Abstract
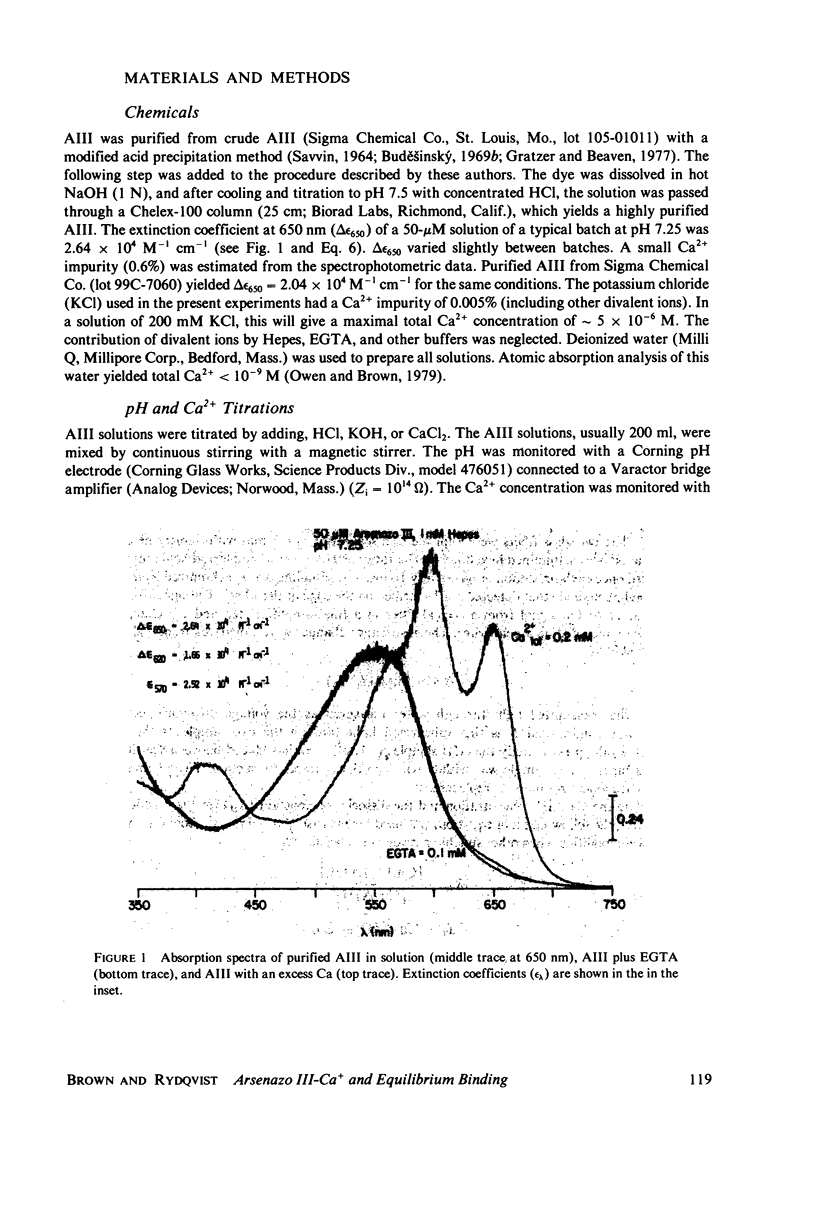
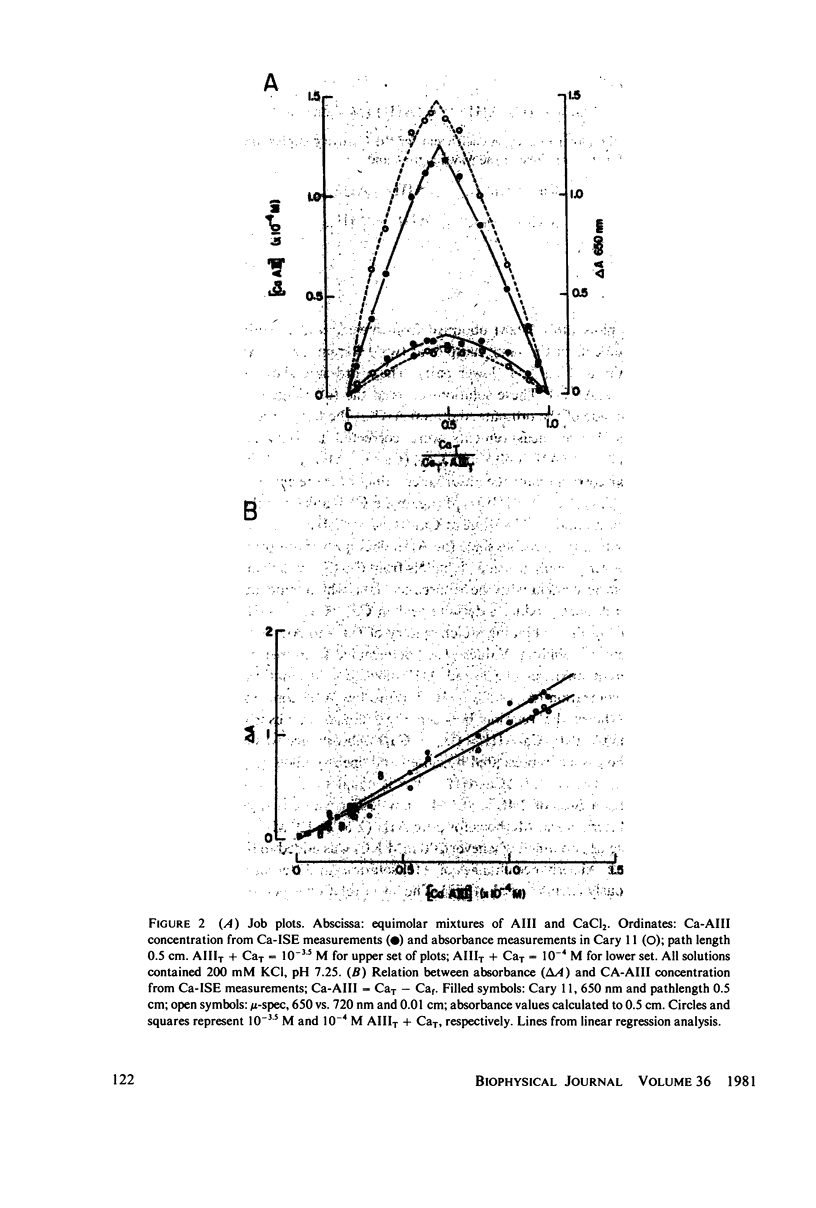
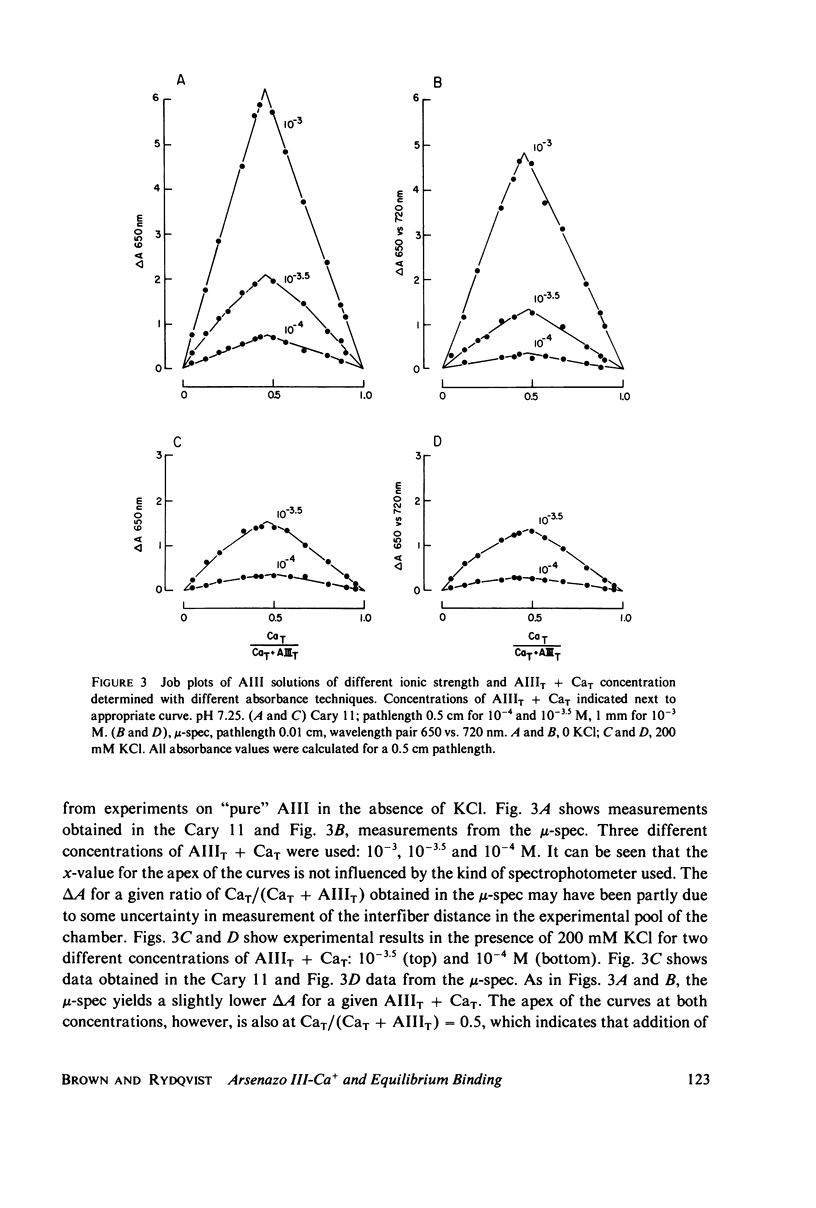
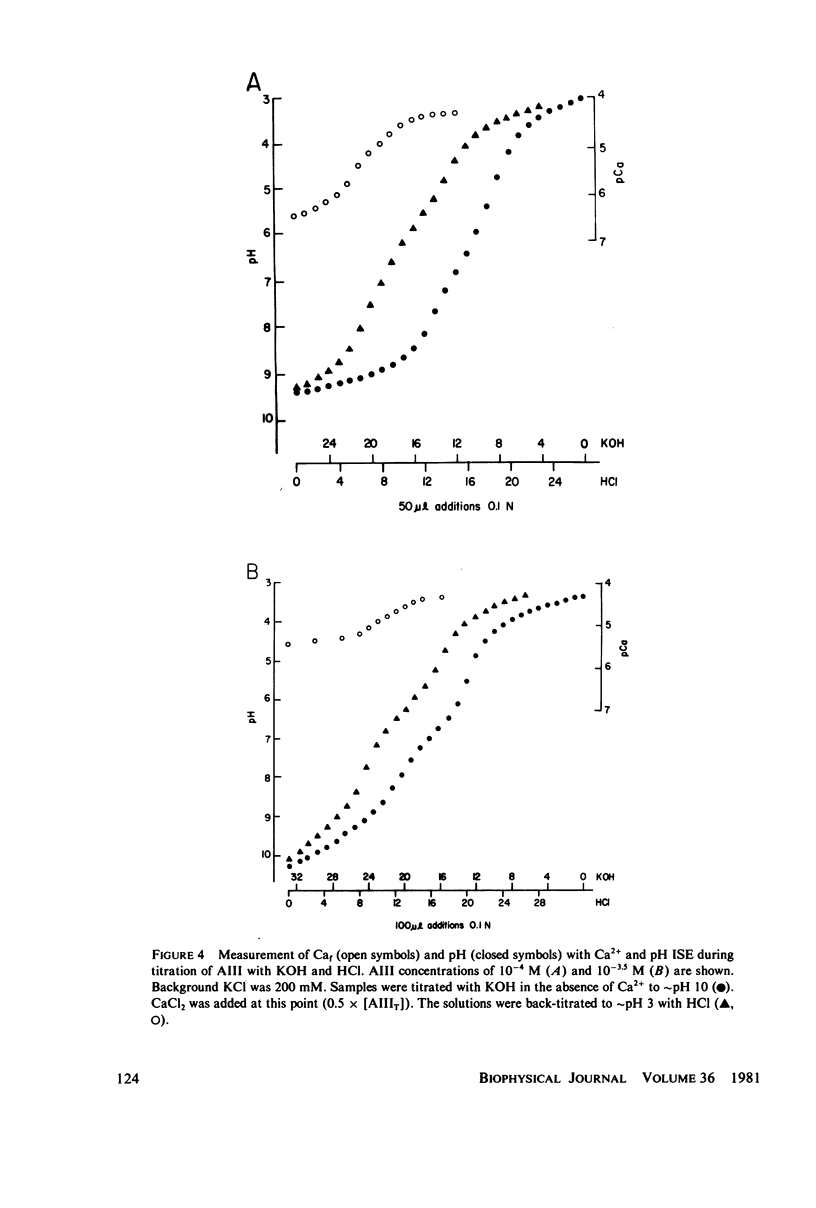
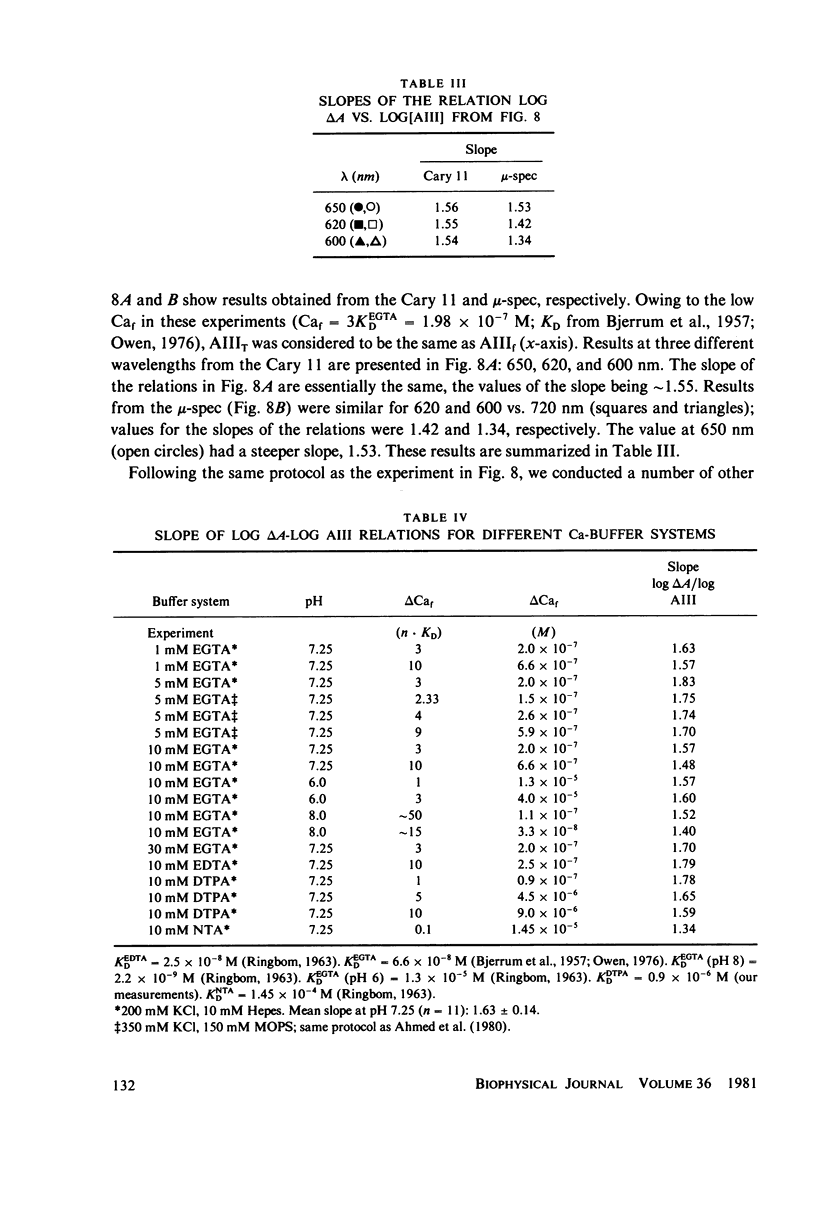
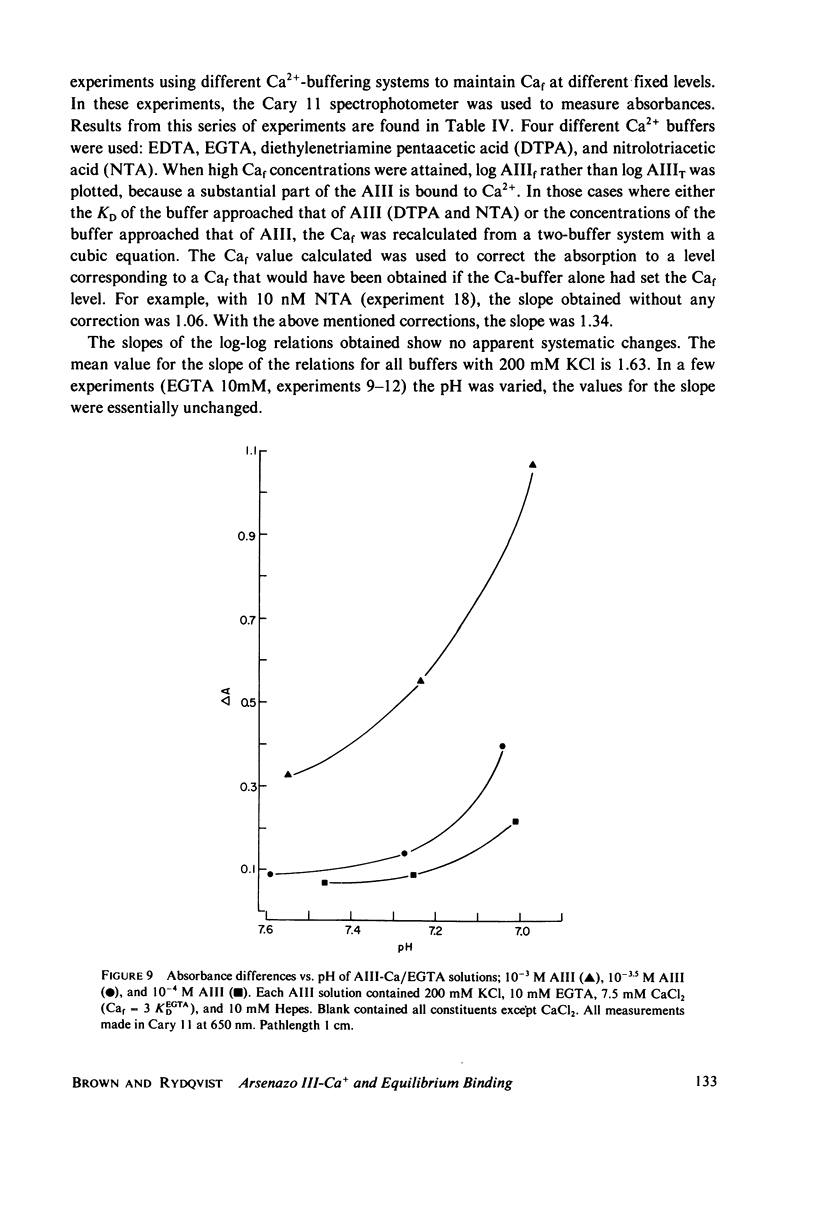
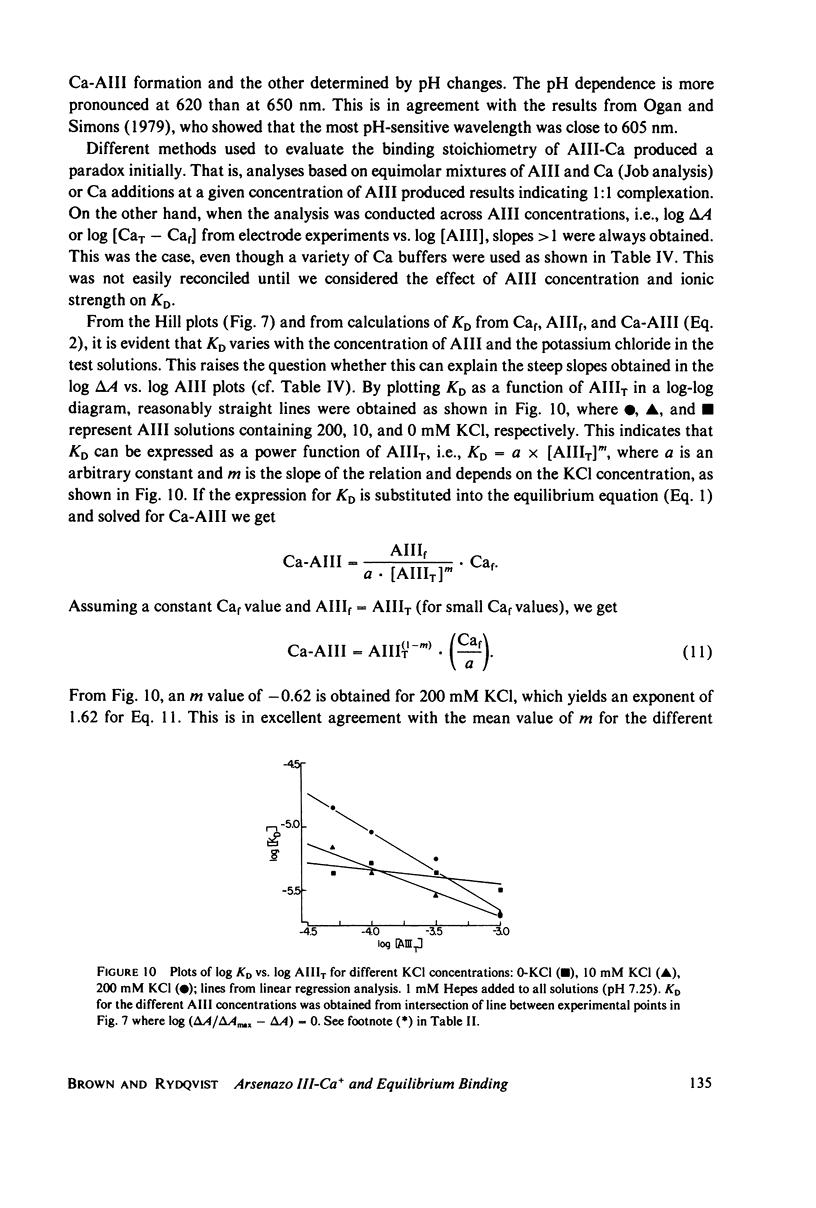
Equilibrium binding properties of the metallochromic indicator Arsenazo III (AIII) were characterized by Ca2+ and acid/base titration. Free calcium was measured directly with Ca2+ ion-sensitive electrodes. Absorbance changes were measured by both a conventional scanning spectrophotometer and a dual wavelength spectrophotometer. Acid/base titration of AIII in conjunction with Ca2+ ion-sensitive electrode measurement and absorbance changes indicate that pH can change AIII absorbance through a change of the K(D) for Ca-AIII formation, and, in addition, that there is a pH-specific component that is not dependent on Ca-AIII formation. THe dissociation constant (K(D)) of AIII varied not only with pH, but with ionic strength and AIII concentration. Studies conducted to examine AIII-Ca stoichiometry resulted in different initial conclusions, depending on the method of analysis. Log delta A-log AIII relations were in accord with previously published results, which indicate that more than one AII binds to one Ca2+ ion. But Job plots. Scatchard analysis, and Hill plots all indicated 1:1 binding. THe method of absorbance measurement, i.e., scanning or dual wavelength did not influence the results. these findings were reconciled on the basis of changes in K(D) with AIII concentration and ionic strength. In 200 mM KCl, K(D) of AIII-Ca varies by a factor of 7 between 10(-4.3) and 10(-3) M AIII. Thus, a disproportionately large amount of Ca-AIII is formed as AIII concentration is increased, which results in slopes greater than unity for log delta A-log AIII relations.
Full text
PDF




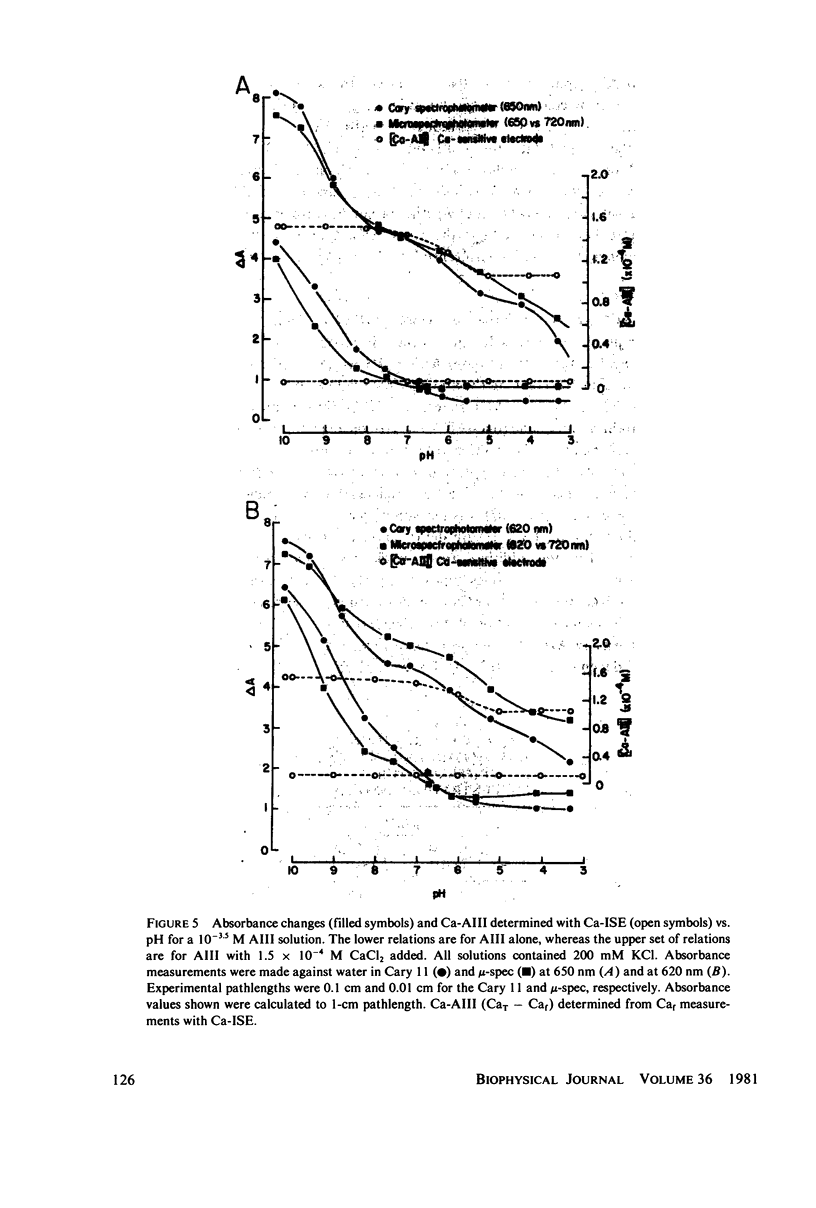

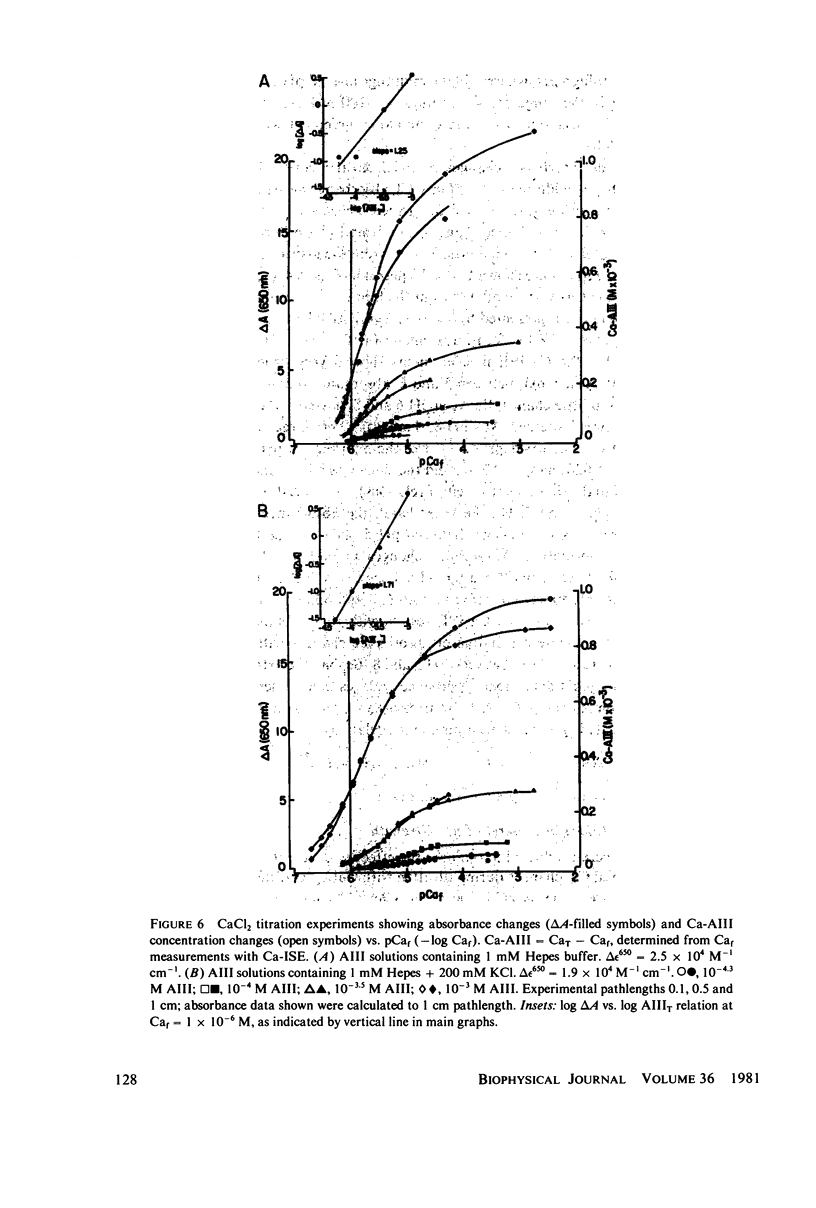

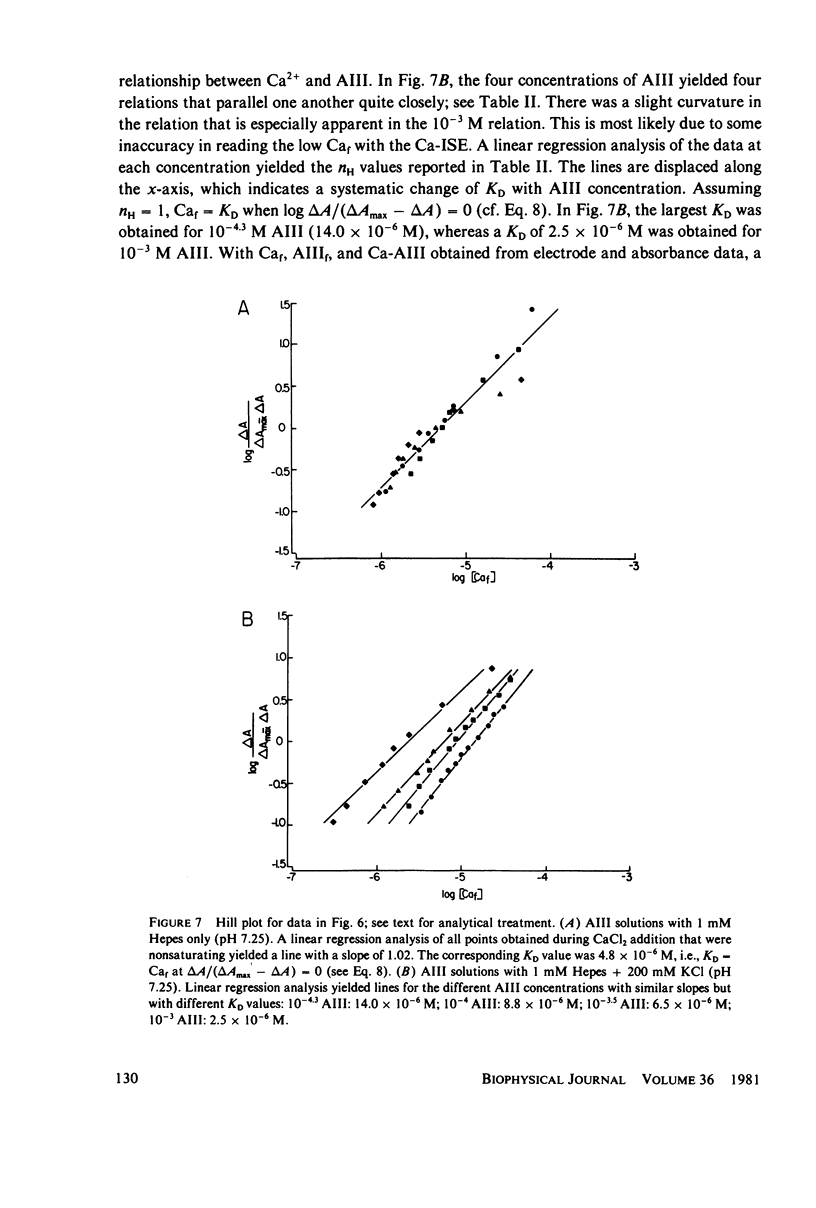
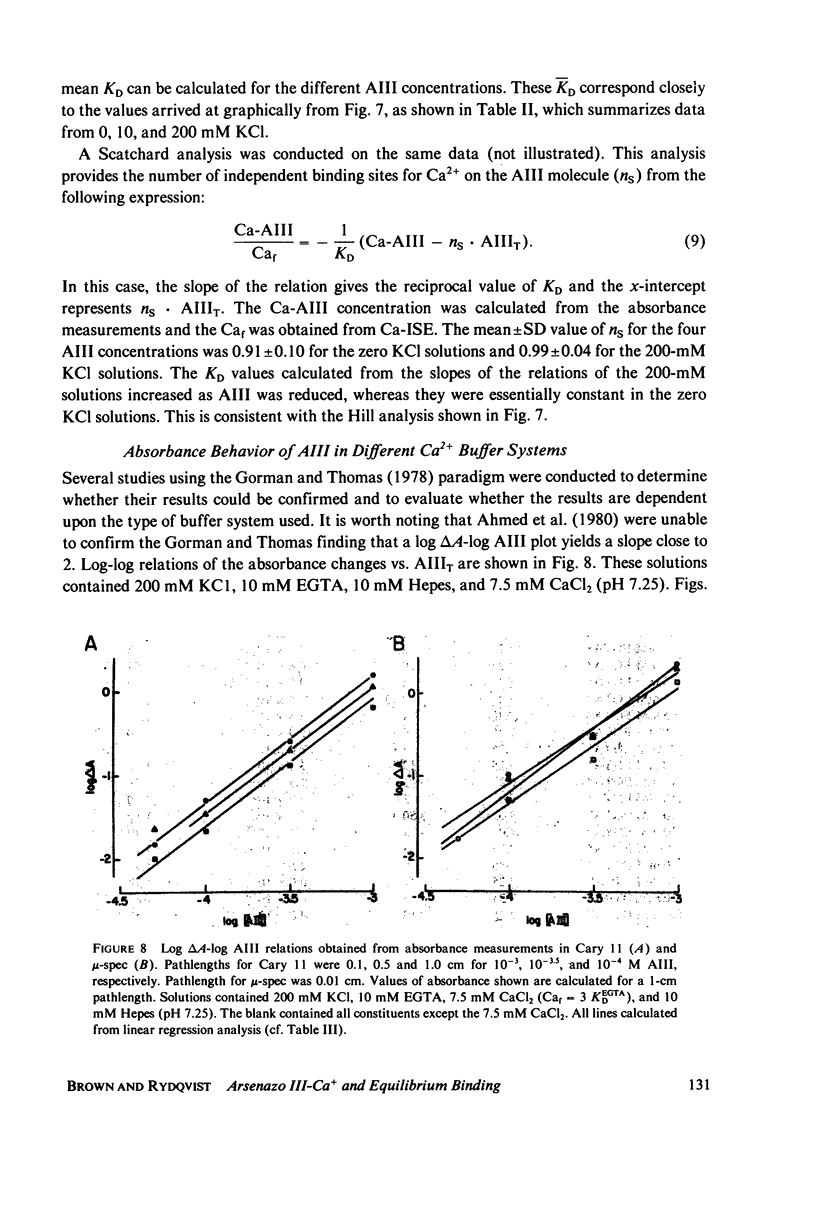



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Intracellular pH changes induced by calcium influx during electrical activity in molluscan neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Apr;75(4):403–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Kragie L., Connor J. A. Stoichiometry and apparent dissociation constant of the calcium-arsenazo III reaction under physiological conditions. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):907–920. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85025-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Tiffert T., Scarpa A., Mullins L. J. Intracellular calcium buffering capacity in isolated squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):355–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Brown P. K., Pinto L. H. Detection of light-induced changes of intracellular ionized calcium concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budesínský B. Acidity of several chromotropic acid azo derivatives. Talanta. 1969 Sep;16(9):1277–1288. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(69)80003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B. Principles of differential spectrophotometry with special reference to the dual wavelength method. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:322–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu V. C., Haynes D. The pH dependence and the binding equilibria of the calcium indicator--arsenazo III. Membr Biochem. 1980;3(3):169–183. doi: 10.3109/09687688009063884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzer W. B., Beaven G. H. Use of the metal-ion indicator, Arsenazo III, in the measurement of calcium binding. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jul;81(1):118–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90604-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. A new mathematical treatment of changes of ionic concentration in muscle and nerve under the action of electric currents, with a theory as to their mode of excitation. J Physiol. 1910 May 11;40(3):190–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogan K., Simons E. R. The influence of pH on arsenazo III. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90555-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V. Arsenazo III forms 2:1 complexes with Ca and 1:1 complexes with Mg under physiological conditions. Estimates of the apparent dissociation constants. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):541–548. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85322-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


