Abstract
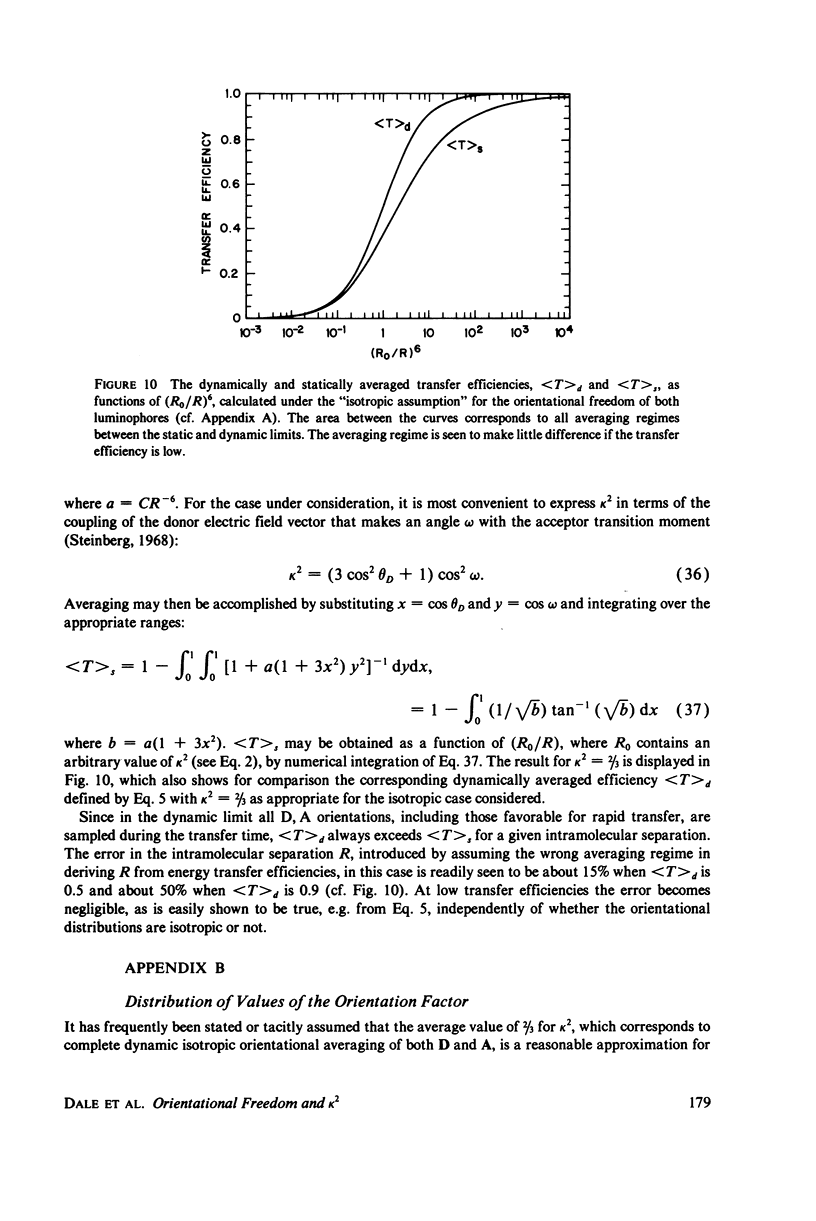
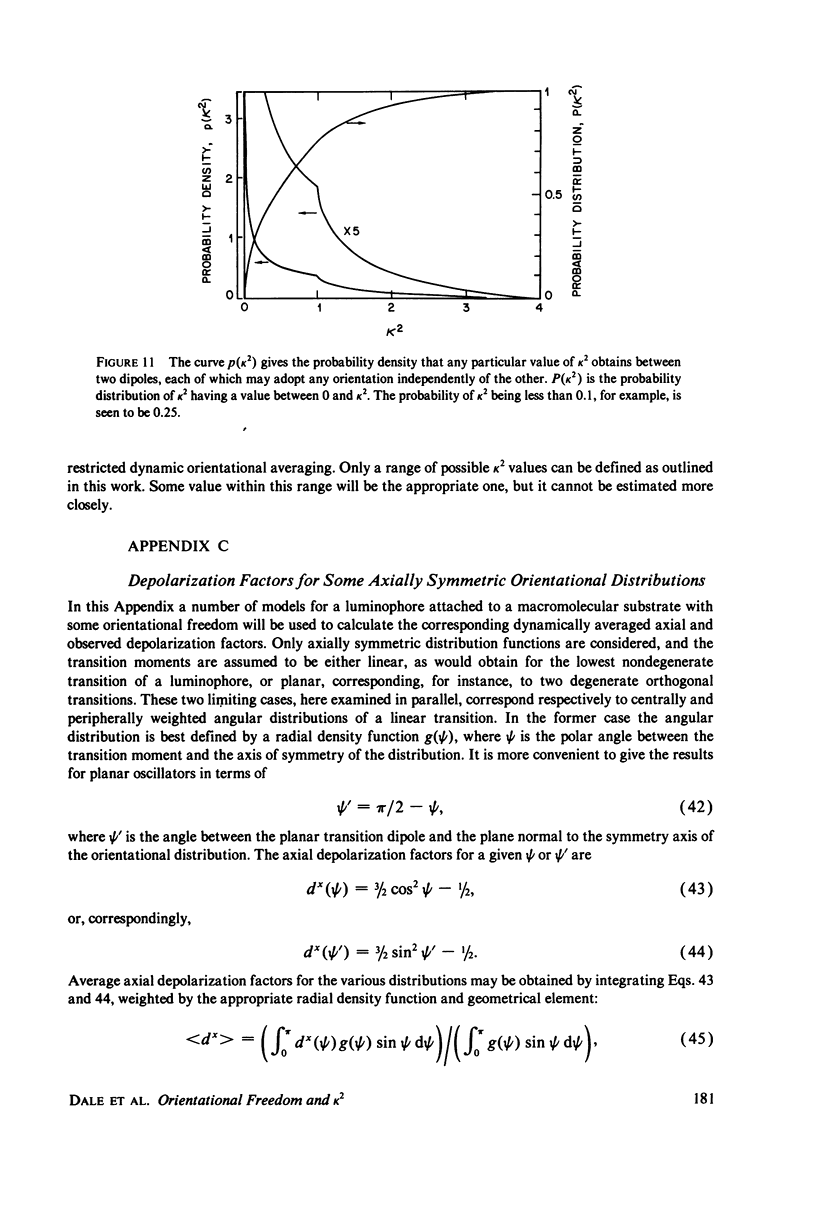
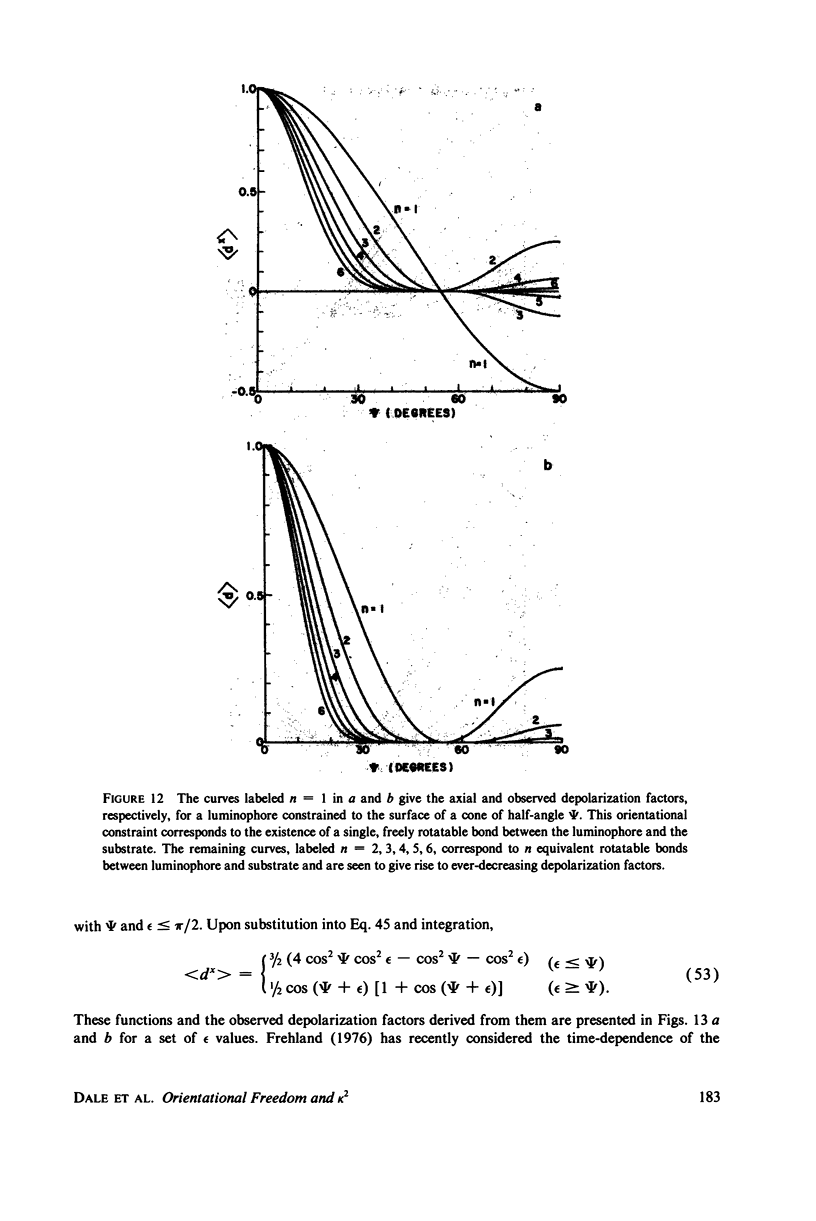
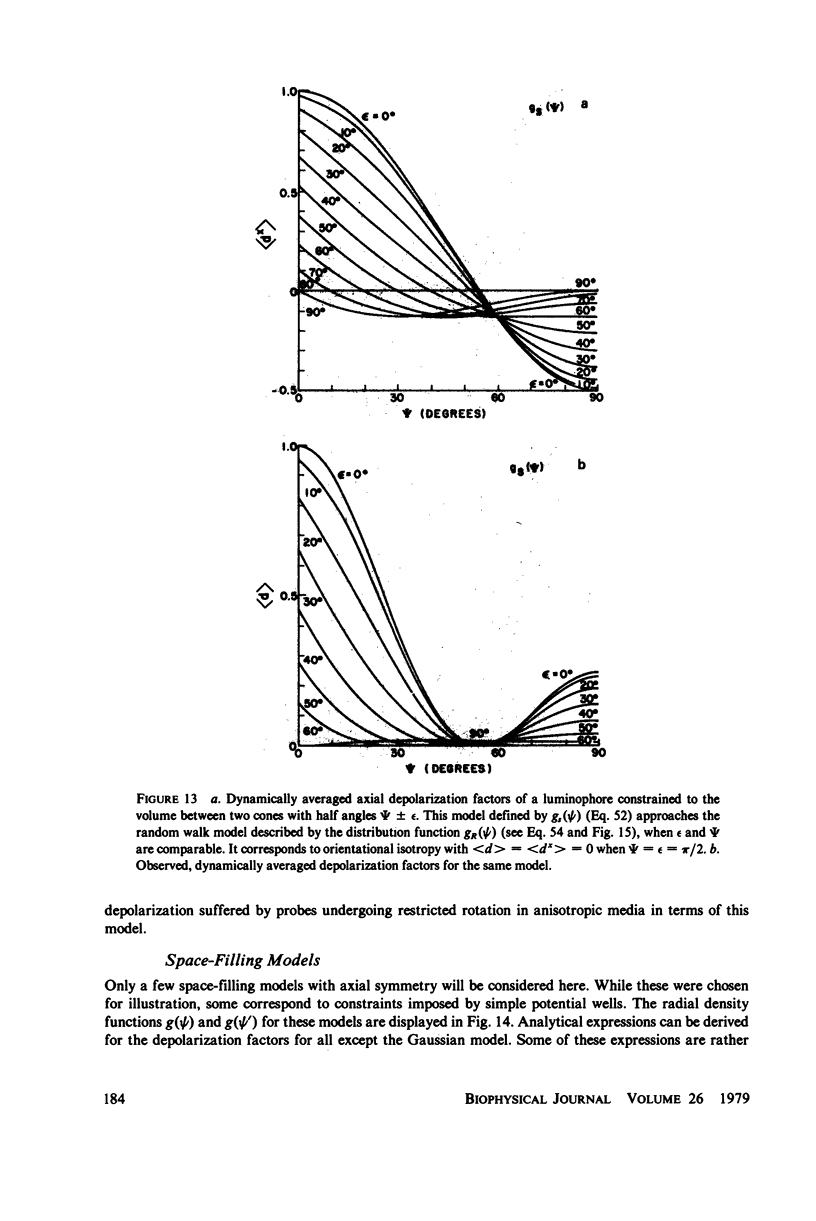
The measurement of the efficiency of Förster long-range resonance energy transfer between donor (D) and acceptor (A) luminophores attached to the same macromolecular substrate can be used to estimate the D-A separation, R. If the D and A transition dipoles sample all orientations with respect to the substrate (the isotropic condition) in a time short compared with the transfer time (the dynamic averaging condition), the average orientation factor less than K2 greater than is 2/3. If the isotropic condition is not satisfied but the dynamic averaging condition is, upper and lower bounds for less than K2 greater than, and thus R, may be obtained from observed D and A depolarizations, and these limits may be further narrowed if the transfer depolarization is also known. This paper offers experimental protocols for obtaining this reorientational information and presents contour plots of less than K2 greater than min and less than K2 greater than max as functions of generally observable depolarizations. This permits an uncertainty to be assigned to the determined value of R. The details of the D and A reoreintational process need not be known, but the orientational distributions are assumed to have at least approximate axial symmetry with respect to a stationary substrate. Average depolarization factors are derived for various orientational distribution functions that demonstrate the effects of various mechanisms for reorientation of the luminophores. It is shown that in general the static averaging regime does not lend itself to determinations of R.
Full text
PDF






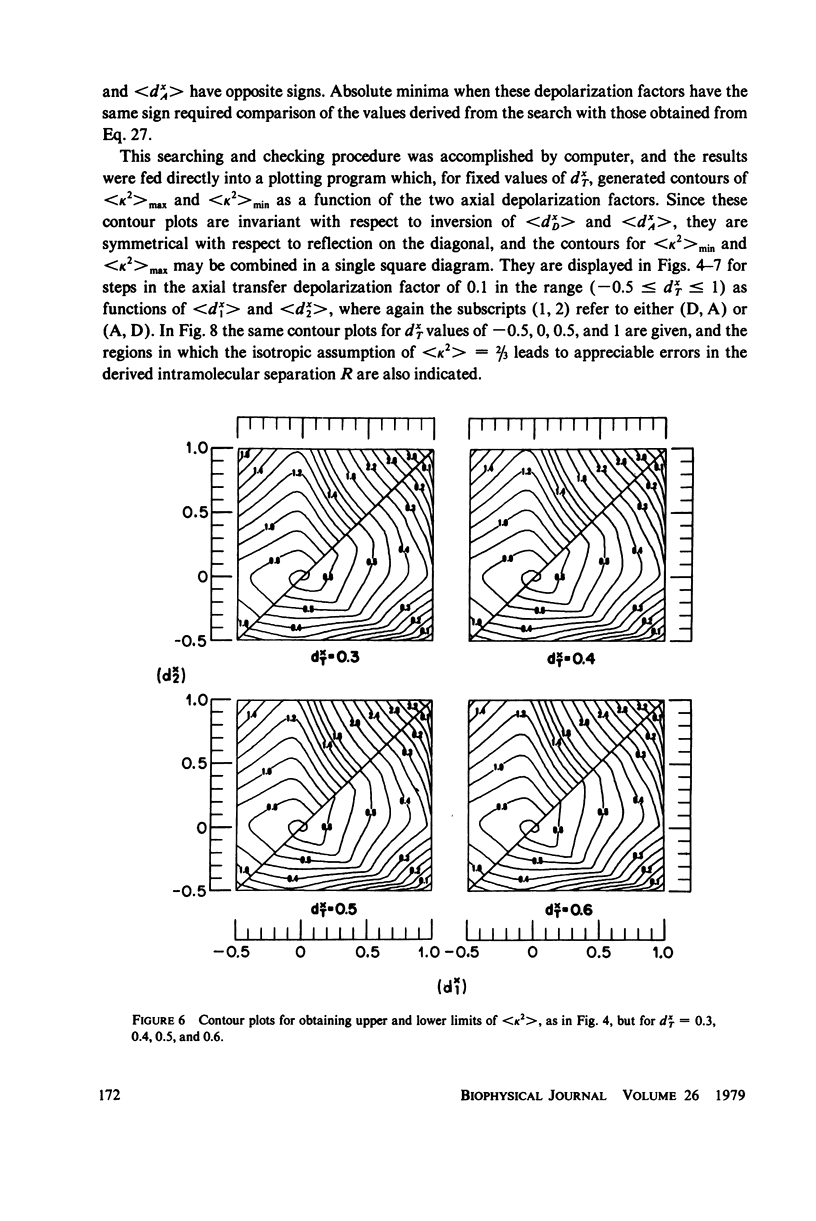
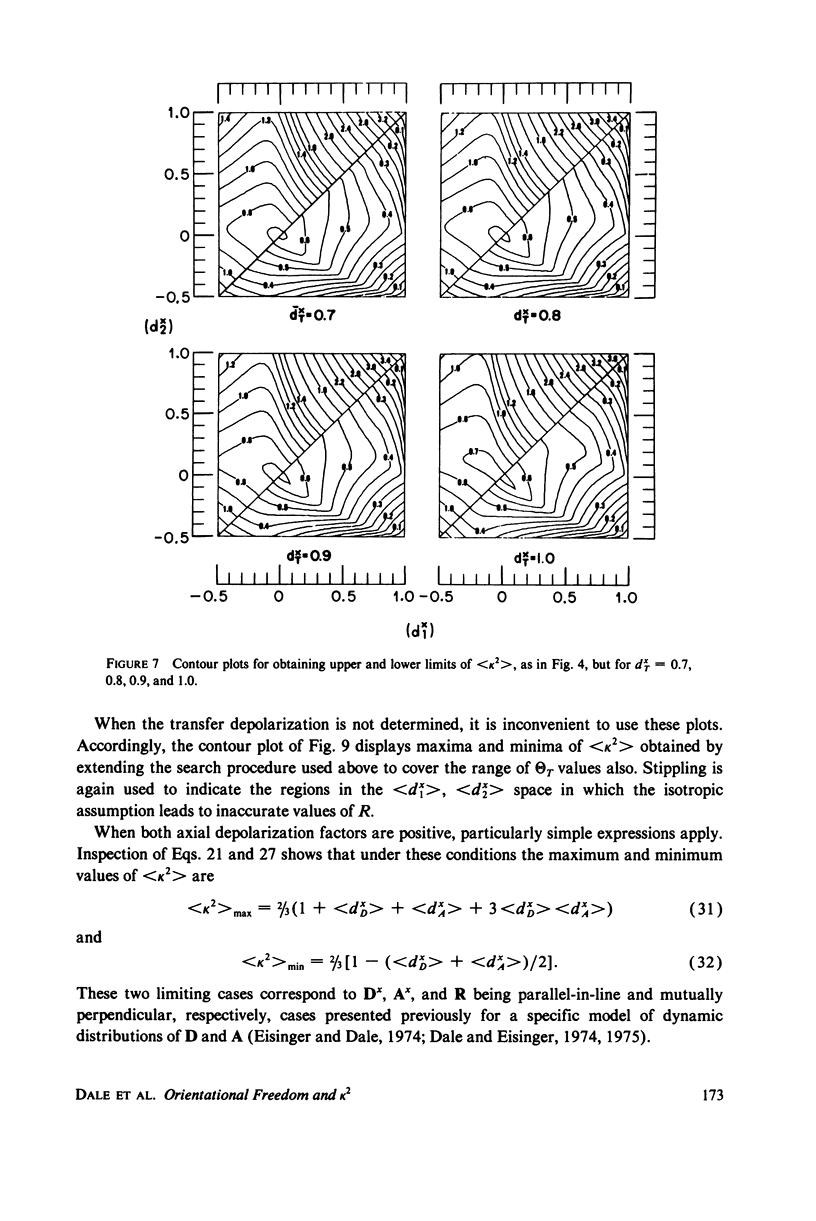
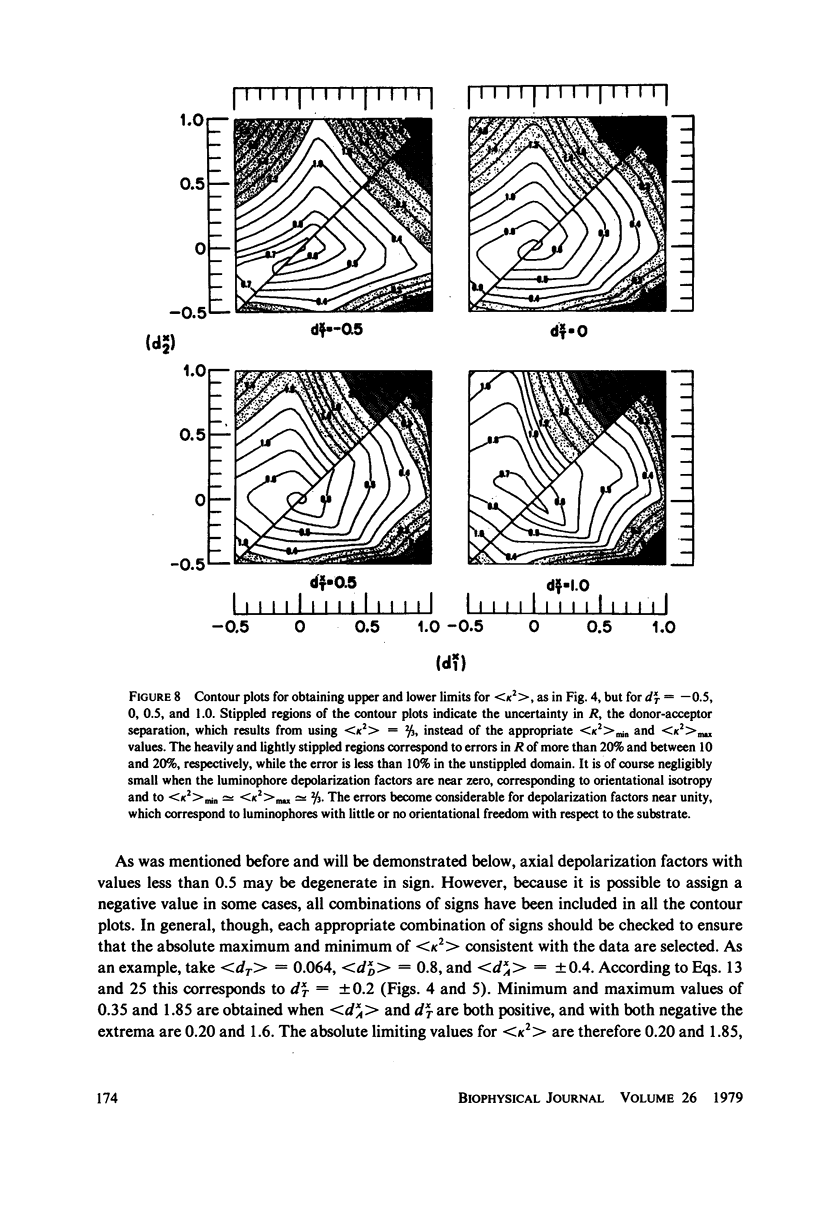
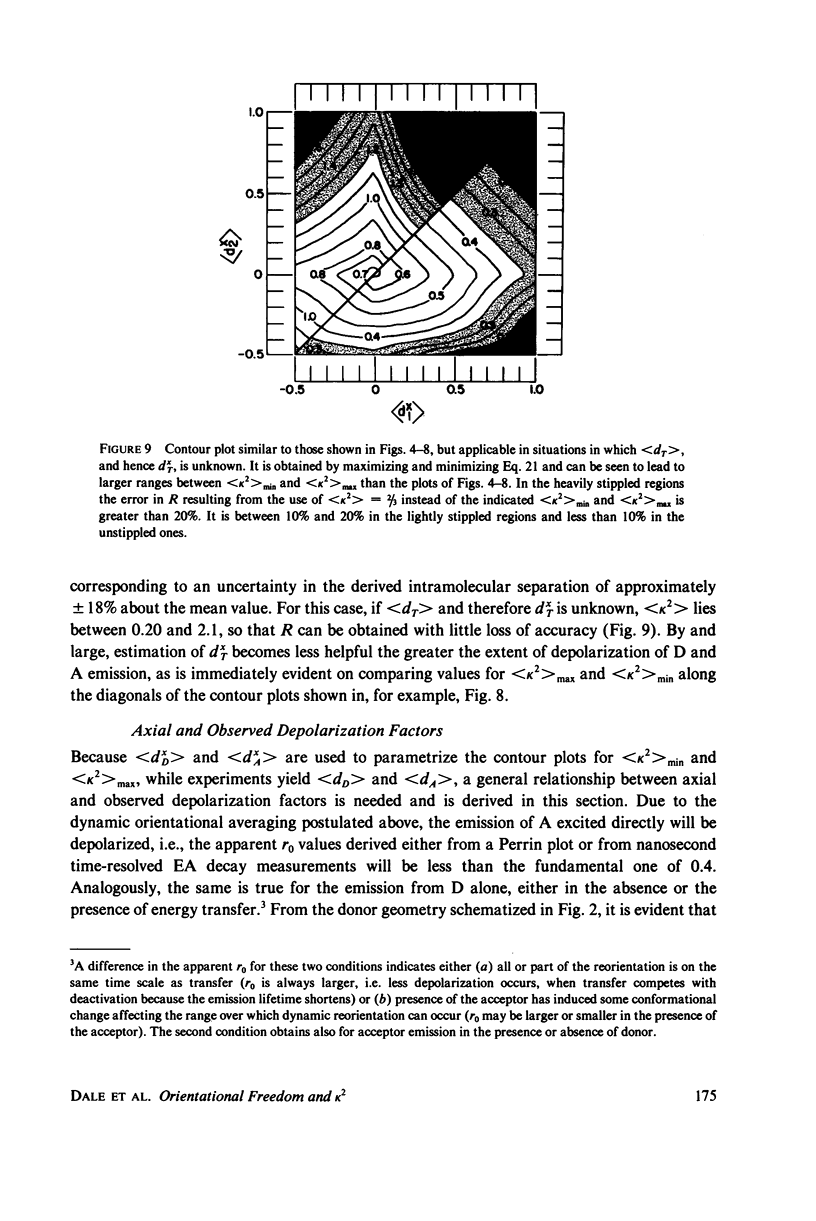










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badley R. A., Martin W. G., Schneider H. Dynamic behavior of fluorescent probes in lipid bilayer model membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):268–275. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berner V. G., Darnall D. W., Birnbaum E. R. Distance measurements between the metal-binding sites in thermolysin using terbium ion as a fluorescent probe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):763–768. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum E. R., Abbott F., Gomez J. E., Darnall D. W. The calcium ion binding site in bovine chymotrypsin A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Pechukas P. Determination of distance distribution functions by singlet-singlet energy transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2099–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R. H., Brand L. Intramolecular transfer of excitation from tryptophan to 1-dimethylaminonaphthalene 5-sulfonamide in a series of model compounds. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):777–787. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. E., Eisinger J. Intramolecular energy transfer and molecular conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):271–273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnall D. W., Abbott F., Gomez J. E., Birnbaum E. R. Fluorescence energy-transfer measurements between the calcium binding site and the specificity pocket of bovine trypsin using lanthanide probes. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5017–5023. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockter M. E., Steinemann A., Schatz G. Mapping of yeast cytochrome c oxidase by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Distances between subunit II, heme a, and cytochrome c bound to subunit III. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Dale R. E. Letter: interpretation of intramolecular energy transfer experiments. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):643–647. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J. Energy transfer and dynamical structure. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):21–33. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Feuer B., Lamola A. A. Intramolecular singlet excitation transfer. Applications to polypeptides. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):3908–3915. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehland E. Dynamical theory of fluorescence polarization in a planar array of oriented pigment molecules. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jan;4(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabor G. Radiationless energy transfer through a polypeptide chain. Biopolymers. 1968 Jun;6(6):809–816. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Haas E., Steinberg I. Z. Evaluation of the distribution of distances between energy donors and acceptors by fluorescence decay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Katchalski-Katzir E., Steinberg I. Z. Effect of the orientation of donor and acceptor on the probability of energy transfer involving electronic transitions of mixed polarization. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5064–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Wilchek M., Katchalski-Katzir E., Steinberg I. Z. Distribution of end-to-end distances of oligopeptides in solution as estimated by energy transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1807–1811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn L. H., Hammes G. G. Structural mapping of aspartate transcarbamoylase by fluorescence energy-transfer measurements: determination of the distance between catalytic sites of different subunits. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2423–2429. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillel Z., Wu C. W. Statistical interpretation of fluorescence energy transfer measurements in macromolecular systems. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2105–2113. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowka D. A., Hammes G. G. Chemical modification and fluorescence studies of chloroplast coupling factor. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5538–5545. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrocks W. D., Jr, Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Energy transfer between terbium (III) and cobalt (II) in thermolysin: a new class of metal--metal distance probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4764–4768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili J., Sjösten J., Eriksson L. E., Ehrström M., Gräslund A., Ehrenberg A. ESR spectral analysis of the molecular motion of spin labels in lipid bilayers and membranes based on a model in terms of two angular motional parameters and rotational correlation times. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 13;382(2):125–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Dynamic structure of lipid bilayers studied by nanosecond fluorescence techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2319–2324. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois R., Lee C. C., Cantor C. R., Vince R., Pestka S. The distance between two functionally significant regions of the 50 S Escherichia coli ribosome: the erythromycin binding site and proteins L7/L12. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):297–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Auld D. S., Valee B. L. Surveyor substrates: energy-transfer gauges of active center topography during catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1383–1389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latt S. A., Auld D. S., Vallee B. L. Distance measurements at the active site of carboxypeptidase A during catalysis. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):3015–3022. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung C. S., Meares C. F. Attachment of fluorescent metal chelates to macromolecules using "bifunctional" chelating agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk C. K. Energy transfer between tryptophans and aromatic ligands in apomyoglobin. Biopolymers. 1971;10(8):1317–1329. doi: 10.1002/bip.360100806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadakis N., Hammes G. G. Fluorescent derivatives of the pyruvate dehydrogenase component of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1890–1896. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Iwanij V., Reich E., Stryer L. Transglutaminase-catalyzed insertion of a fluorescent probe into the protease-sensitive region of rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2163–2168. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. B., Hammes G. G. Fluorescence energy transfer measurements in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli with chemically modified lipoic acid. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5234–5241. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd G. B., Papadakis N. Fluorescence energy-transfer measurements between coenzyme A and flavin adenine dinucleotide binding sites of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2888–2893. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:819–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Haugland R. P. Energy transfer: a spectroscopic ruler. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):719–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu S. C., Wu C. W., Hastings J. W. Structural studies on bacterial luciferase using energy transfer and emission anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):987–993. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K., Takahashi M. Fluorescence energy transfer between heterologous active sites of affinity-labeled aspartokinase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1548–1554. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Yarbrough L. R., Wu F. Y., Hillel Z. Spatial relationship of the sigma subunit and the rifampicin binding site in RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2097–2104. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Hartig P. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Use of a distant reporter group as evidence for a conformational change in a sensory receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


