Abstract
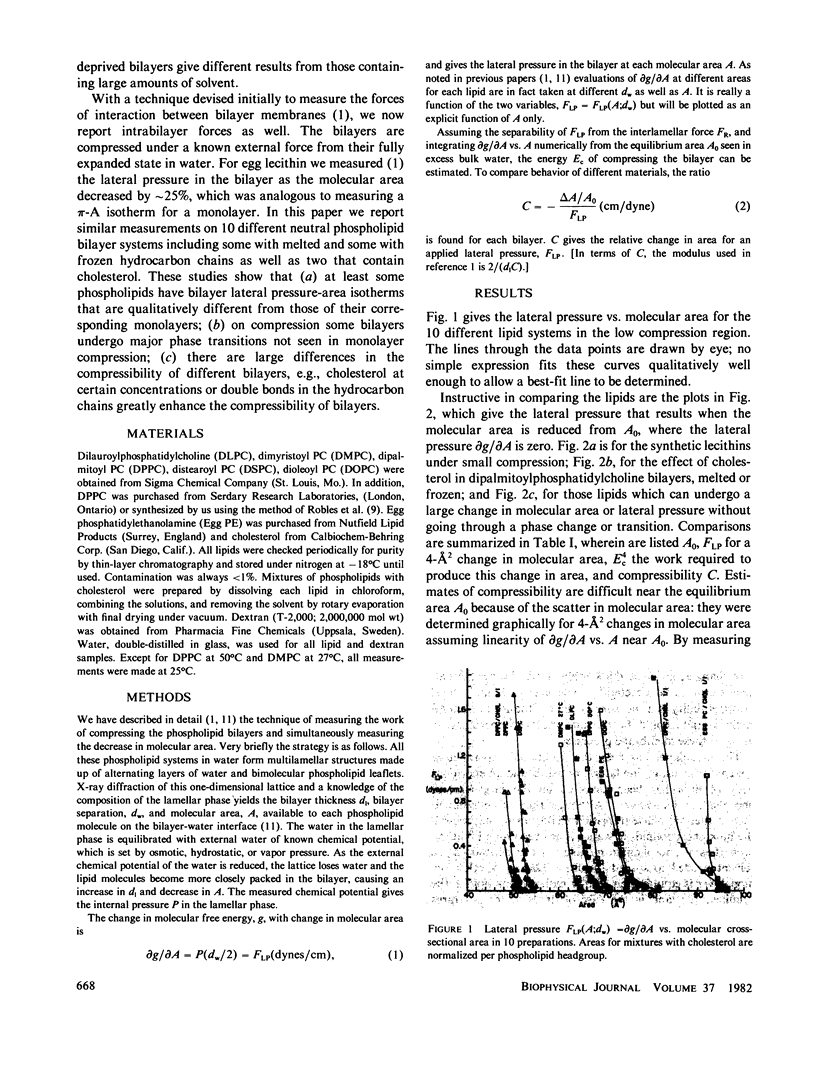
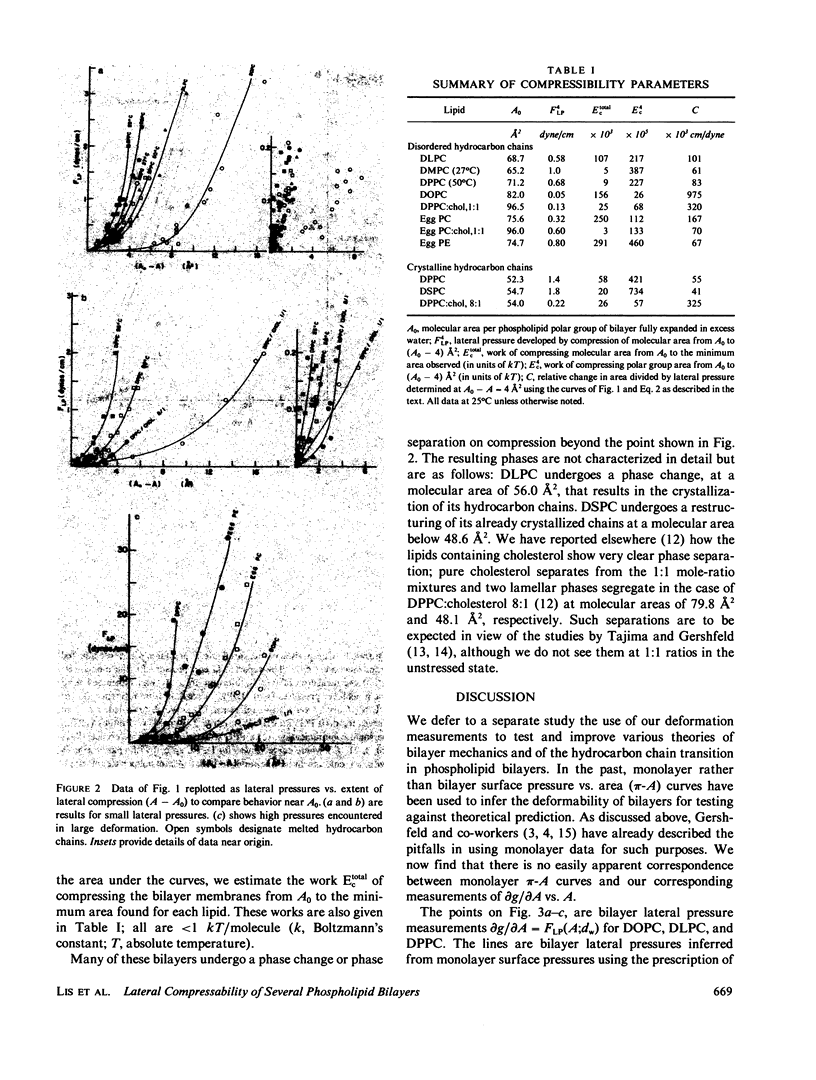
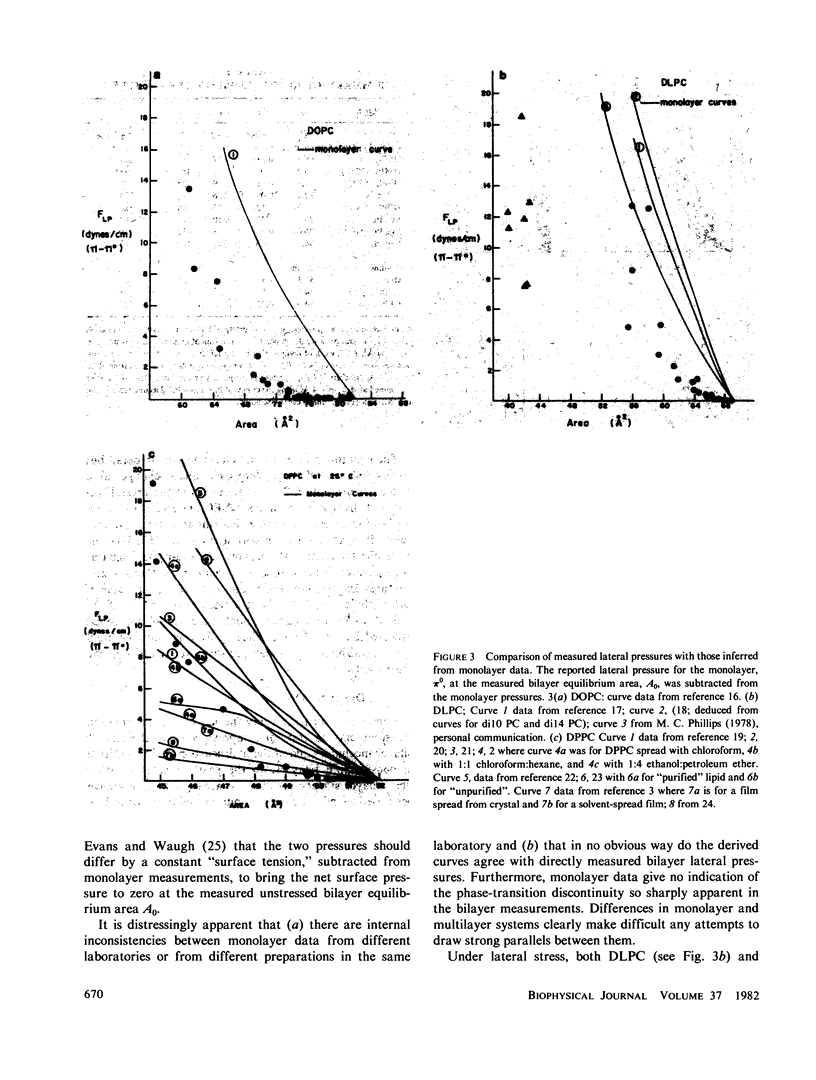
Lateral compressibilities of bilayers in multilayer lattices are given for 10 phospholipid preparation:dilauryl-, dimyristoyl-, dipalmitoyl-, distearoyl-, and dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (PC); egg phosphatidylethanolamine (PE); as well as cholesterol-containing bilayers of dipalmitoyl PC or of egg PC. Bilayer deformability is highly nonlinear and does not permit description in terms of a simple modulus. The presence of cholesterol or C=C bonds (dioleoyl PC) increases deformability, but freezing of acyl chains does not cause dramatic stiffening of the bilayer. Lateral compression of dilauryl PC an dimyristoyl PC causes a transition from "melted" to "frozen" acyl chains above the normal transition temperatures. Our measurements do not correspond in any obvious way to lateral compressibilities in monolayers at the air-water interface.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez O., Latorre R. Voltage-dependent capacitance in lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85505-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero Robles E., van den Berg D. Synthesis of lecithins by acylation of O-(sn-glycero-3-phosphoryl) choline with fatty acid anhydrides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 17;187(4):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Joos P. Interaction between lecithins and cholesterol at the air-water and oil-water interfaces. Chem Phys Lipids. 1968 Feb;2(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(68)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershfeld N. L. Equilibrium studies of lecithin-cholesterol interactions I. Stoichiometry of lecithin-cholesterol complexes in bulk systems. Biophys J. 1978 Jun;22(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85500-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershfeld N. L., Tajima K. Spontaneous formation of lecithin bilayers at the air-water surface. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):708–709. doi: 10.1038/279708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn L. W., Gershfeld N. L. Equilibrium and metastable states in lecithin films. Biophys J. 1977 Jun;18(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85615-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili J. N., Marcelja S., Horn R. G. Physical principles of membrane organization. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 May;13(2):121–200. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos P., Demel R. A. The interaction energies of cholesterol and lecithin in spread mixed monolayers at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok R., Evans E. Thermoelasticity of large lecithin bilayer vesicles. Biophys J. 1981 Sep;35(3):637–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84817-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeNeveu D. M., Rand R. P. Measurement and modification of forces between lecithin bilayers. Biophys J. 1977 May;18(2):209–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85608-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: Lenses and the compression of black lipid membranes by an electric field. Biophys J. 1975 Jan;15(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85793-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., McAlister M., Fuller N., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Interactions between neutral phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):657–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Stamatoff J. Perturbation of membrane structure by uranyl acetate labeling. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):475–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84908-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. C., Chapman D. Monolayer characteristics of saturated 1,2,-diacyl phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) and phosphatidylethanolamines at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. C., Hauser H., Paltauf F. The inter- and intra-molecular mixing of hydrocarbon chains in lecithin-water systems. Chem Phys Lipids. 1972 Mar;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(72)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A., Henry J. A., Lis L. J., McAlister M. The effect of cholesterol on measured interaction and compressibility of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):959–968. doi: 10.1139/o80-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. O., SCHULMAN J. H. BINDING OF METAL IONS TO MONOLAYERS OF LECITHINS, PLASMALOGEN, CARDIOLIPIN, AND DICETYL PHOSPHATE. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. O., Schulman J. H. Influence of calcium, cholesterol, and unsaturation on lecithin monolayers. J Lipid Res. 1967 May;8(3):215–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima K., Gershfeld N. L. Equilibrium studies of lecithin-cholesterol interactions. II. Phase relations in surface films: analysis of the "condensing" effect of cholesterol. Biophys J. 1978 Jun;22(3):489–500. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85501-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H. Letter: Comments on "electrical breakdown of bimolecular lipid membranes as an electromechanical instability". Biophys J. 1974 Feb;14(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)70007-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


