Abstract
The Hodgkin-Huxley kinetic parameters, alpha h and beta h, which govern the rate of recovery from and development of sodium channel inactivation, respectively, have been measured as a function of membrane potential and external pH using a three-pulse protocol. alpha h but not beta h is substantially accelerated by reducing external pH from 7.4 to 6.4. The alpha h vs. voltage curve appears to be selectively shifted in the depolarizing direction by approximately 12 mV for this pH change, giving an apparent, h infinity curve shift of approximately 6 mV in the same direction (less inactivation).
Full text
PDF
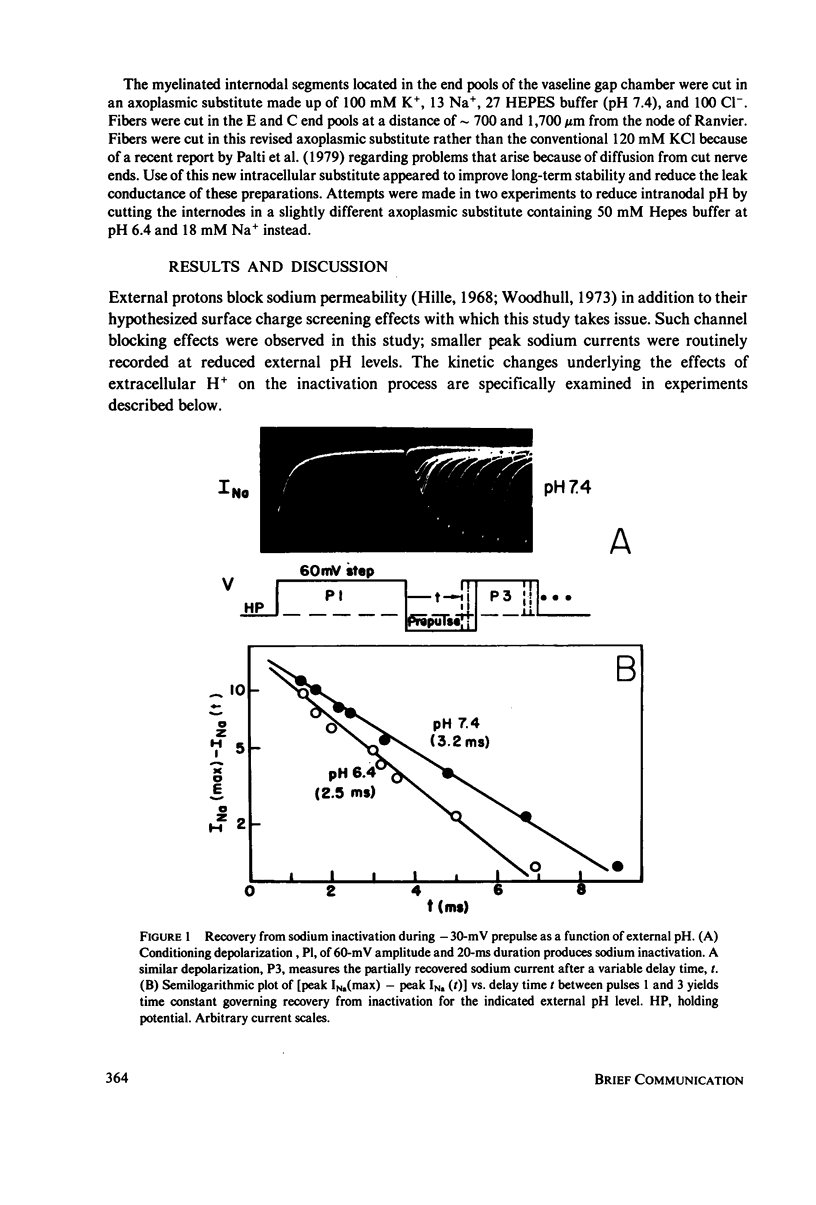
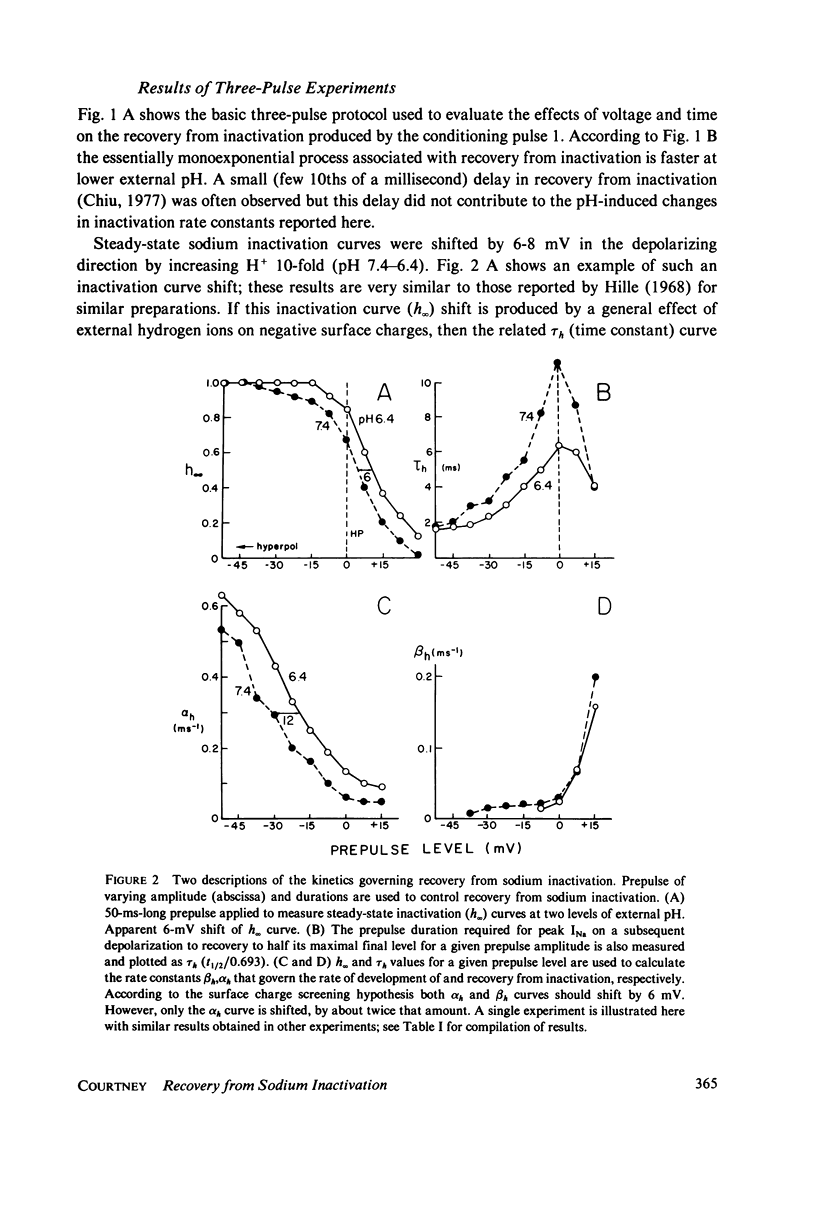
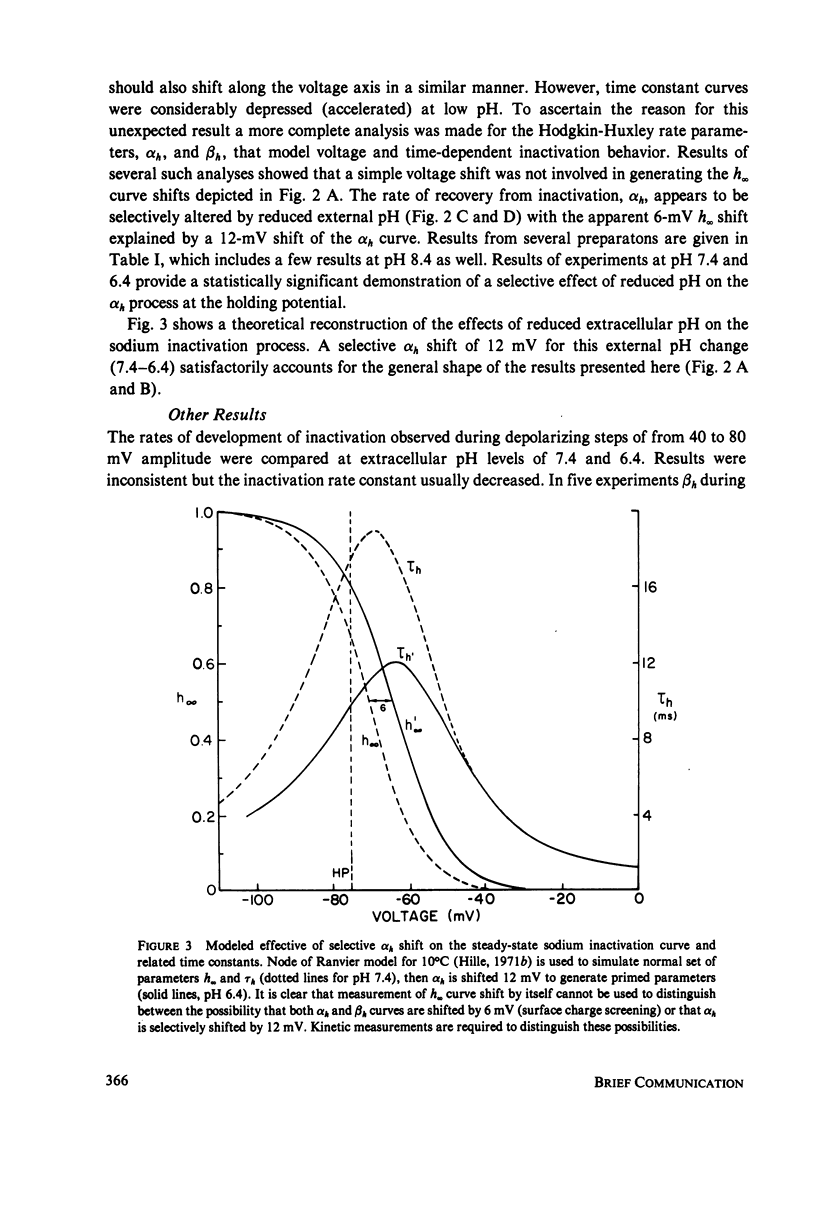


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodwick M. S., Eaton D. C. Sodium channel inactivation in squid axon is removed by high internal pH or tyrosine-specific reagents. Science. 1978 Jun 30;200(4349):1494–1496. doi: 10.1126/science.26973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Fioravanti R., Prestipino G., Wanke E. Action of extracellular pH on Na+ and K+ membrane currents in the giant axon of Loligo vulgaris. J Membr Biol. 1978 Nov 8;43(4):295–315. doi: 10.1007/BF01871693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Mrose H. E., Ritchie J. M. Anomalous temperature dependence of the sodium conductance in rabbit nerve compared with frog nerve. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):327–328. doi: 10.1038/279327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palti Y., Gold R., Stämpfli R. Diffusion of ions in myelinated nerve fibers. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85275-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


