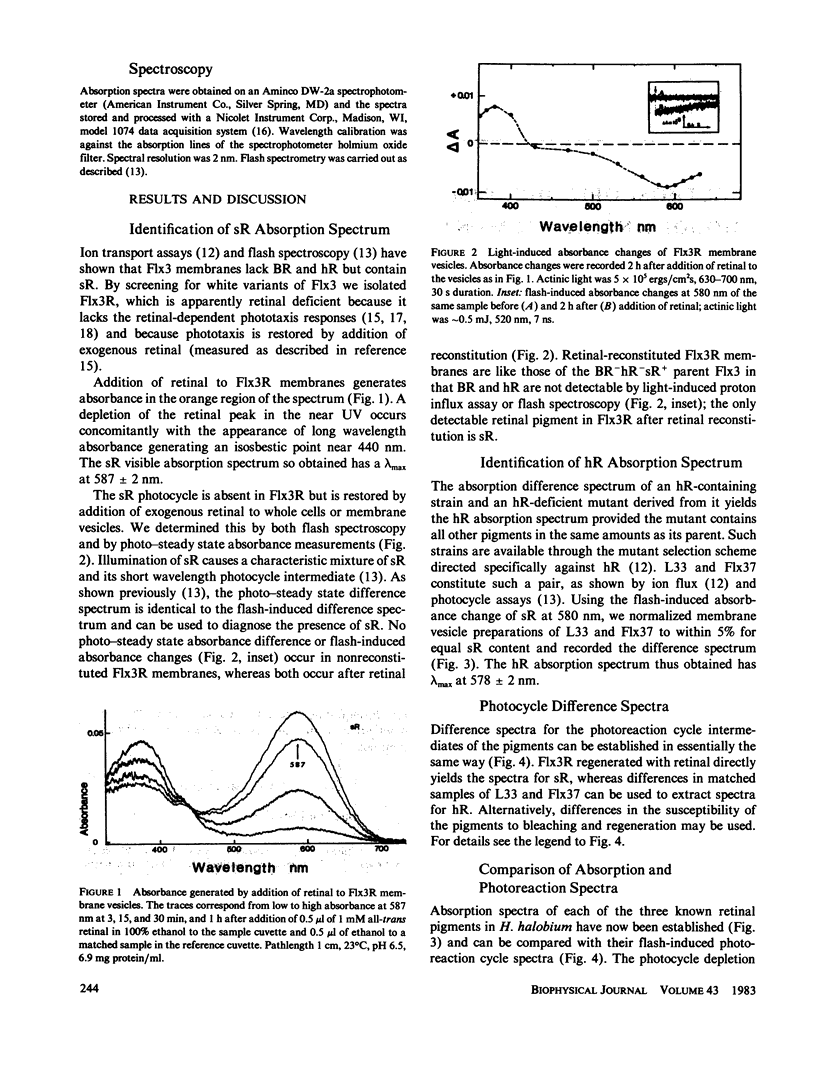
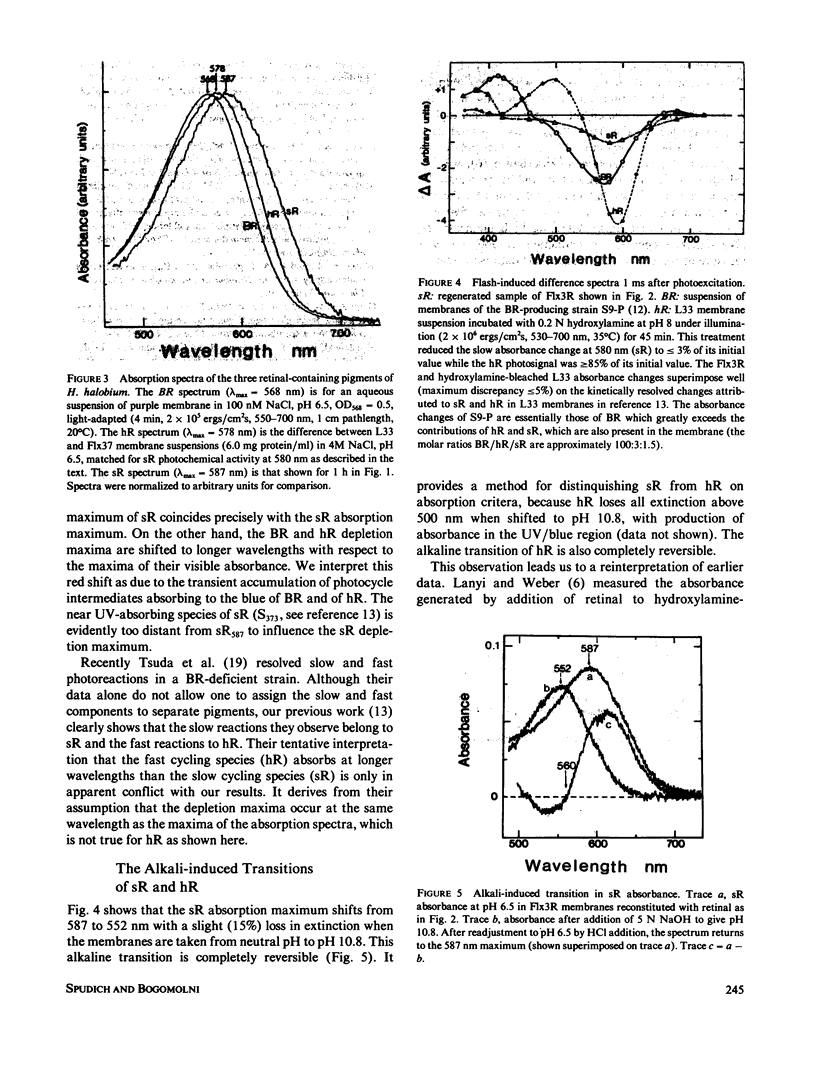
Abstract
Membranes of Halobacterium halobium contain two photochemically reactive retinal pigments in addition to the proton pump bacteriorhodopsin. One, halorhodopsin, is also an electrogenic ion pump with a fast (on a scale of milliseconds) photoreaction cycle. The other, s-rhodopsin, is active in the same spectral region, but has a much slower photoreaction cycle (on a scale of seconds). S-rhodopsin is not an electrogenic ion pump and its properties suggest it functions as the receptor pigment for phototaxis. All three pigments have very similar absorption spectra. The recent isolation of mutants deficient in both bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin and in retinal synthesis has allowed us to resolve the absorption spectra of s-rhodopsin and halorhodopsin. At neutral pH s-rhodopsin has an absorption maximum at 587 +/- 2 nm and halorhodopsin at 578 +/- 2 nm. At pH 10.8, lambda max for s-rhodopsin is shifted to 552 nm and extinction decreases slightly (15%) while halorhodopsin loses all extinction above 500 nm. Both effects are fully reversible and allow determination of the amounts of s-rhodopsin and halorhodopsin in membrane preparations containing both pigments. Both pigments were present in earlier studies of H. halobium membranes, and in view of these findings, several observations must be reinterpreted.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogomolni R. A., Baker R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Action spectrum and quantum efficiency for proton pumping in Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2152–2159. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Identification of a third rhodopsin-like pigment in phototactic Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Hildebrand E. Sensory transduction in Halobacterium halobium: retinal protein pigment controls UV-induced behavioral response. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Sep-Oct;34(9-10):841–847. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-9-1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. V., Lanyi J. K. Proton movements in response to a light-driven electrogenic pump for sodium ions in Halobacterium halobium membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10986–10994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Weber H. J. Spectrophotometric identification of the pigment associated with light-driven primary sodium translocation in Halobacterium halobium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley E. V., MacDonald R. E. A second mechanism for sodium extrusion in Halobacterium halobium: a light-driven sodium pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. E., Greene R. V., Clark R. D., Lindley E. V. Characterization of the light-driven sodium pump of Halobacterium halobium. Consequences of sodium efflux as the primary light-driven event. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11831–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno-Yagi A., Mukohata Y. ATP synthesis linked to light-dependent proton uptake in a rad mutant strain of Halobacterium lacking bacteriorhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jan;199(1):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukohata Y., Kaji Y. Light-induced membrane-potential increase, ATP synthesis, and proton uptake in Halobacterium halobium, R1mR catalyzed by halorhodopsin: Effects of N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, triphenyltin chloride, and 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylidenemalononitrile (SF6847). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jan;206(1):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobert B., Lanyi J. K. Halorhodopsin is a light-driven chloride pump. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10306–10313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling W., Schimz A. Photosensory retinal pigments in Halobacterium halobium. Biophys Struct Mech. 1980;6(2):165–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00535752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Hazemoto N., Kondo M., Kamo N., Kobatake Y., Terayama Y. Two photocycles in halobacterium halobium that lacks bacteriorhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):970–976. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


