Abstract
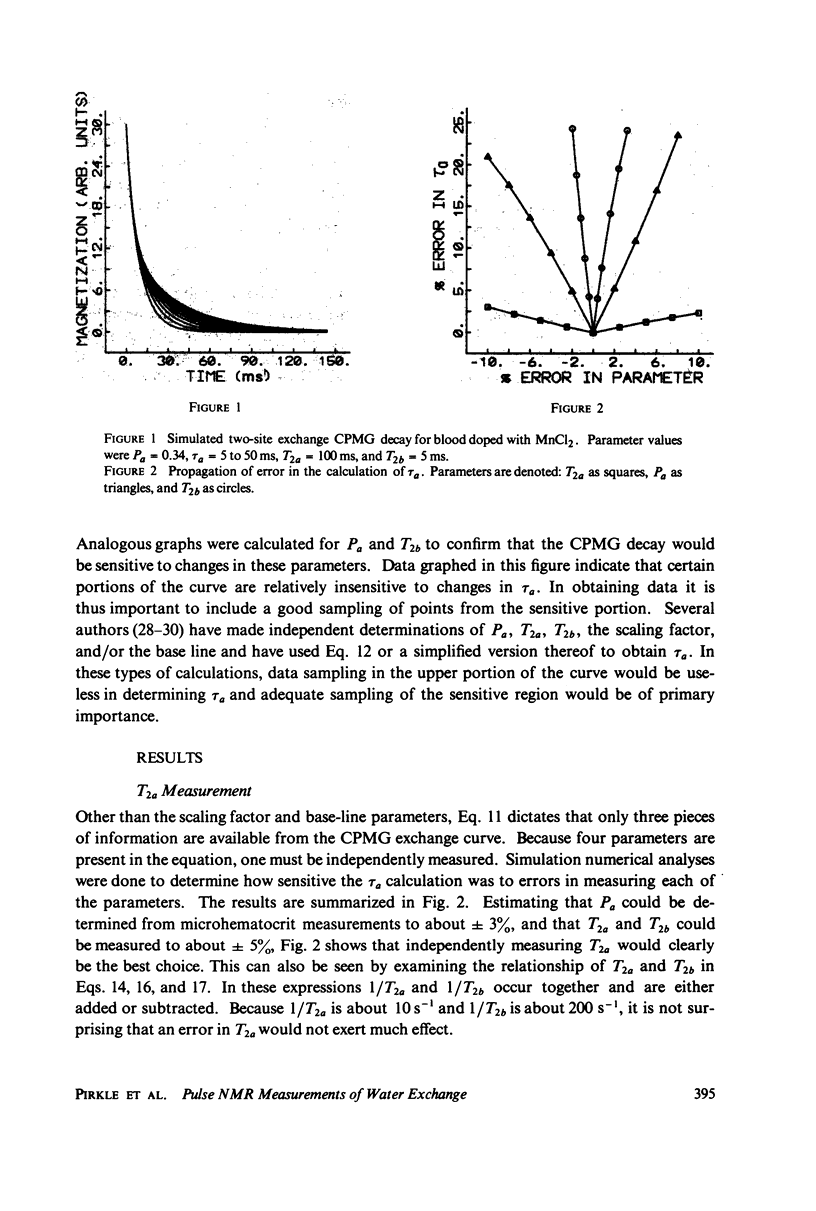
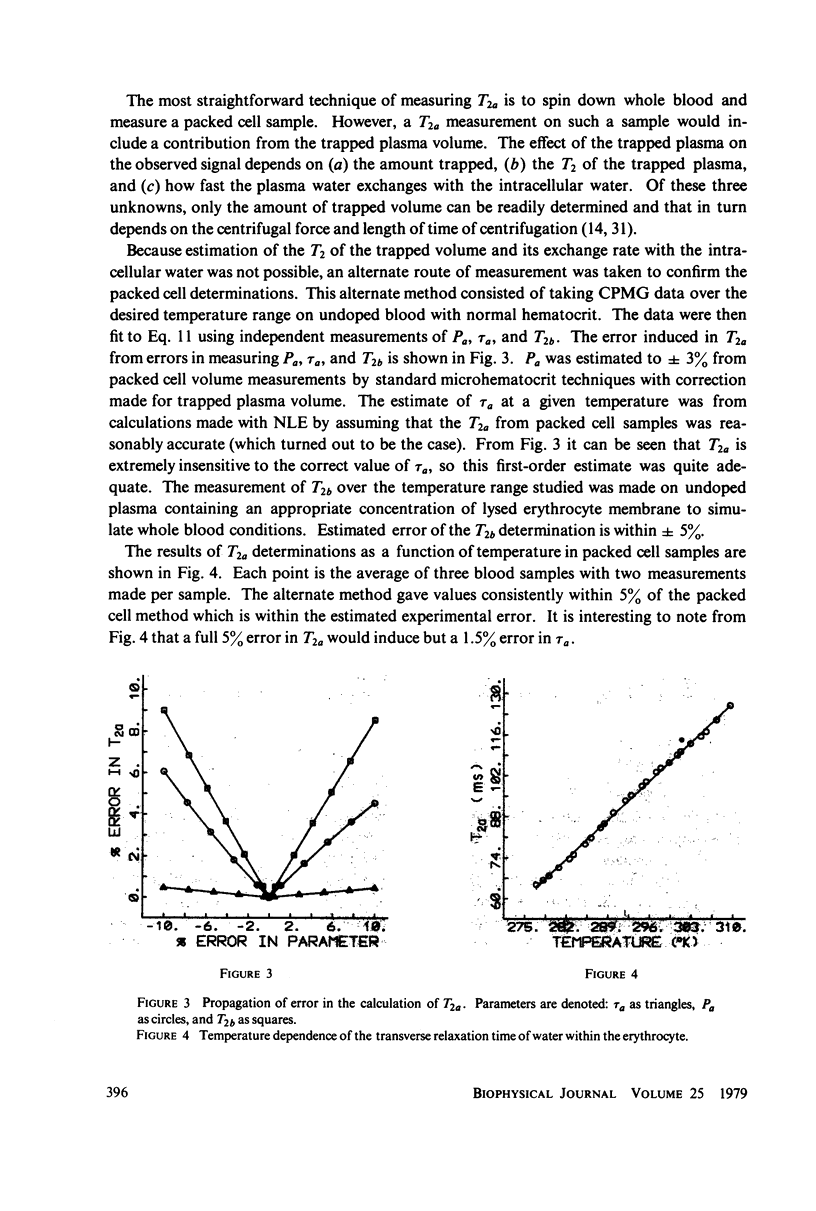
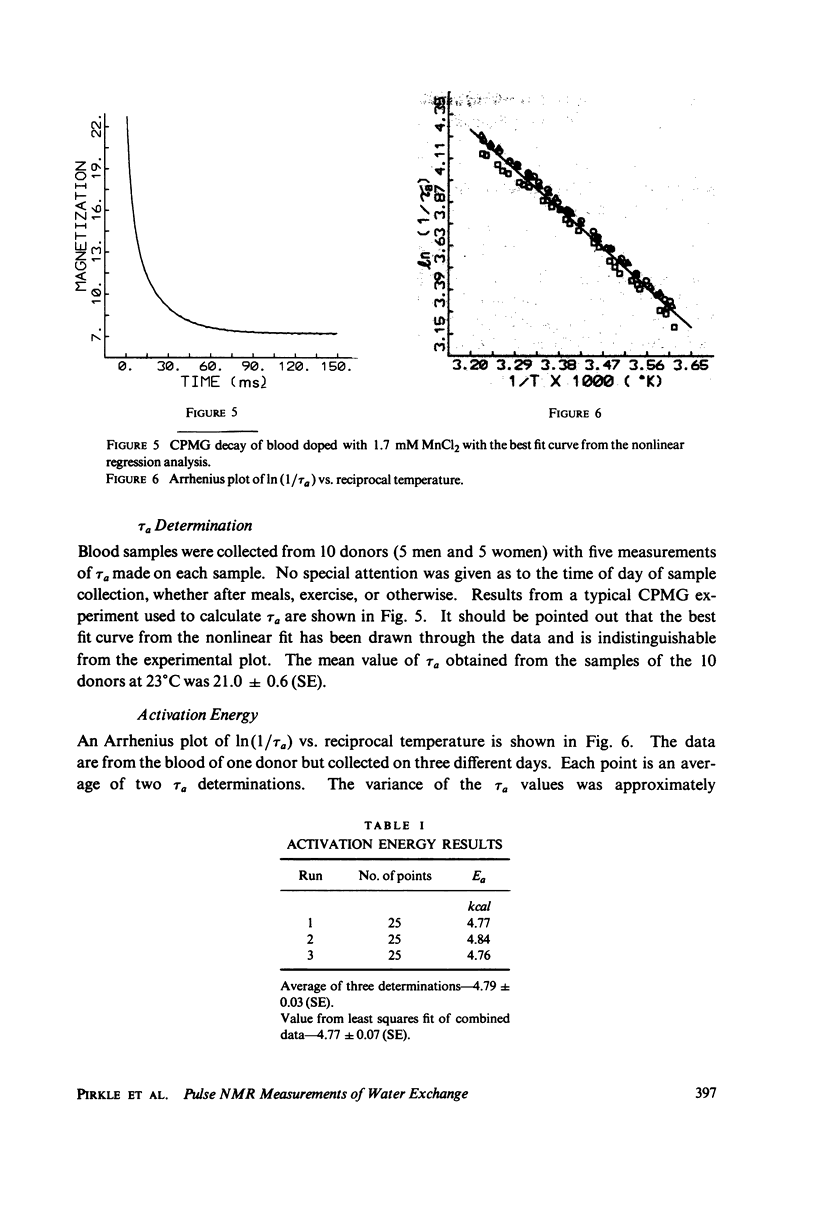
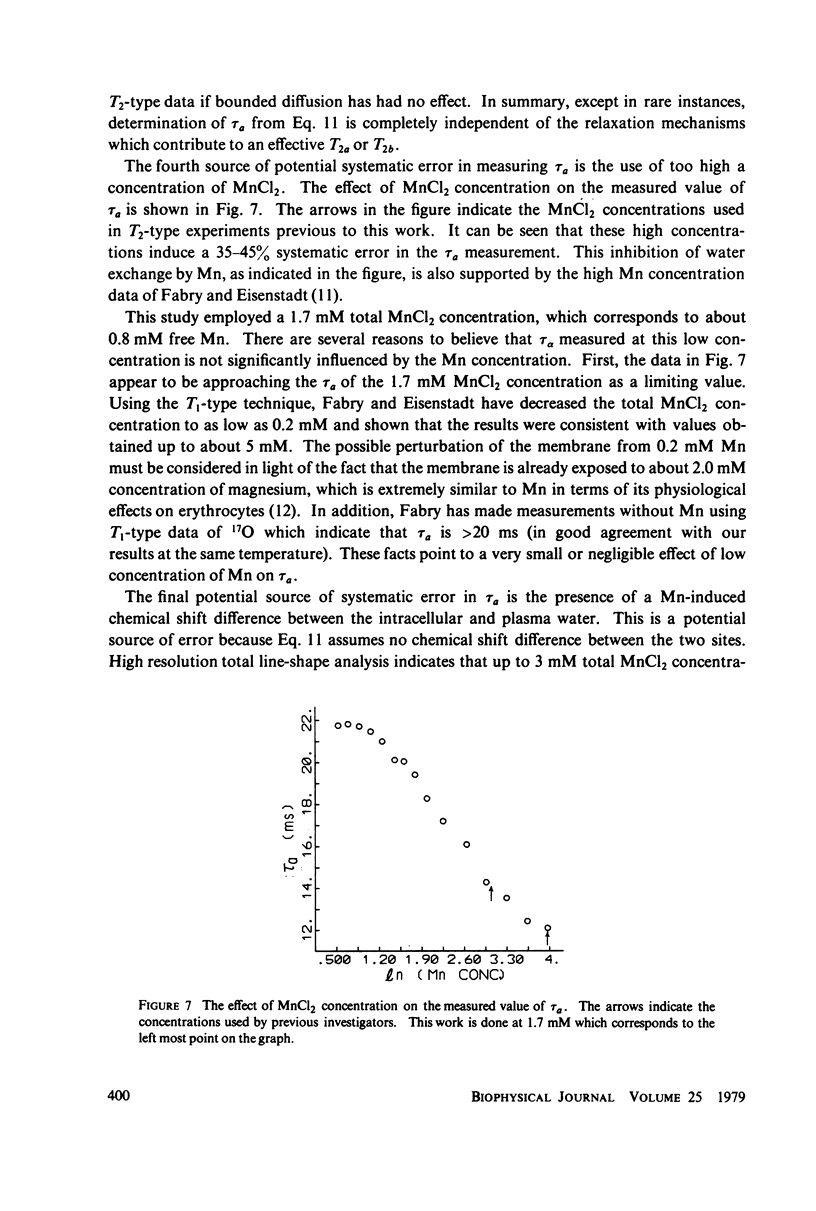
A simple, precise, and rapid pulse nuclear magnetic resonance technique for measuring the rate of water exchange across the erythrocyte membrane is presented. The technique is based upon the nonlinear fit of Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) transverse relaxation time data of blood doped with 1.7 mM MnCl2 to the general two-compartment exchange condition. Previous approaches using CPMG data required high MnCl2 concentrations (25-53 nM), shown in this work to induce systematic errors ranging from 35 to 45%. At 23 degrees C the average residence time of a water molecule inside the erythrocyte (tau a) is 21.0 +/- 0.6 ms (SE). The Arrhenius plot for water exchange is linear over the range of 3 degrees - 37 degrees C and th Arrhenius activation energy is 4.79 +/- 0.03 kcal (SE). This value does not differ significantly from the energy required for bulk water flow. Results are compared with previous determinations, and sources of systematic error in tau a and the activation energy are evaluated.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allerhand A., Gutowsky H. S., Jonas J., Meinzer R. A. Nuclear magnetic resonance methods for determining chemical-exchange rates. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Jul 20;88(14):3185–3193. doi: 10.1021/ja00966a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrasko J. Water diffusion permeability of human erythrocytes studied by a pulsed gradient NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):304–311. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTON T. C., BROWN D. A. WATER PERMEABILITY OF THE FETAL ERYTHROCYTE. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:839–849. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien D. Y., Macey R. I. Diffusional water permeability of red cells. Independence on osmolality. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon T., Outhred R. Water diffusion permeability of erythrocytes using an NMR technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):354–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS F. E., KENYON K., KIRK J. A rapid titrimetric method for determining the water content of human blood. Science. 1953 Sep 4;118(3062):276–277. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3062.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M. E., Eisenstadt M. Water exchange between red cells and plasma. Measurement by nuclear magnetic relaxation. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85886-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giberman E. Determination of the trapped volume in a pellet of red blood cells. Experientia. 1973 Sep 15;29(9):1083–1085. doi: 10.1007/BF01946733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER E., LEVY M. R., ALLEN R. L., Jr Red cell electrolytes in patients with edema. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Jan;57:32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King V. A study of the mechanism of water transfer across frog skin by a comparison of the permeability of the skin to deuterated and tritiated water. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):529–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILDVAN A. S., COHN M. MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF THE INTERACTION OF THE MANGANOUS ION WITH BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:910–919. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I., Farmer R. E. Inhibition of water and solute permeability in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 7;211(1):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morariu V. V., Benga G. Evaluation of a nuclear magnetic resonance technique for the study of water exchange through erythrocyte membranes in normal and pathological subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 19;469(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P., Sha'afi R. I. Effect of PCMBS on water transfer across biological membranes. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Jun;83(3):449–456. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGANELLI C. V., SOLOMON A. K. The rate of exchange of tritiated water across the human red cell membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):259–277. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price H. D., Thompson T. E. Properties of liquid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: temperature dependence of water permeability. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):443–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redwood W. R., Haydon D. A. Influence of temperature and membrane composition on the water permeability of lipid bilayers. J Theor Biol. 1969 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich G. T., Sha'afi I., Romualdez A., Solomon A. K. Effect of osmolality on the hydraulic permeability coefficient of red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Dec;52(6):941–954. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.6.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Gary-Bobo C. M. Water and nonelectrolytes permeability in mammalian red cell membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:103–146. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shporer M., Civan M. M. NMR study of -17-O from H2-17-O in human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. K. Characterization of biological membranes by equivalent pores. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May;51(5 Suppl):335S+–335S+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira F. L., Sha'afi R. I., Solomon A. K. The state of water in human and dog red cell membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Apr;55(4):451–466. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEED R. I., ROTHSTEIN A. The uptake of divalent manganese ion by mature normal human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Nov;44:301–314. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipp A., James T. L., Kuntz I. D., Shohet S. B. Water proton magnetic resonance studies of normal and sickle erythrocytes. Temperature and volume dependence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


