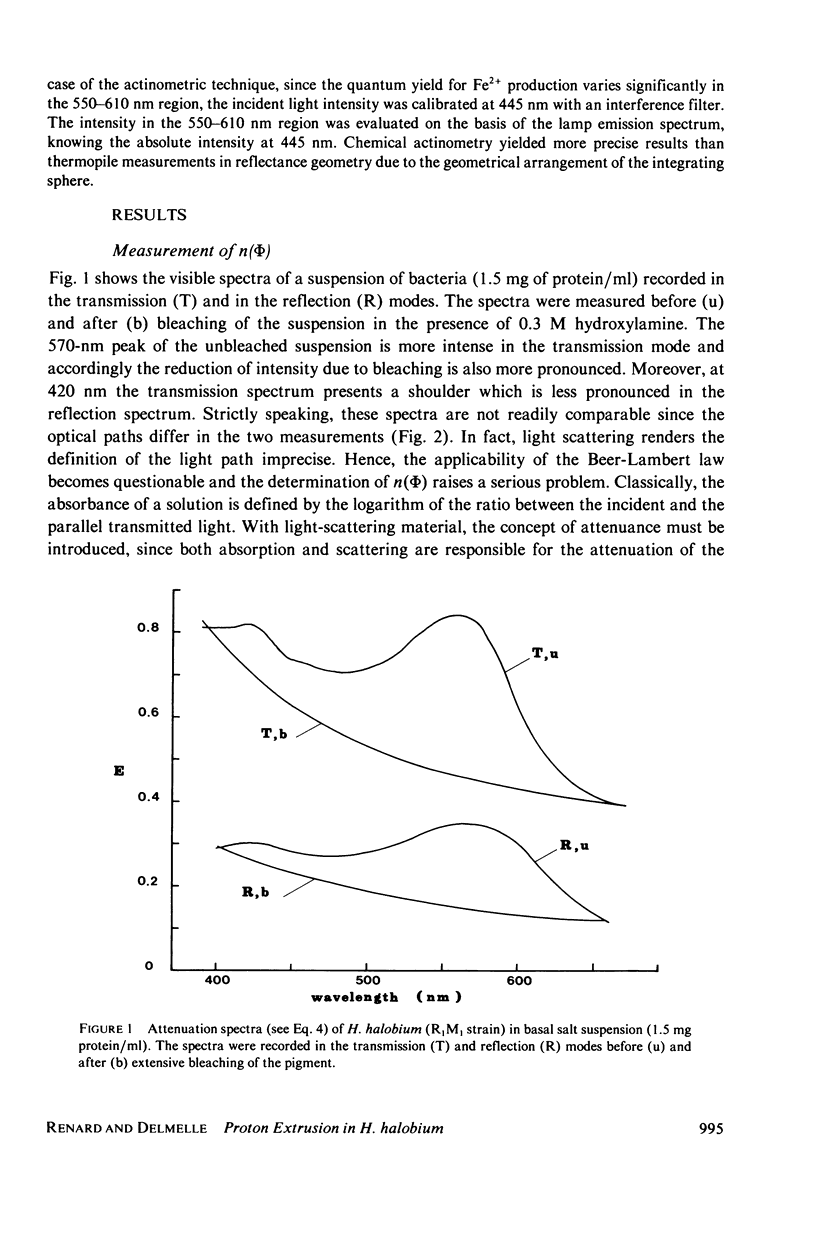
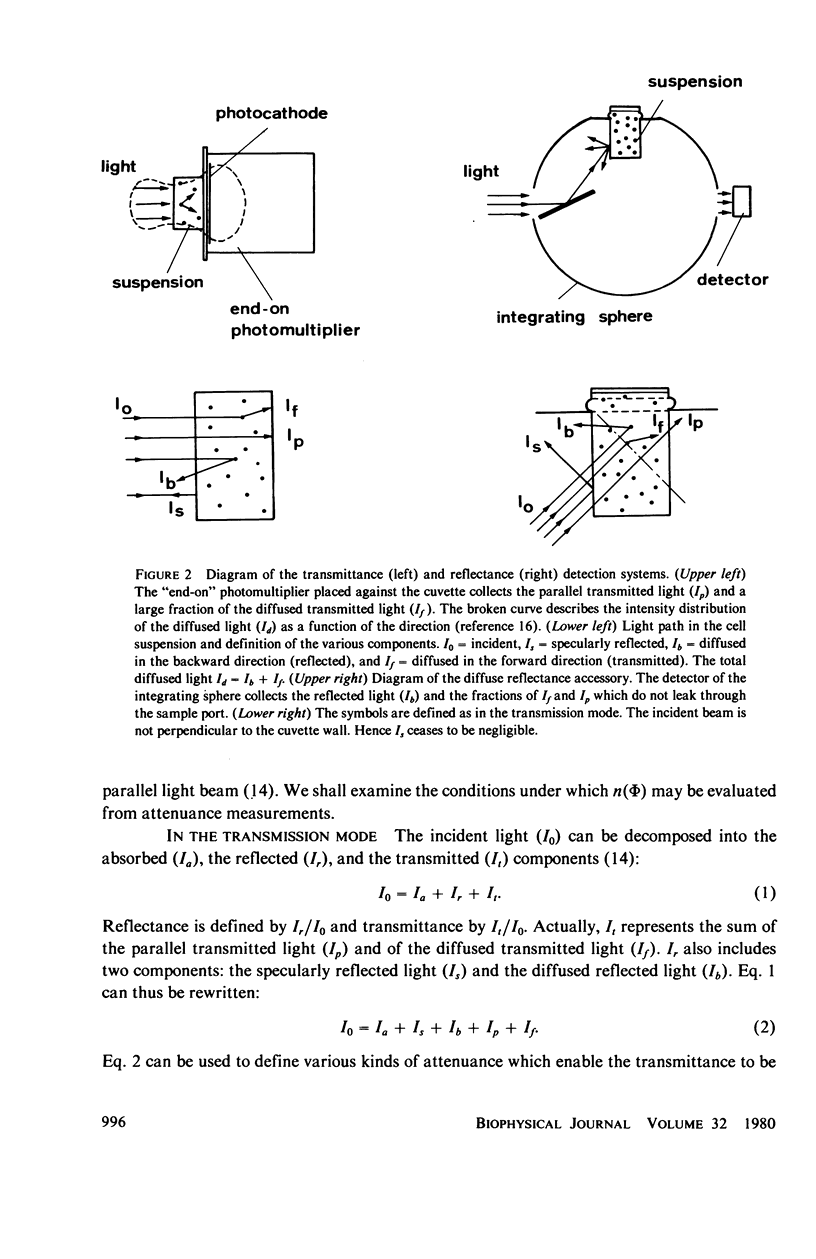
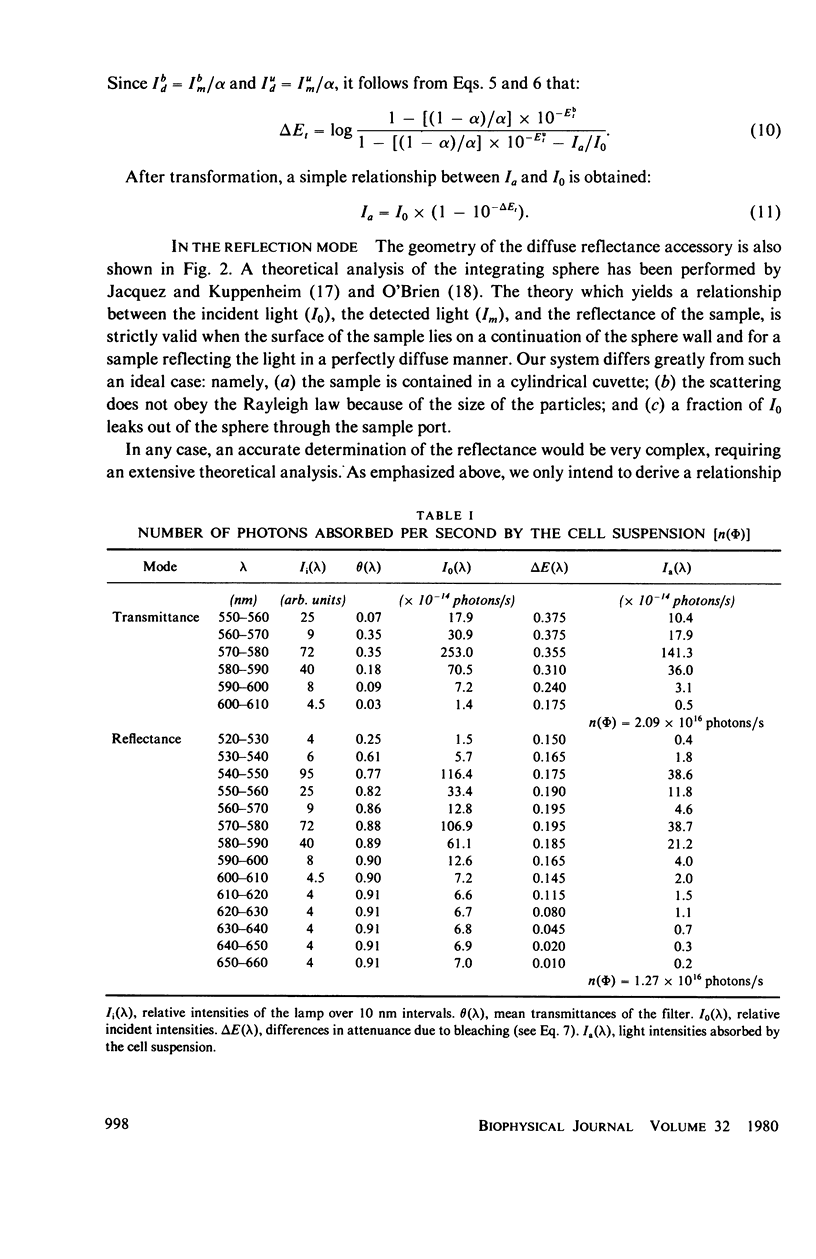
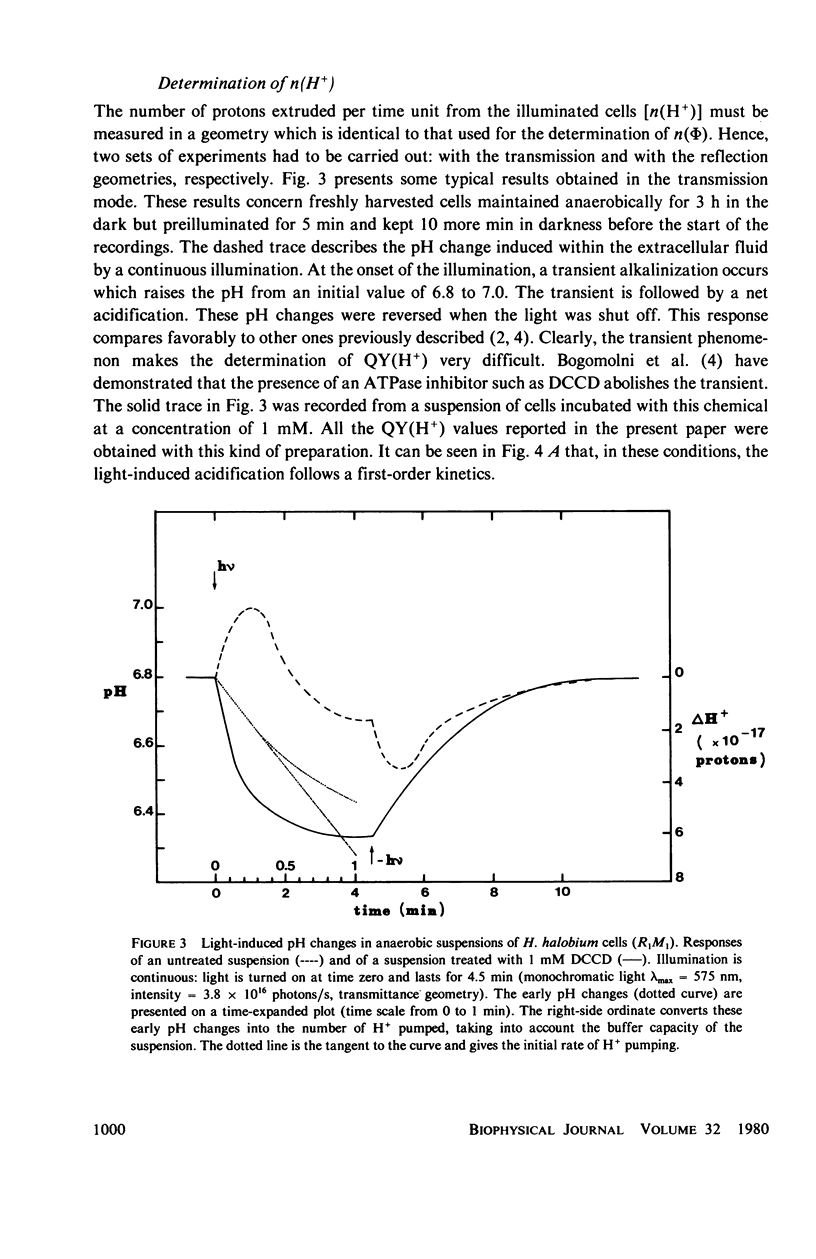
Abstract
The quantum yield for light-induced proton extrusion in Halobacterium halobium cells pretreated with an ATPase inhibitor was measured between pH 5 and 9 using two separate spectrophotometric techniques. The transmittance of the cell suspension was measured with a spectrometer equipped with "end-on" photomultipliers, whereas the reflectance was measured using a light-integrating sphere. The potentialities of the two techniques are critically compared. These measurements are used to evaluate the intensities of light absorbed by the cells. Since the initial rates of proton release into the extracellular medium were simultaneously measured, the quantum yield values [QY(H+)] could be determined. The results obtained with the two techniques are in reasonable agreement. QY(H+) is 0.64 at pH 5.9 and decreases gradually to 0.28 at alkaline pH values.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Rottenberg H., Caplan S. R. An estimation of the light-induced electrochemical potential difference of protons across the membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):557–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B., Cassim J. Y. Effects of bleaching and regeneration on the purple membrane structure of Halobaterium halobium. Biophys J. 1977 Sep;19(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(77)85588-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B., Ebrey T. G. The quantum efficiency for the photochemical conversion of the purple membrane protein. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85636-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Baker R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Light-driven proton translocations in Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 9;440(1):68–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A. Light energy conservation processes in Halobacterium halobium cells. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1833–1839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Caplan S. R. Stimulation of ATP synthesis in Halobacterium halobium R1 by light-induced or artifically created proton electrochemical potential gradients across the cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 15;423(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Garty H., Bakker E. P., Klemperer G., Rottenberg H., Caplan S. R. Kinetic analysis of light-induced pH changes in bacteriorhodopsin-containing particles from Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4691–4698. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Klemperer G., Eisenbach M., Caplan S. R. The direction of light-induced pH changes in purple membrane suspensions. Influence of pH and temperature. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt C. R., Kalisky O., Rosenfeld T., Ottolenghi M. The quantum efficiency of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85635-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt C. R., Ottolenghi M., Korenstein R. On the primary quantum yields in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):839–843. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85732-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Ebrey T. G. Energy transfer in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85470-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Racker E. Light-dependent proton and rubidium translocation in membrane vesicles from Halobacterium halobium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):1054–1061. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., MacDonald R. E. Light-dependent cation gradients and electrical potential in Halobacterium halobium cell envelope vesicles. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1824–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Oesterhelt D. Light-induced changes of the pH gradient and the membrane potential in H. halobium. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Hess B. Reversible photolysis of the purple complex in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):316–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ort D. R., Parson W. W. The quantum yield of flash-induced proton release by bacteriorhodopsin-containing membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1979 Feb;25(2 Pt 1):341–353. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(79)85296-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Stoeckenius W. Reconstitution of purple membrane vesicles catalyzing light-driven proton uptake and adenosine triphosphate formation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):662–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


