Abstract
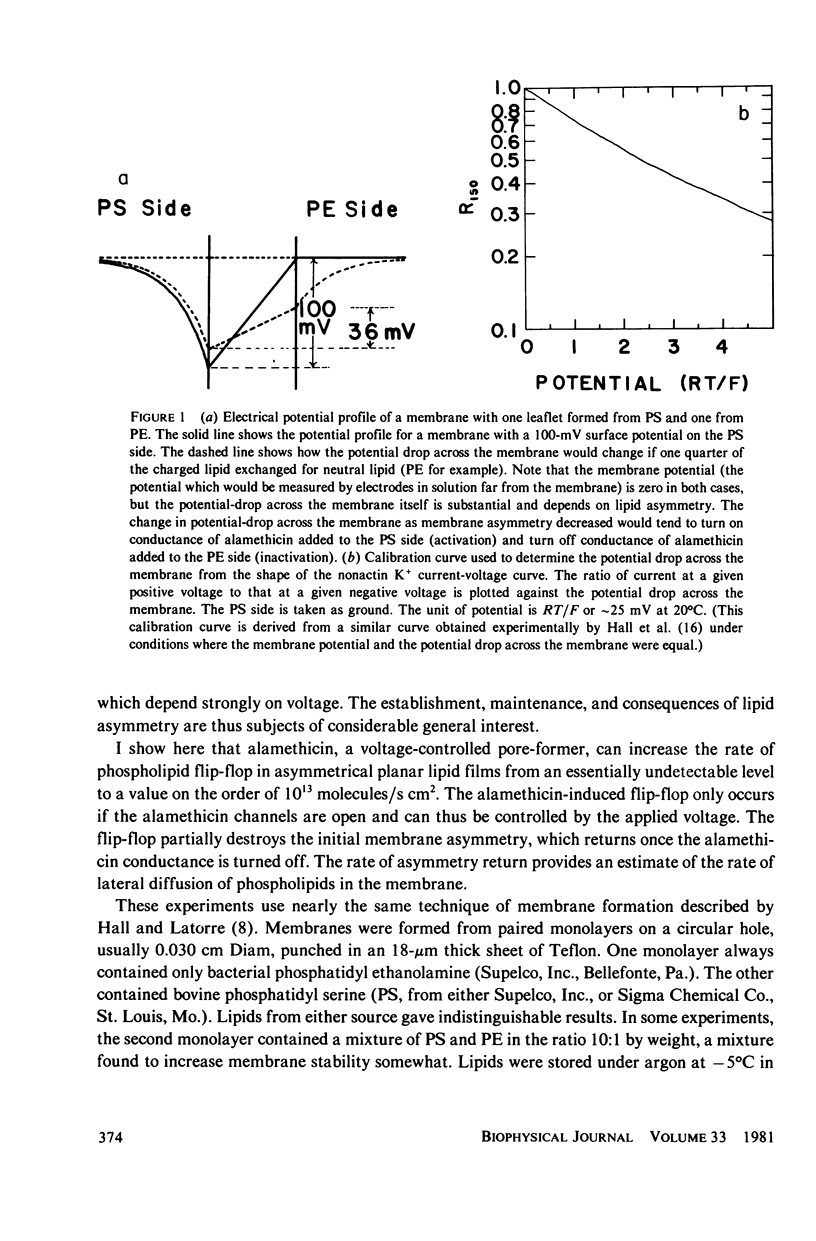
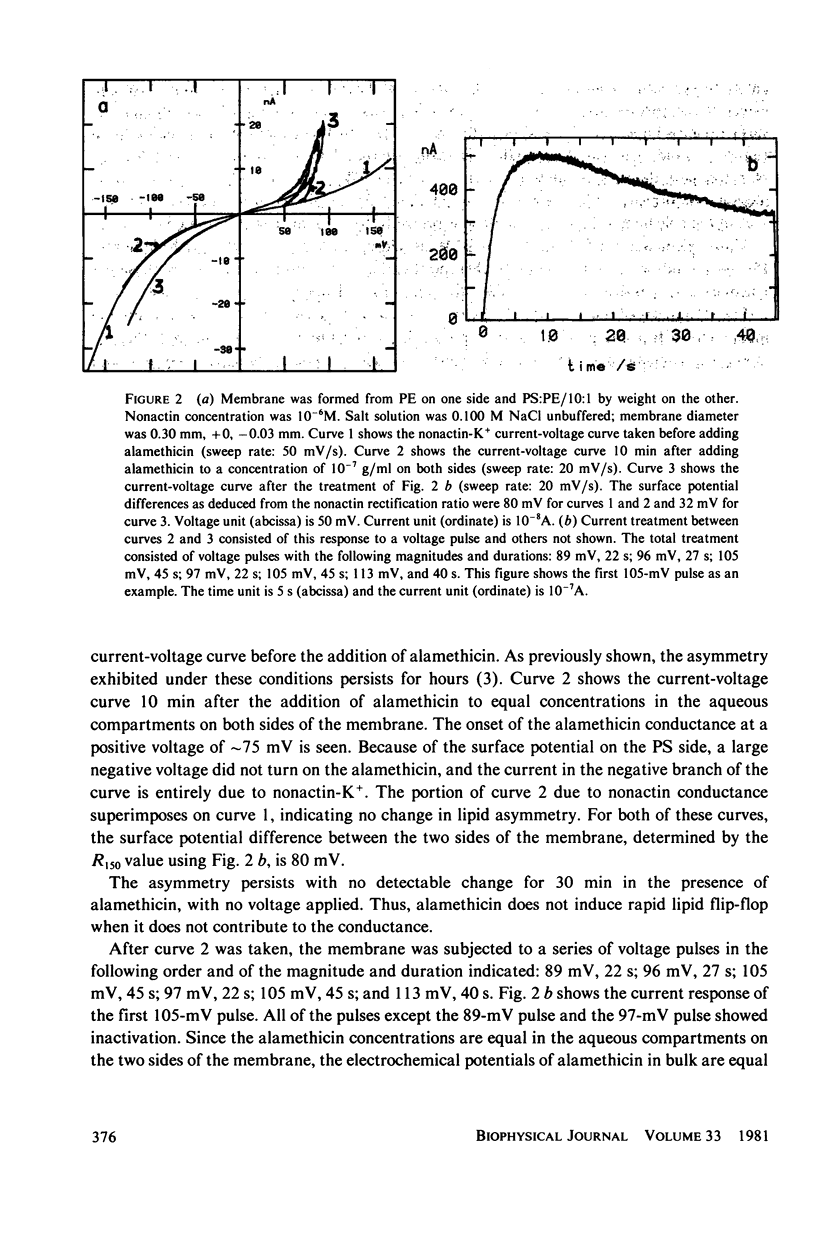
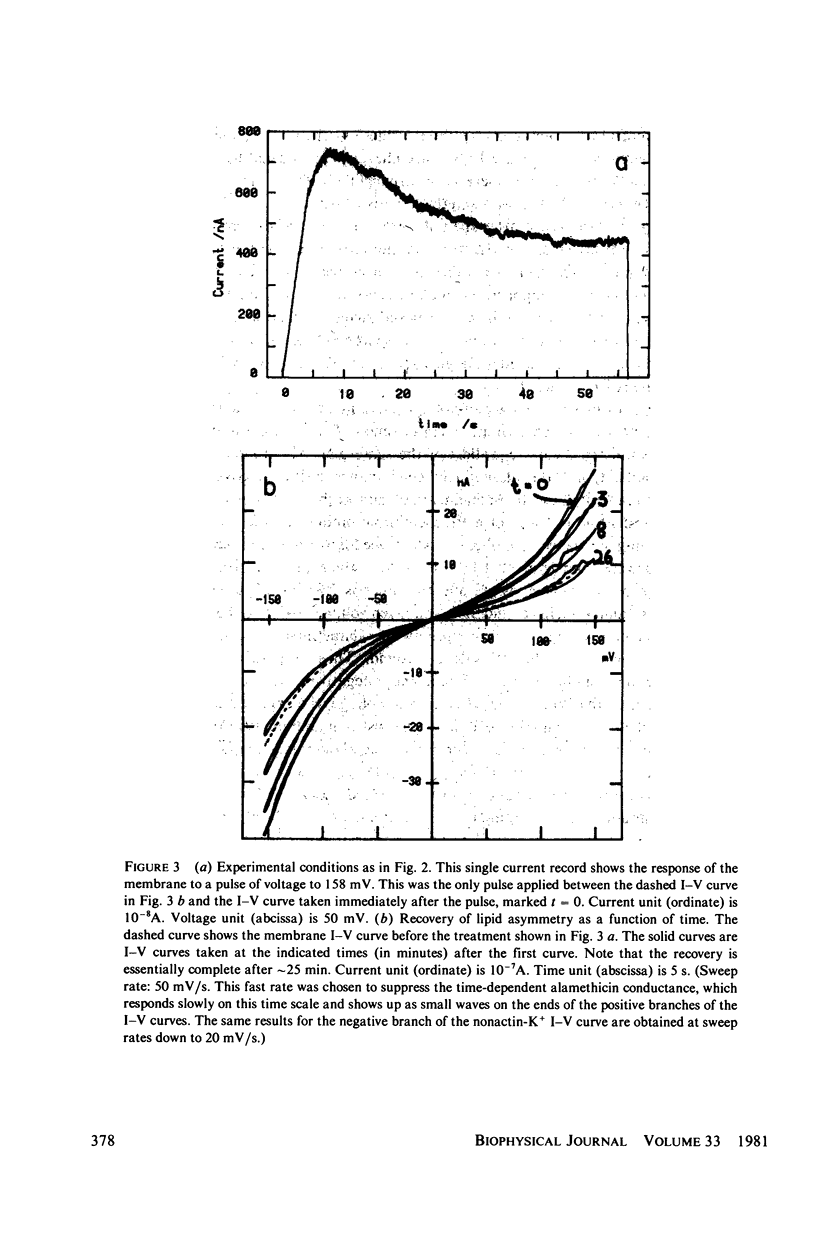
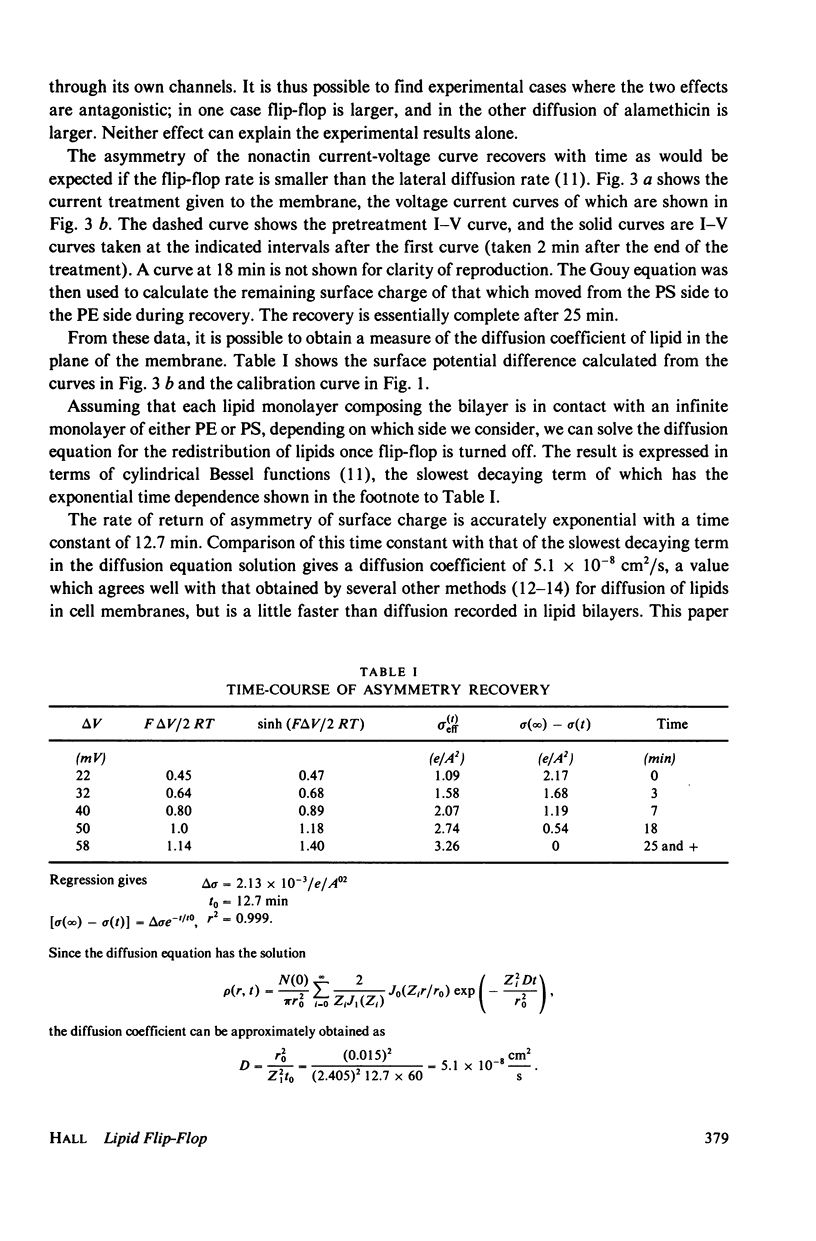
Alamethicin appears to allow voltage-dependent lipid exchange ("flip-flop") between leaflets of a planar bilayer. In membranes with one leaflet of phosphatidyl serine and one of phosphatidyl ethanolamine, the shape of the nonactin current-voltage curve accurately reports the difference in surface potential between the two sides of the membrane. The surface potential is itself a good measure of membrane asymmetry. Alamethicin added to the bathing solutions of an asymmetric membrane does not per se reduce the membrane asymmetry, but turning on the alamethicin conductance by application of a voltage pulse does. Immediately after application of a voltage pulse, large enough to turn on the alamethicin conductance, the asymmetry of the nonactin-K+ current voltage curve decreases, in some cases, nearly to zero. During the pulse, the alamethicin conductance activates if a decrease in surface potential favors turn-on of the alamethicin conductance or inactivates if a decrease in surface potential favors turn-off of the alamethicin conductance. After the pulse, the nonactin-K+ asymmetry returns to its original value if the alamethicin conductance is not turned on. The time-course of this return allows an estimate of the diffusion constant of lipid in the planar bilayer. The value obtained is 5.1 x 10(-8) cm2/s.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergelson L. D., Barsukov L. I. Topological asymmetry of phospholipids in membranes. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):224–230. doi: 10.1126/science.327544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. A., Moronne M. M. Interaction of charged lipid vesicles with planar bilayer lipid membranes: detection by antibiotic membrane probes. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(3):409–416. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. J., Latorre R. Inactivation of the alamethicin-induced conductance caused by quaternary ammonium ions and local anesthetics. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Apr;73(4):425–451. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.4.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg M., Hall J. E., Mead C. A. The nature of the voltage-dependent conductance induced by alamethicin in black lipid membranes. J Membr Biol. 1973 Dec 31;14(2):143–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01868075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. F., Koppel D. E., Barak L. S., Wolf D. E., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion in planar lipid bilayers. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):305–306. doi: 10.1126/science.831279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Latorre R. Nonactin-K+ complex as a probe for membrane asymmetry. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85667-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer R. J., Muller R. U., Finkelstein A. Inactivation of monazomycin-induced voltage-dependent conductance in thin lipid membranes. II. Inactivation produced by monazomycin transport through the membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):731–748. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Axelrod J. Identification and properties of two methyltransferases in conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1718–1721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Hall J. E. Dipole potential measurements in asymmetric membranes. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):361–363. doi: 10.1038/264361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Dawidowicz E. A. Asymmetric exchange of vesicle phospholipids catalyzed by the phosphatidylcholine exhange protein. Measurement of inside--outside transitions. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2809–2816. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Webb W. W., Elson E. L. Lateral transport of a lipid probe and labeled proteins on a cell membrane. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):307–309. doi: 10.1126/science.556653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood D., Montal M. Transmembrane lipid migration in planar asymmetric bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 2009 Jan 1;15(5):417–434. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85827-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


