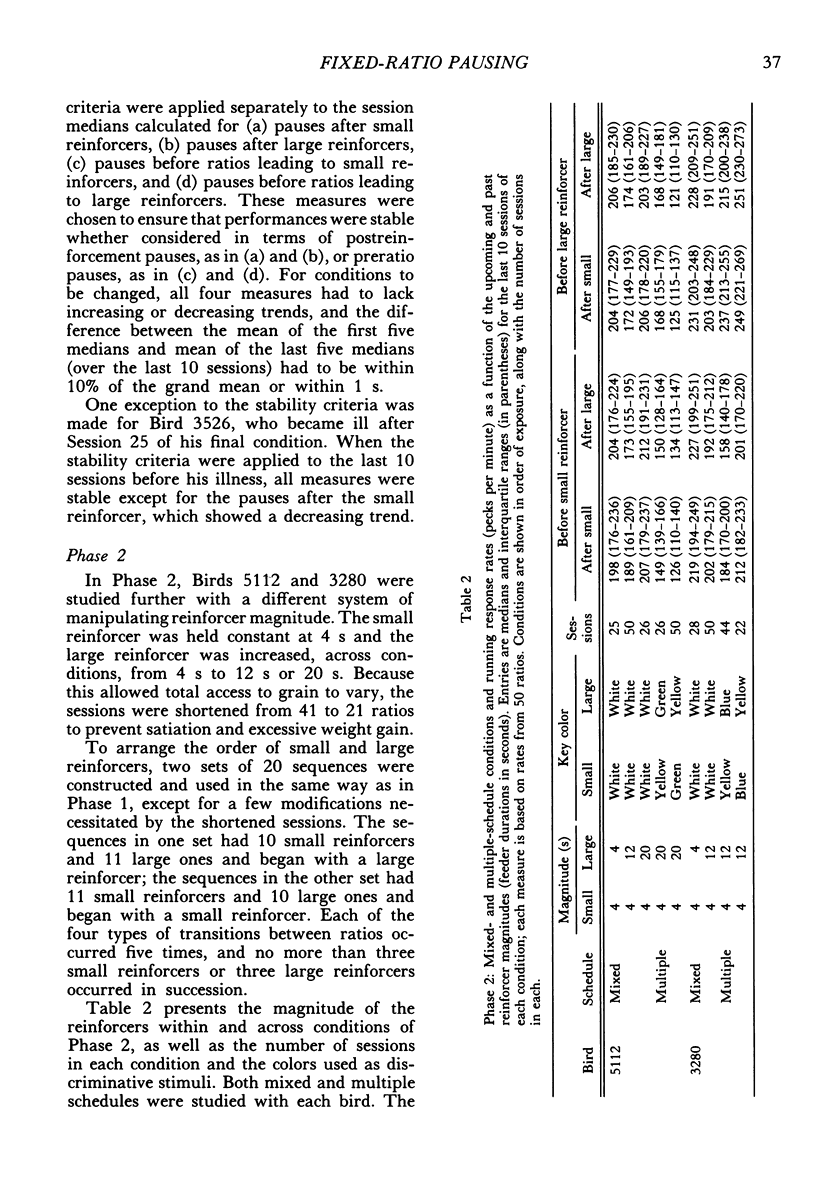
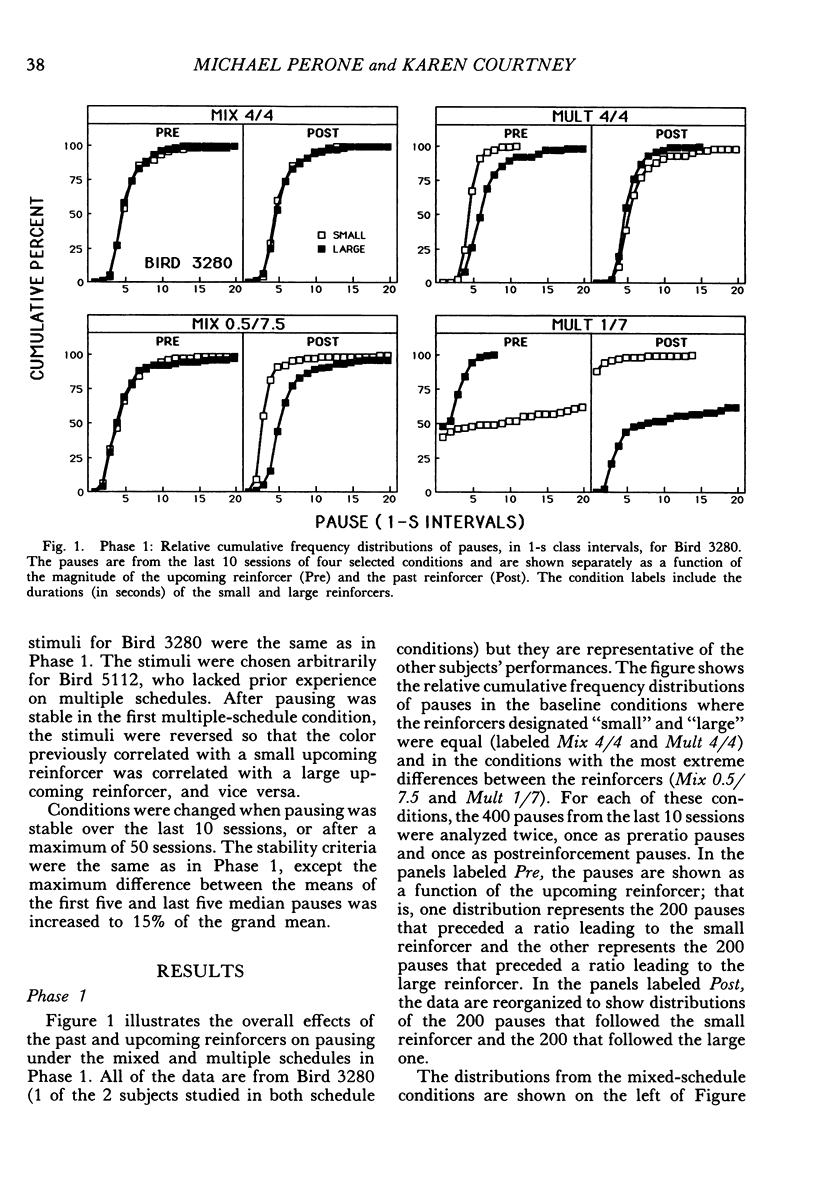
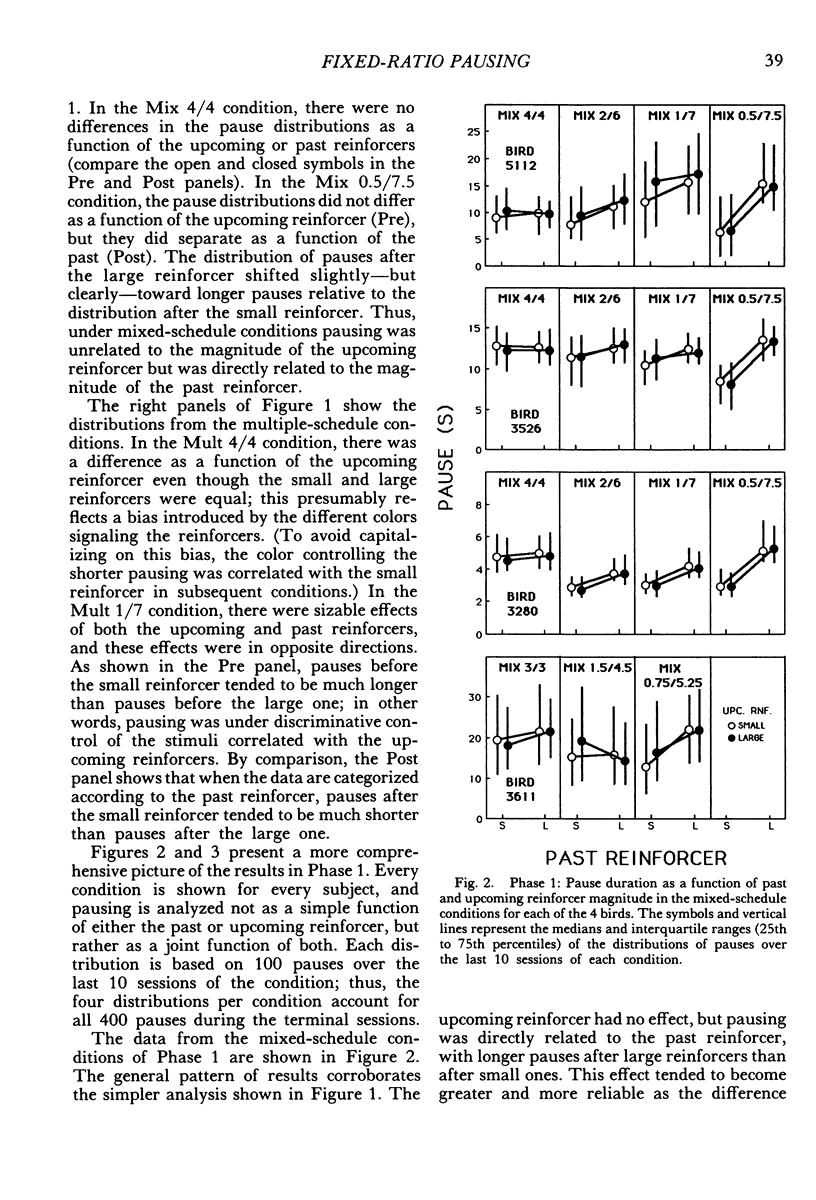
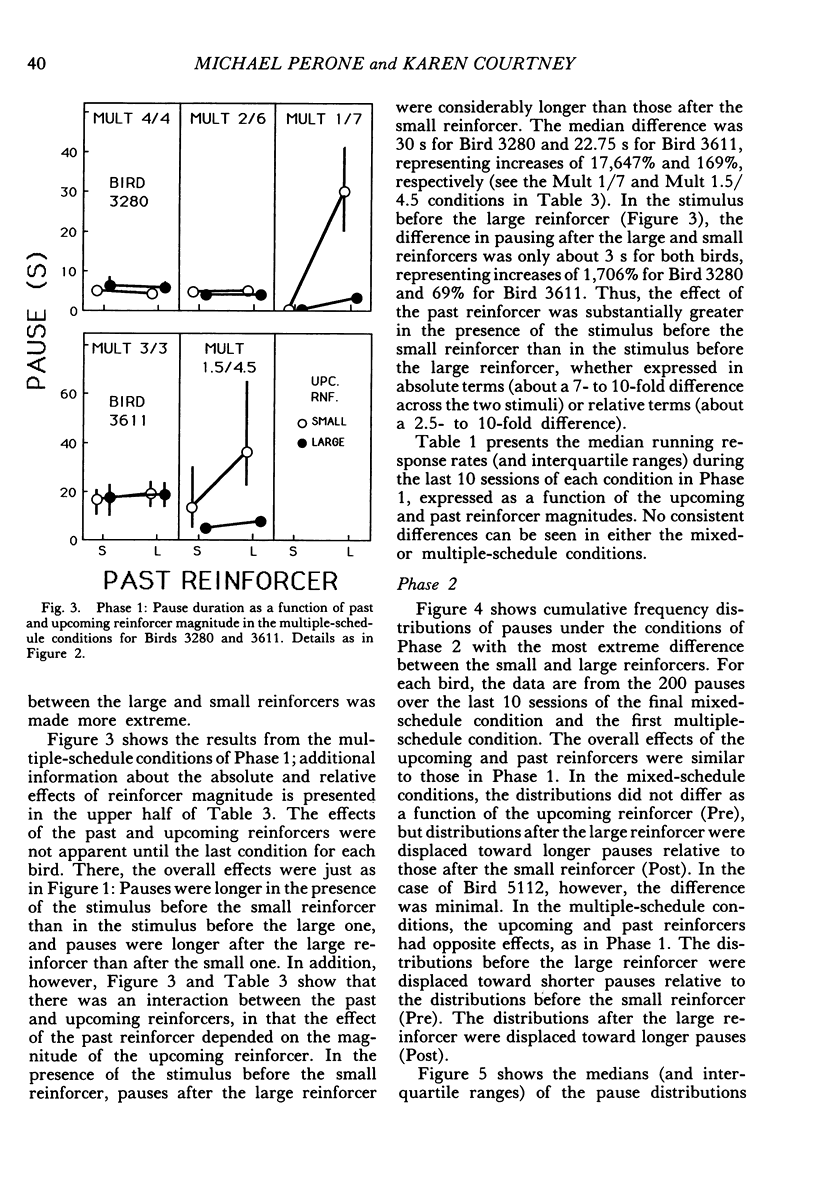
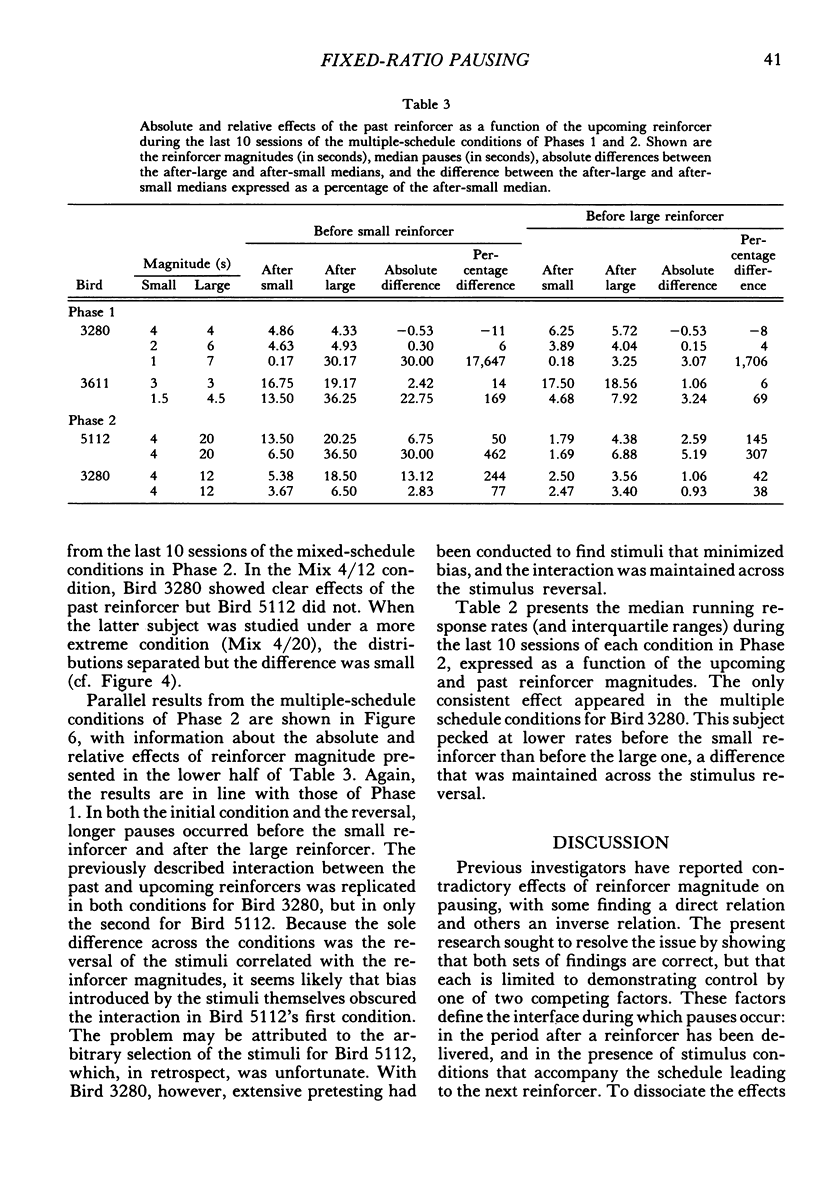
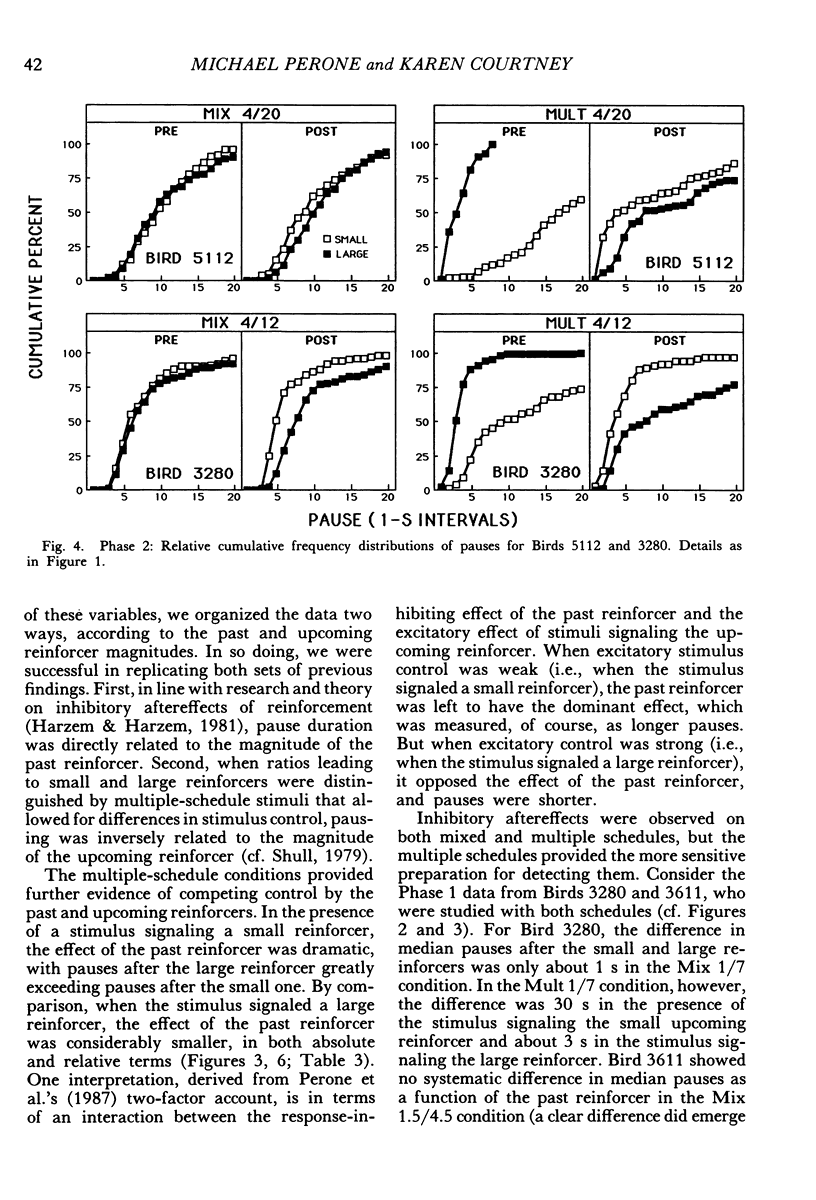
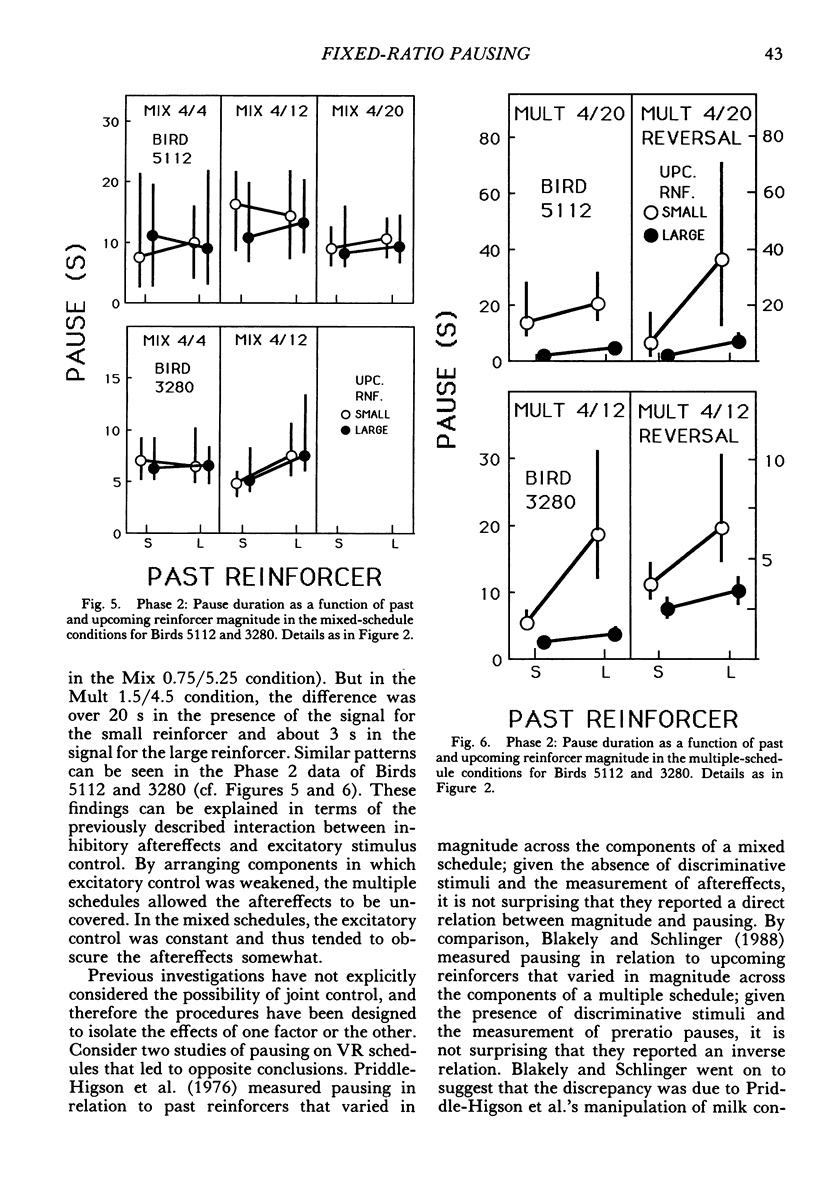
Pigeons responded on fixed-ratio schedules ending in small or large reinforcers (grain presentations of different duration) interspersed within each session. In mixed-schedule conditions, the response key was lit with a single color throughout the session, and pausing was directly related to the past reinforcer (longer pauses after large reinforcers than after small ones). In multiple-schedule conditions, different colors accompanied the ratios ending in small and large reinforcers, and pausing was affected by the upcoming reinforcer as well as the past one. Pauses were shorter before large reinforcers than before small ones, but they continued to be longer after large reinforcers than after small ones. The influence of the past reinforcer was modulated by the magnitude of the upcoming reinforcer; in the presence of the stimulus before the small reinforcer, the effect of the past reinforcer was enhanced relative to its effect in the stimulus before the large reinforcer. These results show that pausing between ratios is jointly determined by two competing factors: past conditions of reinforcement and stimuli correlated with upcoming conditions.
Keywords: preratio pause, postreinforcement pause, reinforcer magnitude, fixed-ratio schedules, stimulus control, inhibitory aftereffects of reinforcement, contrast, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Felton M., Lyon D. O. The post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):131–134. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harzem P., Lowe C. F., Priddle-Higson P. J. Inhibiting function of reinforcement: magnitude effects on variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jul;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C., Fallon D. Behavioral aftereffects of reinforcement and its omission as a function of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):459–468. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. Reinforcement frequency and contingency as factors in fixed-ratio behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):391–395. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Davey G. C., Harzem P. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on interval and ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):553–560. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Harzem P. Species differences in temporal control of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Nov;28(3):189–201. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigson H. W., Gay R. A. An investigation of conditions determining contrast effects in differential reward conditioning. J Exp Psychol. 1967 Sep;75(1):37–42. doi: 10.1037/h0024917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R. W. The effect of reinforcement magnitude upon responding under fixed-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):605–608. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R. W. The effect of small sequential changes in fixed-ratio size upon the post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):589–593. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priddle-Higson P. J., Lowe C. F., Harzem P. Aftereffects of reinforcement on variable-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):347–354. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider D. P., Kametani N. N. Interreinforcement time, work time, and the postreinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Sep;42(2):305–319. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlinger H., Blakely E., Kaczor T. Pausing under variable-ratio schedules: Interaction of reinforcer magnitude, variable-ratio size, and lowest ratio. J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 Jan;53(1):133–139. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.53-133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Effect of reinforcement duration on fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jan;13(1):9–11. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. Another look at contrast in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):345–384. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. The following schedule of reinforcement as a fundamental determinant of steady state contrast in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 May;35(3):293–310. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


