Abstract
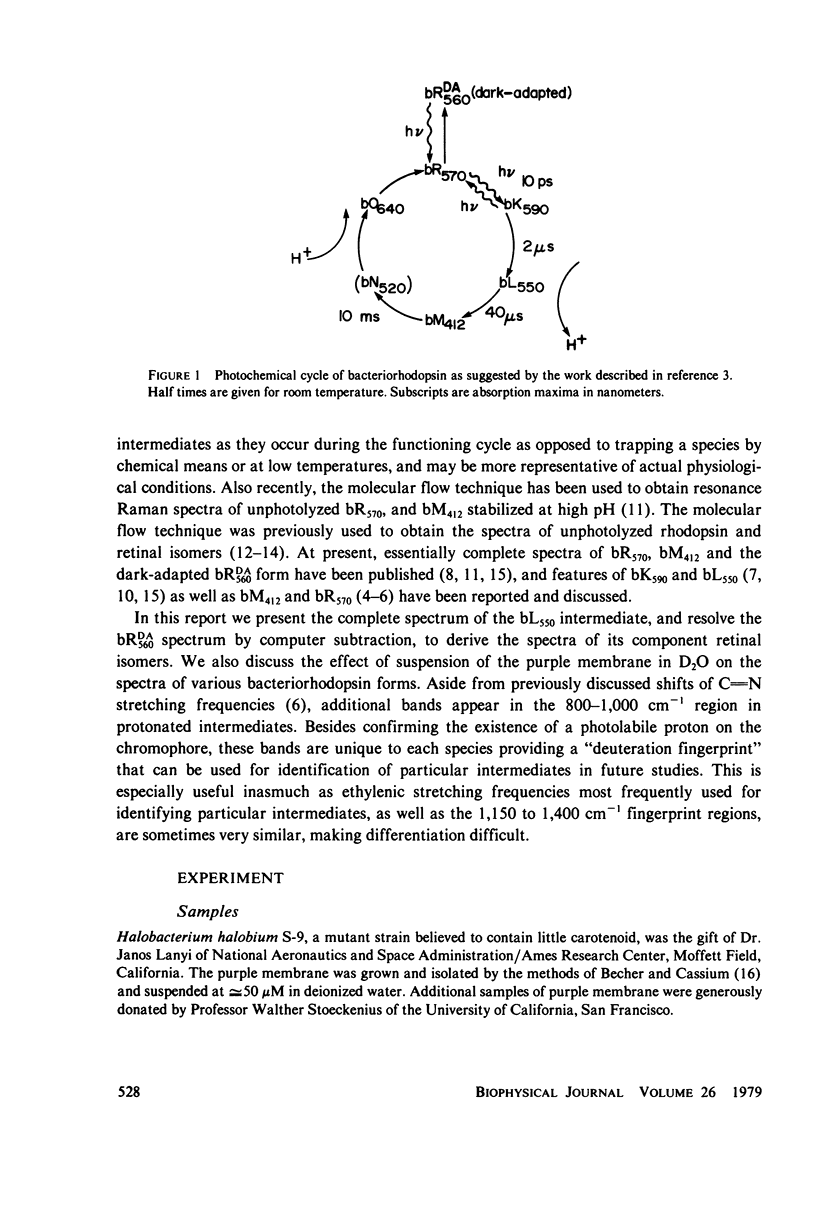
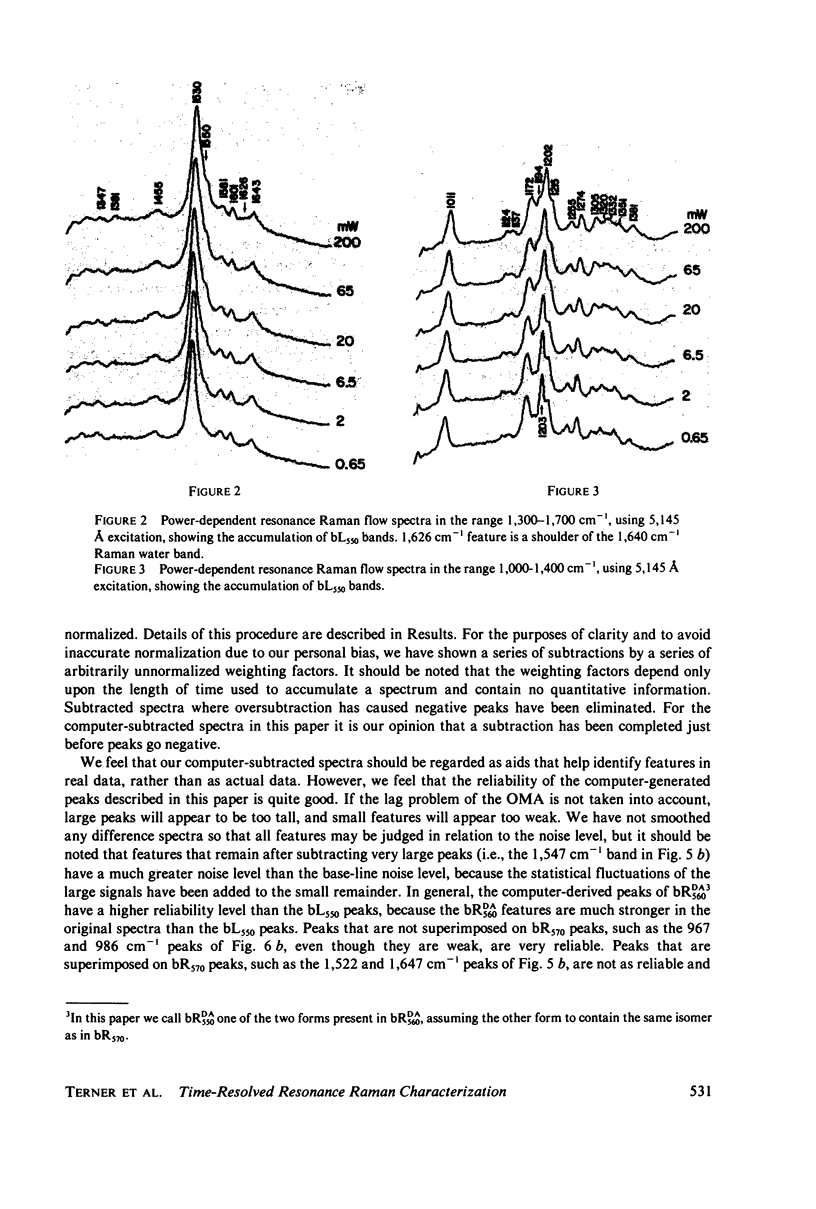
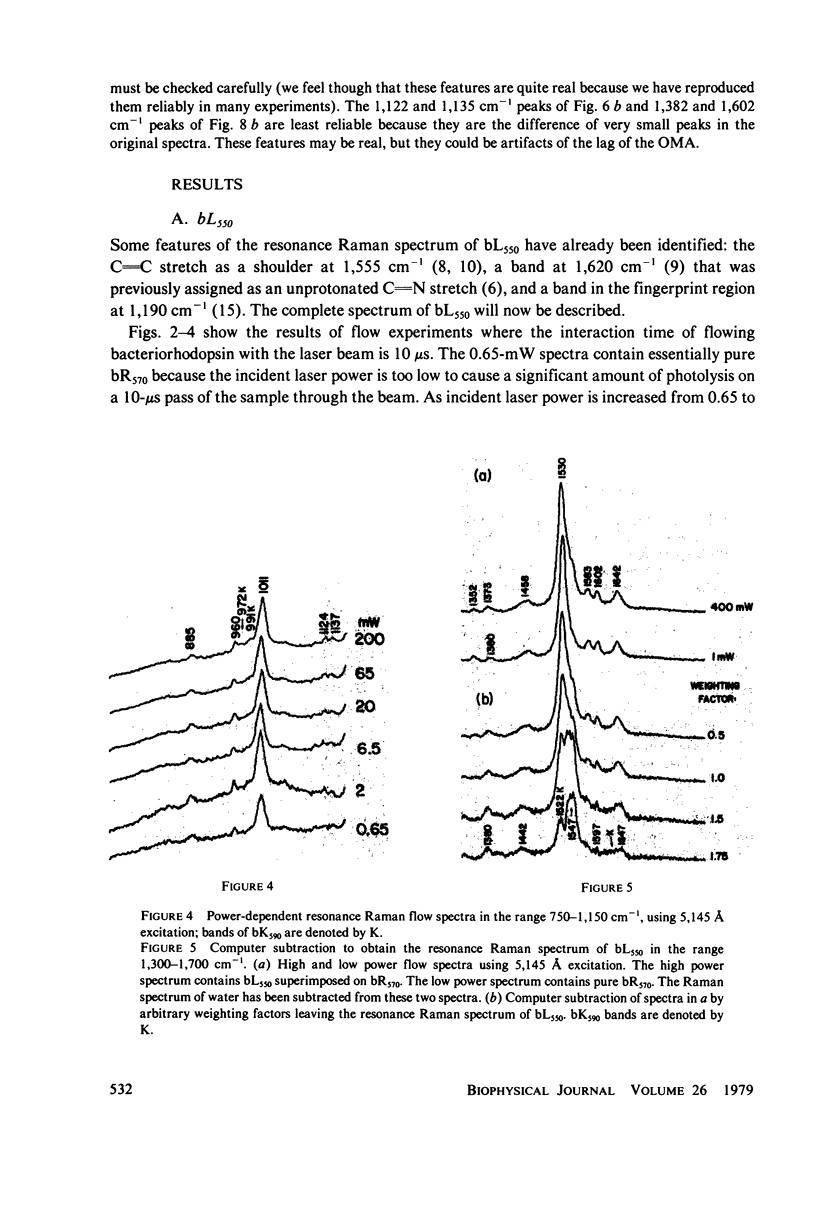
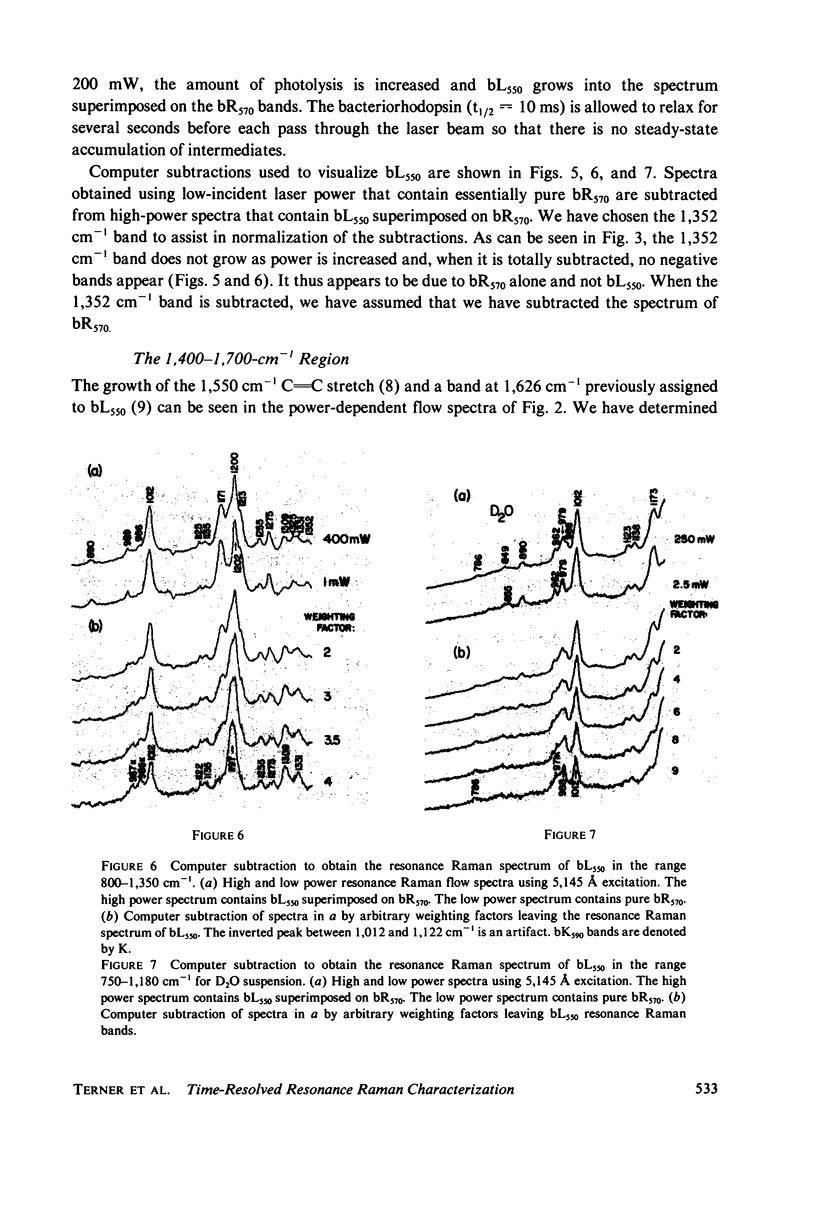
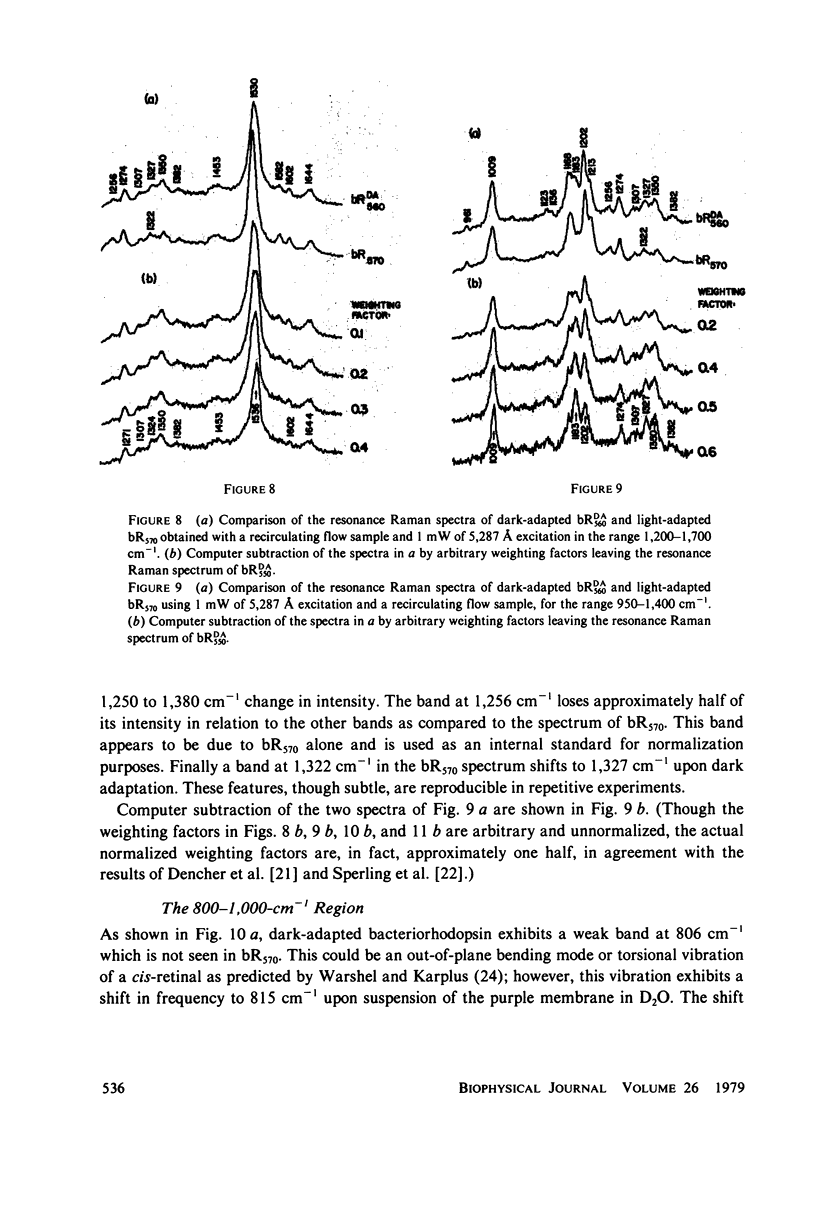
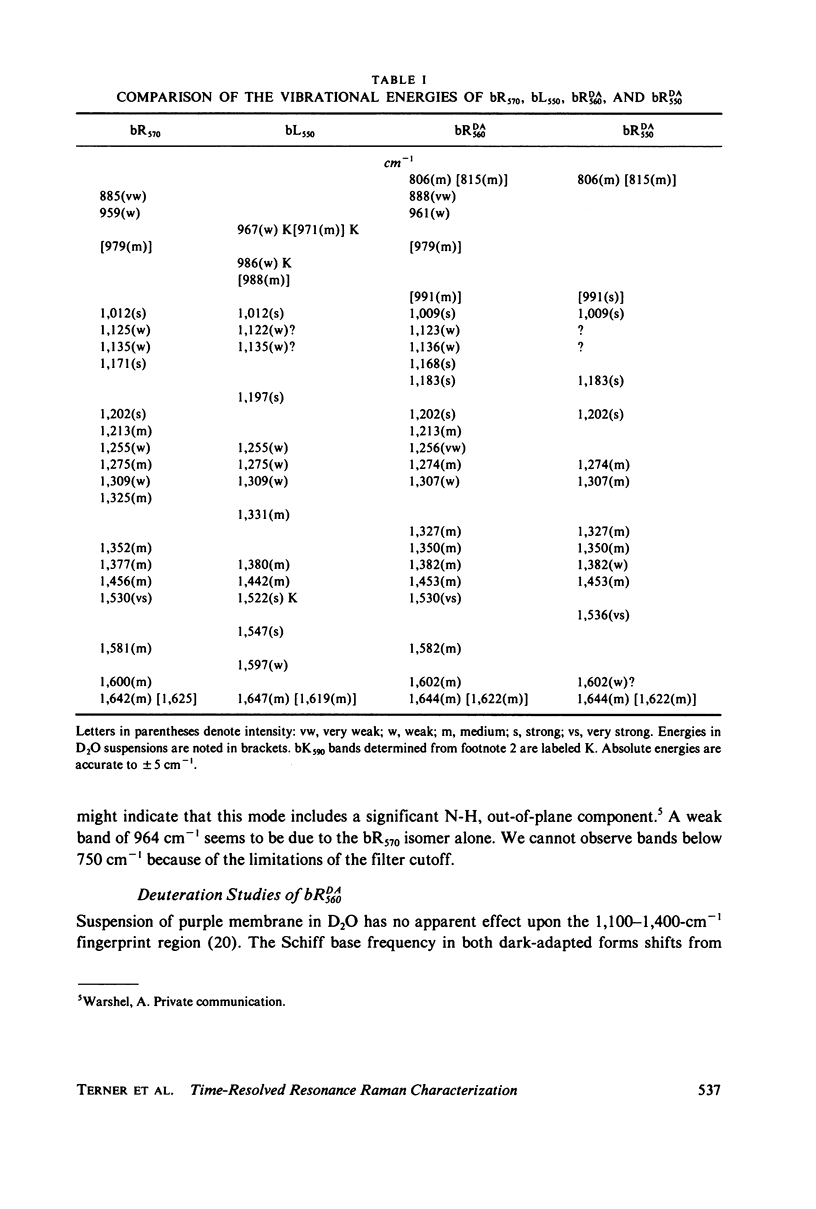
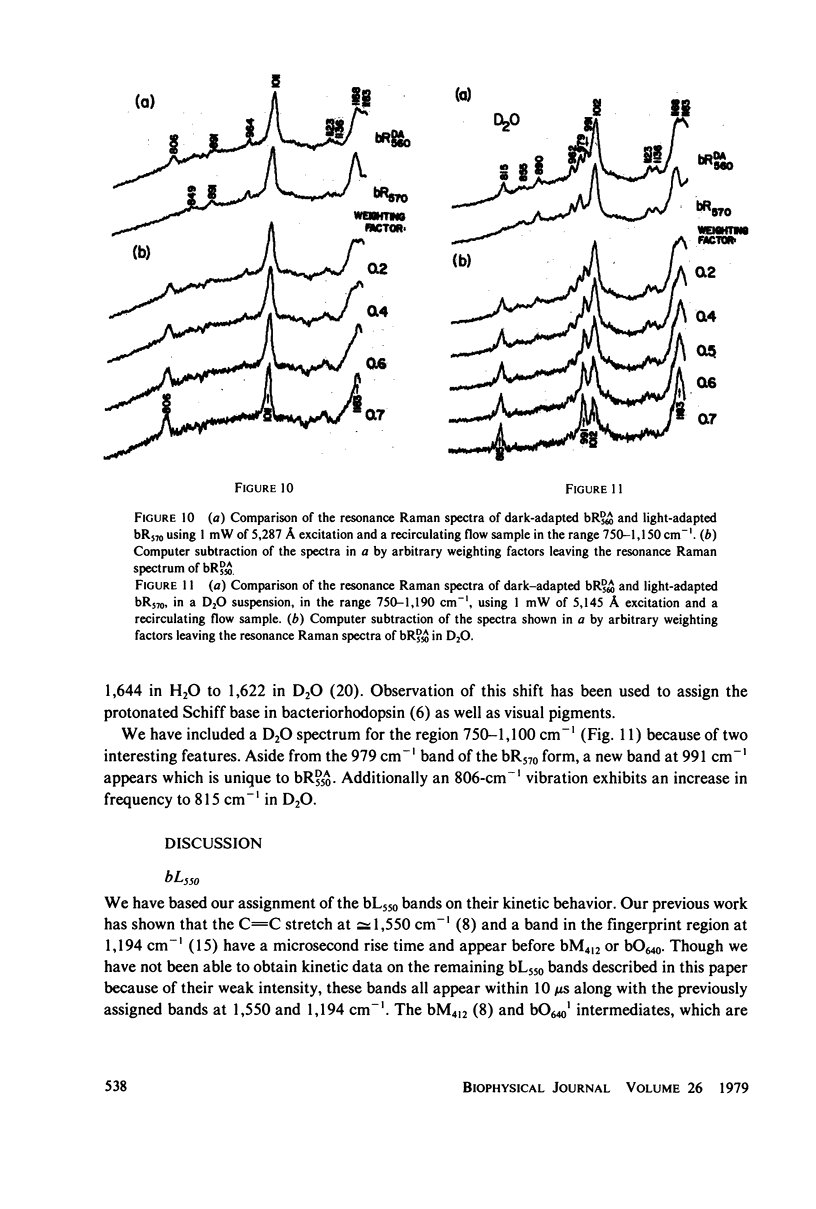
The resonance Raman spectrum of the second intermediate in the bacteriorhodopsin cycle, bL550, is obtained by a simple flow technique. The Schiff base linkage in this intermediate appears to be protonated, contrary to previous suggestion. The fingerprint region of the spectrum of bL550 does not closely match those of any presently available model Schiff bases of retinal isomers, though some comparisons can be made. The resonance Raman spectrum of dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin is obtained and decomposed by computer subtraction of the spectrum of bR570. The remaining spectrum does not match the spectra of any model compounds presently in the literature. The spectra of bL550 and dark-adapted bRDA/560 from purple membrane in H2O are compared to those in D2O. It is found that changes in the spectrum occur in the 1,600 - 1,650 cm-1 region as well as in the 800 - 1,000 cm-1 region, but apparently not in the fingerprint region (1,100 - 1,400 cm-1). The possibilities of conformational changes of the retinal chromophore in the light adaptation process as well as the photosynthetic cycle are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aton B., Doukas A. G., Callender R. H., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. Resonance Raman studies of the purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2995–2999. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender R. H., Doukas A., Crouch R., Nakanishi K. Molecular flow resonance Raman effect from retinal and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1621–1629. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion A., El-Sayed M. A., Terner J. Resonance Raman kinetic spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin on the microsecond time scale. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):369–375. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85555-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campion A., Terner J., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):659–661. doi: 10.1038/265659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber B. P., Yager P., Peticolas W. L. Interpretation of biomembrane structure by Raman difference spectroscopy. Nature of the endothermic transitions in phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):161–176. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85516-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde M. E., Gill D., Kilponen R. G., Rimai L. Raman spectra of Schiff bases of retinal (models of visual photoreceptors). J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Dec 15;93(25):6776–6780. doi: 10.1021/ja00754a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E. What does Halobacterium tell us about photoreception? Biophys Struct Mech. 1977 Apr 21;3(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00536457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Greenberg A. D., Dinur U., Ebrey T. G. Visual-pigment spectra: implications of the protonation of the retinal Schiff base. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4593–4599. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. More evidence that light isomerises the cheomophore of purple membrane protein. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):87–88. doi: 10.1038/272087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J., Bogomolni R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Tunable laser resonance raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4462–4466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. The molecular mechanism of excitation in visual transduction and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):549–553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. A., Lewis A. Kinetic resonance Raman spectroscopy: dynamics of deprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.841330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. A., Lewis A. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of the retinylidene chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin (bR570), bR560, M421, and other intermediates: structural conclusions based on kinetics, analogues, models, and isotopically labeled membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4722–4735. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R., Freedman T. B., Stryer L. Resonance Raman studies of the conformation of retinal in rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):367–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R., Oseroff A. R., Stryer L. Rapid-flow resonance Raman spectroscopy of photolabile molecules: rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R. Resonance Raman spectroscopy of the photoreceptor-like pigment of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1973 May 4;243(5401):22–24. doi: 10.1038/243022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn R., Verma A. L., Bernstein H. J., Kates M. Structural studies of bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium cutirubrum by resonance Raman spectroscopy. Can J Biochem. 1974 Sep;52(9):774–781. doi: 10.1139/o74-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettei M. J., Yudd A. P., Nakanishi K., Henselman R., Stoeckenius W. Identification of retinal isomers isolated from bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1955–1959. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling W., Carl P., Rafferty Ch, Dencher N. A. Photochemistry and dark equilibrium of retinal isomers and bacteriorhodopsin isomers. Biophys Struct Mech. 1977 Jun 29;3(2):79–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00535798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., Campion A., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin on the millisecond timescale. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terner J., El-Sayed M. A. Time-resolved resonance Raman characterization of the intermediates of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1978 Oct;24(1):262–264. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85372-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Karplus M. Calculation of pi-pi excited state conformations and vibronic structure of retinal and related molecules. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Sep 4;96(18):5677–5689. doi: 10.1021/ja00825a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


