Abstract
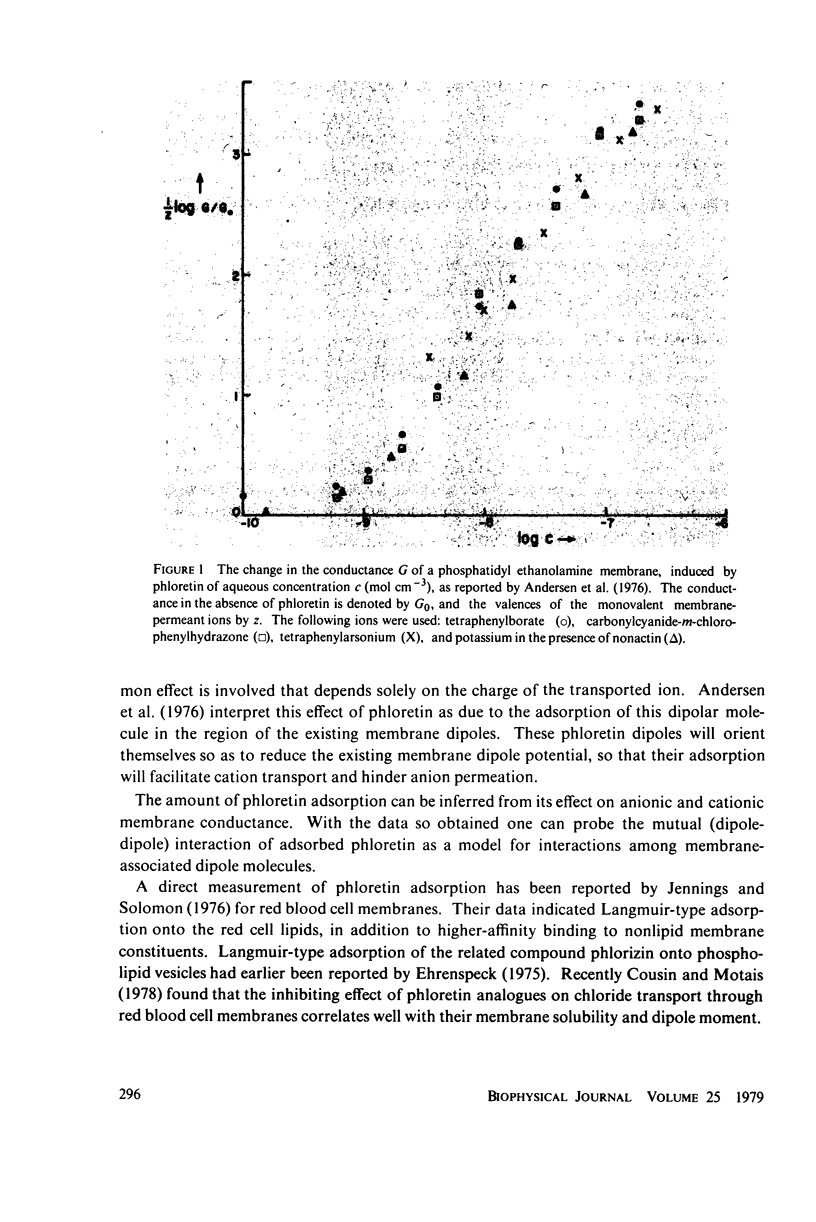
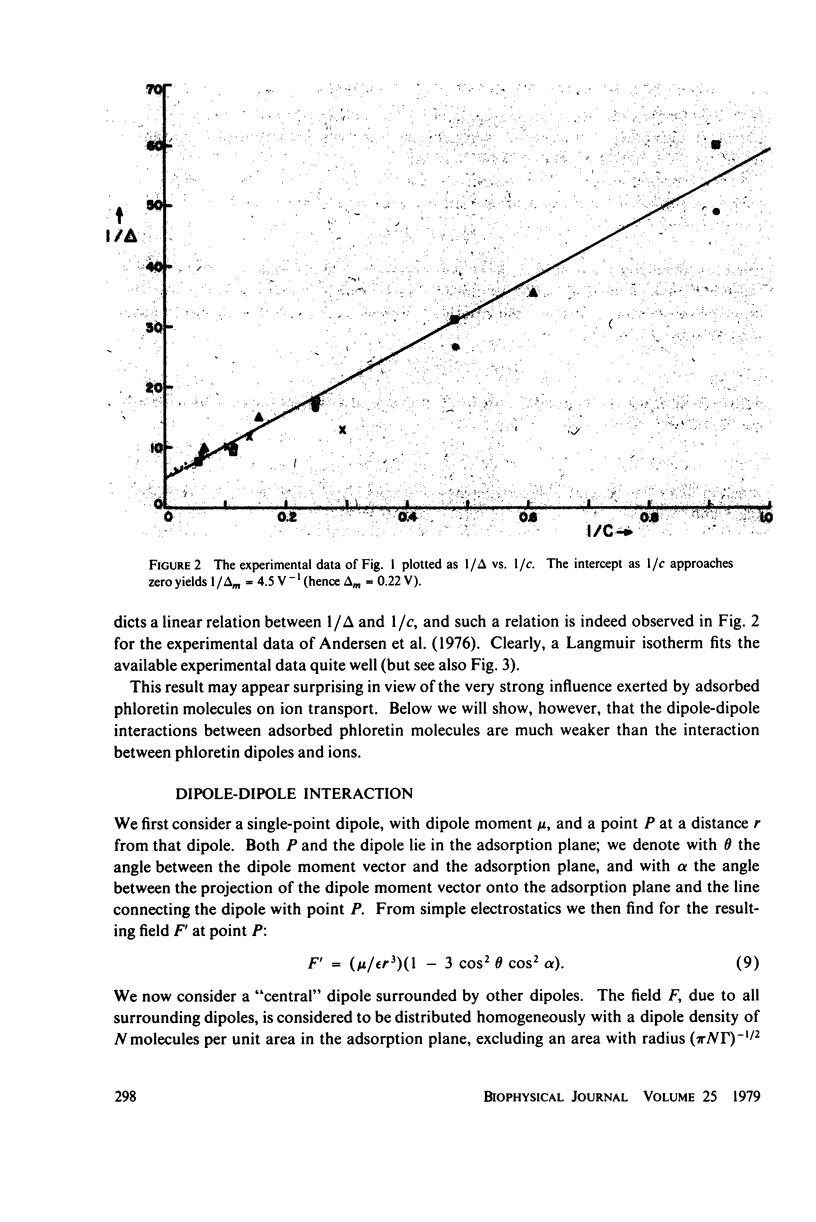
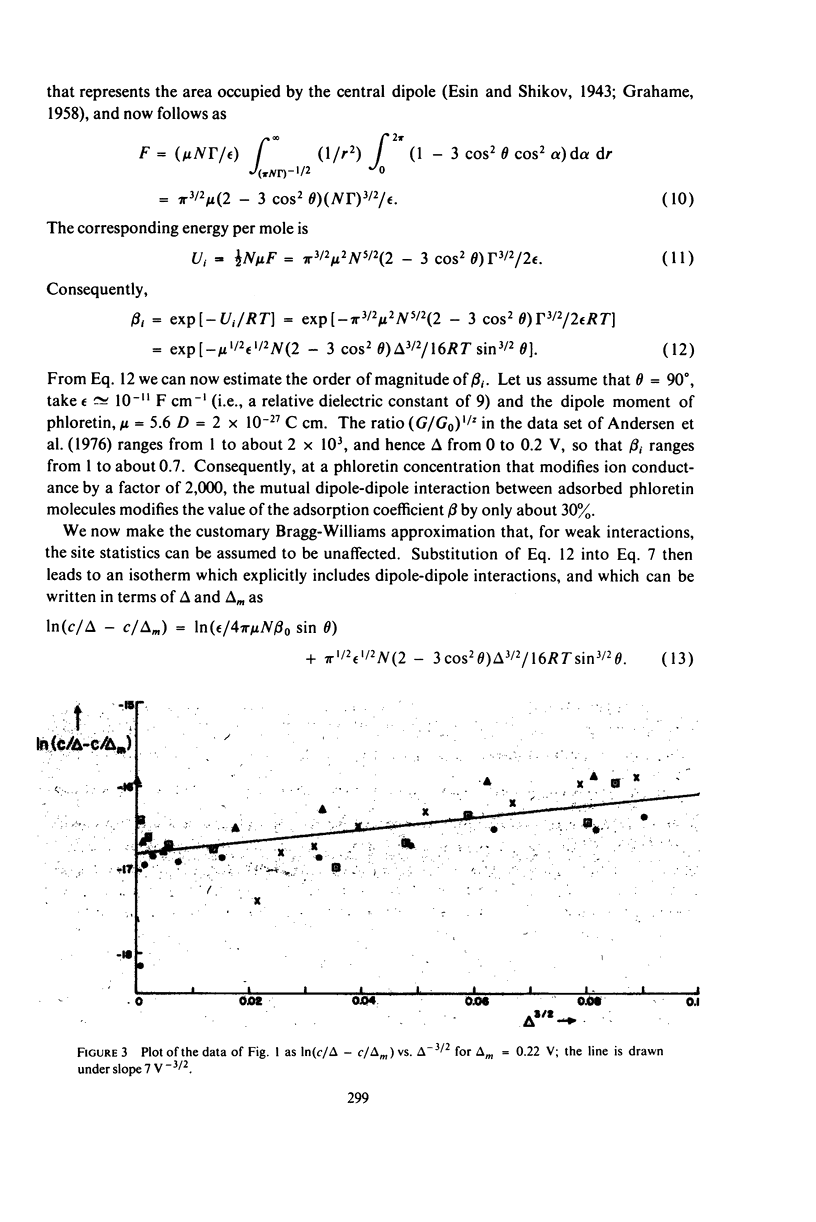
The effect of uncharged, dipolar phloretin on anion and cation conductance through a black lipid membrane can be used to study its adsorption behavior. The adsorption of phloretin can be described by a Langmuir isotherm with weak dipole-dipole interaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. S., Finkelstein A., Katz I., Cass A. Effect of phloretin on the permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):749–771. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L., Solomon A. K. Interaction between phloretin and the red blood cell membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):381–397. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. A., Topaly V. P. Pronitsaemost' bimolekuliarnykh fosfolipidnykh membran dlia zhirorastvorimykh ionov. Biofizika. 1969 May-Jun;14(3):452–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. Salicylates and phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1973 May 25;243(5404):234–236. doi: 10.1038/243234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


