Abstract
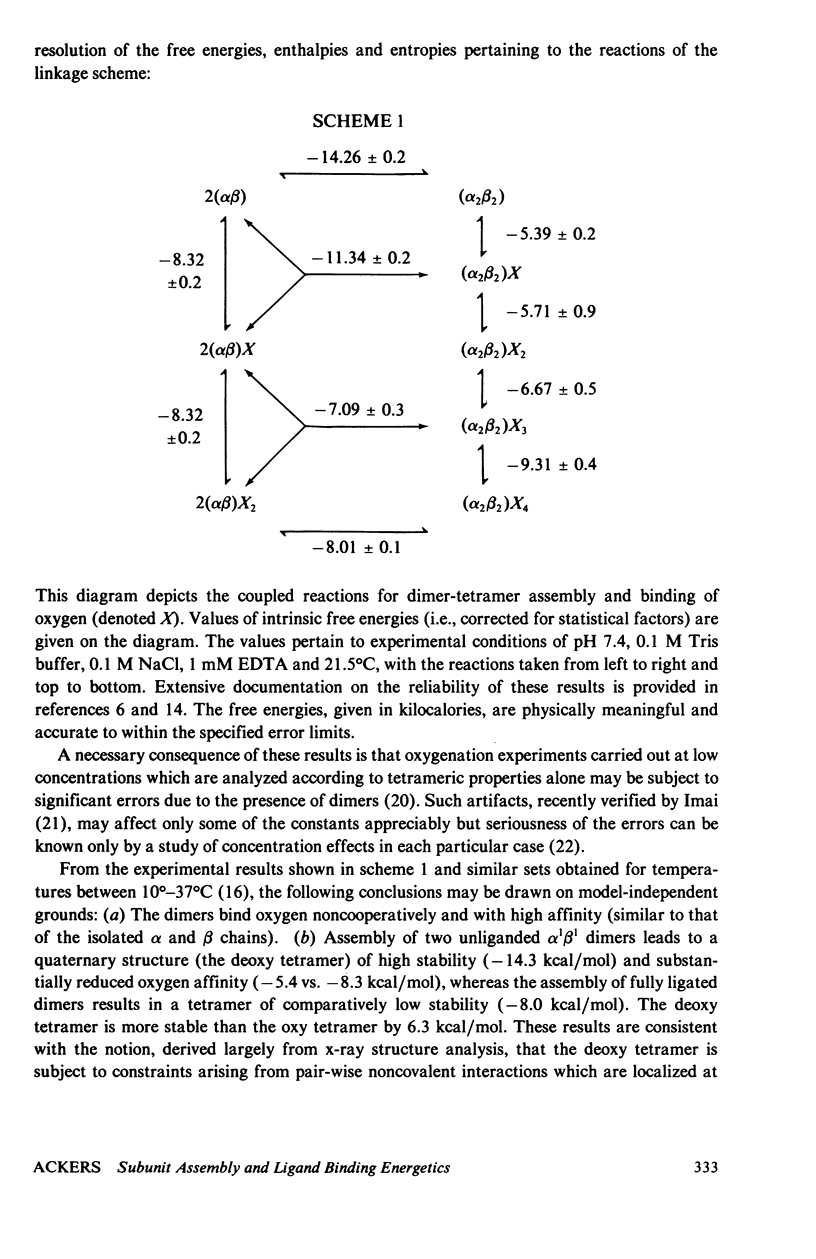
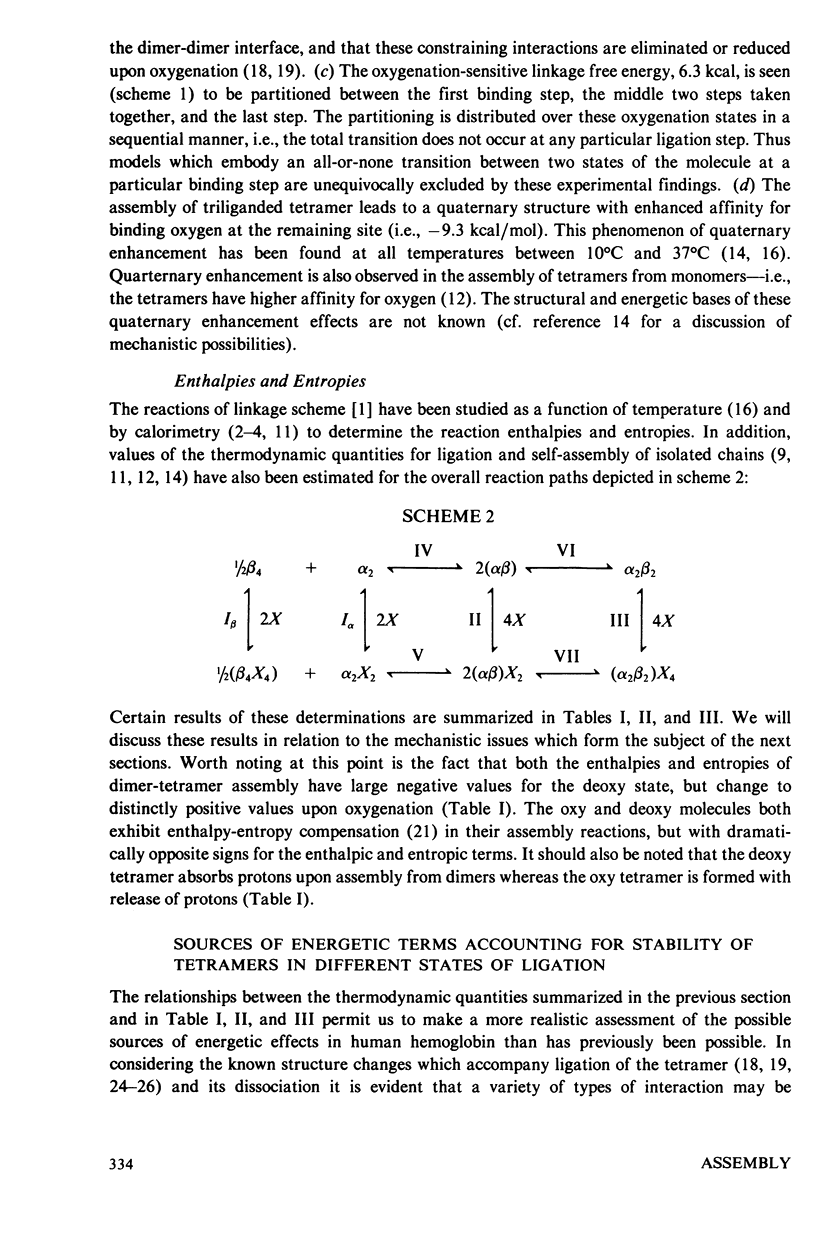
An extensive and self-consistent set of thermodynamic properties has recently been established for the coupled processes of subunit assembly and ligand binding (oxygen and protons) in human hemoglobin. The resulting thermodynamic values permit a consideration of the possible sources of energetic terms accounting for stability of the tetrameric quaternary structures at different stages of ligation, and of the possible sources of cooperative energy. The analysis indicates that: (a) The change in buried surface ara upon oxygenation (i.e., hydrophobic stabilization) does not play a dominant role in stabilizing the unliganded tetramer relative to the liganded tetramer. (b) The pattern of enthalpic and entropic contributions to the free energies of dimer-tetramer. (c) The thermodynamic results are consistent with a dominant role of increased hydrogen bond formation in the deoxy quaternary structure. (d) Within tetramers the variation in free energy for successive oxygenation steps arises from both enthalpic and entropic contributions and the enthalpic contributions are almost entirely attributable to the heats of Bohr proton release. At pH 7.4 the pattern of thermodynamic values suggests that a large contribution to the free energy of cooperativity may arise from the energetics of Bohr proton release. It is suggested that a combination of proton ionization and hydrogen bonding may account for the main energetic features of cooperativity. Possible contributions from fluctuation behavior cannot presently be evaluated.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONINI E., WYMAN J., BRUNORI M., FRONTICELLI C., BUCCI E., ROSSI-FANELLI A. STUDIES ON THE RELATIONS BETWEEN MOLECULAR AND FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES OF HEMOGLOBIN. V. THE INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON THE BOHR EFFECT IN HUMAN AND IN HORSE HEMOGLOBIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackers G. K., Halvorson H. R. The linkage between oxygenation and subunit dissociation in human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atha D. H., Ackers G. K. Calorimetric determination of the heat of oxygenation of human hemolgobin as a function of pH and the extent of reaction. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2376–2383. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J., Chothia C. Haemoglobin: the structural changes related to ligand binding and its allosteric mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):175–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzinger T. H. Thermodynamics, chemical reactions and molecular biology. Nature. 1971 Jan 8;229(5280):100–102. doi: 10.1038/229100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield J. R., Rossi-Bernardi L., Roughton F. J. Direct calorimetric studies on the heats of ionization of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):777–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Janin J. Principles of protein-protein recognition. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):705–708. doi: 10.1038/256705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Wodak S., Janin J. Role of subunit interfaces in the allosteric mechanism of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3793–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermi G. Three-dimensional fourier synthesis of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 2-5 A resolution: refinement of the atomic model. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R. Conformational equilibria in -and -chymotrypsin. The energetics and importance of the salt bridge. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(2):497–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaud H. T., Barisas B. G., Gill S. J. Enthalpy changes for hemoglobin-ligand interactions: revised calorimetric data. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1389–1394. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaud H. T., Gill S. J., Barisas B. G., Gersonde K. Heats of carbon monoxide binding by hemoglobin M Iwate. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4584–4589. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gersonde K., Noll L., Gaud H. T., Gill S. J. A calorimetric study of the CO Bohr effect of monomeric haemoglobins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):577–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K. Thermodynamic aspects of the co-operativity in four-step oxygenation equilibria of haemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 15;133(2):233–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip S. H., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on subunit assembly in human hemoglobin. Temperature dependence of the dimer-tetramer association constants for oxygenated and unliganded hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):82–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Ackers G. K. Resolvability of Adair constants from oxygenation curves measured at low hemoglobin concentration. Biophys Chem. 1977 Jun;7(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)87017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Halvorson H. R., Ackers G. K. Oxygenation-linked subunit interactions in human hemoglobin: analysis of linkage functions for constituent energy terms. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5363–5371. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Imai K., Jones R. T., Faruqui A. R., Fogg J., Baldwin J. M. Role of Bohr group salt bridges in cooperativity in hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 24;534(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladner R. C., Heidner E. J., Perutz M. F. The structure of horse methaemoglobin at 2-0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):385–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumry R., Rajender S. Enthalpy-entropy compensation phenomena in water solutions of proteins and small molecules: a ubiquitous property of water. Biopolymers. 1970;9(10):1125–1227. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360091002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Ackers G. K., Gaud H. T., Gill S. J. Thermodynamic studies on ligand binding and subunit association of human hemoglobins. Enthalpies of binding O2 and CO to subunit chains of hemoglobin A. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2875–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Ackers G. K. Quaternary enhancement in binding of oxygen by human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on the oxygenation and subunit association of human hemoglobin. Temperature dependence of the linkage between dimer-tetramer association and oxygenation state. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2881–2887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Johnson M. L., Ackers G. K. Oxygenation-linked subunit interactions in human hemoglobin: experimental studies on the concentration dependence of oxygenation curves. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5350–5362. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2211–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):726–739. doi: 10.1038/228726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Structure and mechanism of haemoglobin. Br Med Bull. 1976 Sep;32(3):195–208. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemeyer M. A., Huehns E. R. On the mechanism of the dissociation of haemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):253–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph S. A., Boyle S. O., Dresden C. F., Gill S. J. A calorimetric study of the binding of carbon monoxide to myoglobin. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):1098–1101. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saroff H. A., Minton A. P. The Hill plot and the energy of interaction in hemoglobin. Science. 1972 Mar 17;175(4027):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4027.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder E., Wollmer A., Kubicki J., Ohlenbusch H. D. Proton-dependent dissociation equilibrium of hemoglobin. 1. A 700-nanometer light-scattering study on horse methemoglobin in the pH range 4.8 to 7.2. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5693–5697. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. M. Heat capacity and entropy changes in processes involving proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes R., Jr, Ackers G. K. Self-association of hemoglobin betaSH chains is linked to oxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):311–314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes R., Jr, Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on subunit assembly in human hemoglobin. Self-association of oxygenated chains (alphaSH and betaSH): determination of stoichiometries and equilibrium constants as a function of temperature. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):74–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes R., Jr, Vickers L. P., Halvorson H. R., Ackers G. K. Reciprocal effects in human hemoglobin: direct measurement of the dimer-tetramer association constant at partial oxygen saturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5493–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr LINKED FUNCTIONS AND RECIPROCAL EFFECTS IN HEMOGLOBIN: A SECOND LOOK. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:223–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


